@Controller와 @RestController의 역할과 차이점에 대해 알아보기 전에, 둘의 근본이 되는 Controller의 역할에 대해 이야기하겠습니다. (여기서 Controller는 Spring MVC에서의 Controller를 의미합니다.)
Controller의 역할은?
제가 생각하는 Controller의 역할은 다음과 같습니다.
- 사용자의 요청을 처리한다.
- 입력되는 데이터를 처리한다.
- 사용자의 요청에 따라 수행할 비즈니스 로직을 결정한다.
- 요청의 결과를 반환한다.
이때, 사용자의 요청을 URI와 매핑하여 각기 다르게 처리합니다.
이를 위해 @RequestMapping 을 이용하여 어떤 URI 요청을 처리할지 결정합니다.
@Controller, @RestController 살펴보기
우선 @Controller docs를 먼저 살펴보겠습니다.
Indicates that an annotated class is a "Controller" (e.g. a web controller).
This annotation serves as a specialization of @Component, allowing for implementation classes to be autodetected through classpath scanning. It is typically used in combination with annotated handler methods based on the RequestMapping annotation.이 애노테이션이 클래스가 "컨트롤러" 임을 나타냅니다. (예: 웹 컨트롤러)
이 애노테이션은 클래스 경로 탐색을 통해 자동으로 탐지되도록 허용함으로써 @Component의 특별성을 제공합니다.
보통 @RequestMapping 이 달린 메서드와 함께 사용됩니다.
또한 내부에 Optional Element로서 String value 만을 가집니다.
이 value는 logical component name을 가리킨다고 합니다. 즉, Controller 클래스가 Bean으로 등록될 때의 이름을 변경하고 싶을 때 사용하는 요소입니다.
다음으로 @RestController docs를 살펴보겠습니다.
A convenience annotation that is itself annotated with @Controller and @ResponseBody.
Types that carry this annotation are treated as controllers where @RequestMapping methods assume @ResponseBody semantics by default.@RestController는 그 자체로 @Controller와 @ResponseBody가 함께 있는 편리한 애노테이션입니다. 이 애노테이션이 포함된 타입은 @RequestMapping가 달린 메서드에 기본적으로 @ResponseBody도 함께 의미합니다.
NOTE: @RestController is processed if an appropriate HandlerMapping-HandlerAdapter pair is configured such as the RequestMappingHandlerMapping-RequestMappingHandlerAdapter pair which are the default in the MVC Java config and the MVC namespace.
주의: @RestController는
RequestMappingHandlerMapping-RequestMappingHanlderAdapter와 같은 기본적인 MVC Java Config와 MVC namespace를 가진HandlerMapping-HandlerAdapter쌍이 설정되었을 때 처리됩니다.
@Controller와 마찬가지로 내부에 String value Element 만을 가집니다. 의미하는 바도 같습니다.
하지만 큰 차이가 하나 있습니다. 바로 @ResponseBody를 포함한다는 것인데요.
그렇다면 @ResponseBody가 무엇인지 알아보기 위해 공식문서를 살펴보겠습니다.
Annotation that indicates a method return value should be bound to the web response body.
As of version 4.0 this annotation can also be added on the type level in which case it is inherited and does not need to be added on the method level.
이 애노테이션이 가리키는 메서드는 웹 응답 body에 값을 반환하는 의무를 가집니다.
버전 4.0부터는 type(class, interface, or enum)에 추가할 수도 있습니다. 이 경우 상속이 되며, 메서드에 추가할 필요가 없습니다.
핵심은 이 애노테이션이 가리키는 메서드는 웹 응답시 body부에 값을 반환한다 입니다.
추가로 'class, interface, enum'에 작성할 수 있고, 이 경우 메서드에 따로 명시를 안해줘도 된다는 것입니다.
결론
그렇다면 이렇게 결론지을 수 있을 것 같습니다.
@Controller는 기본적으로 웹 MVC에서 Controller의 역할을 한다.
@RestController는 @Controller에 @ResponseBody의 의미를 함께 가진다. 따라서 해당 컨트롤러 내 모든 메서드들은 반환 시, 웹 응답 body부에 값을 넣어 반환한다.
즉, 사용자의 요청에 따라 데이터의 형식을 다르게 반환하고 싶을 때, 이 둘을 구분해서 사용해야 합니다.
코드로 비교하기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>This is tmpPage.html</title>
</head>
<body>
This is tmpPage.html
</body>
</html>@Controller
public class JustController {
@GetMapping("/Controller")
public String justController() {
return "tmpPage";
}
@GetMapping("/RestController")
@ResponseBody
public String restController() {
return "tmpPage";
}
}
두 메서드는 URI를 각각 "/Controller", "/RestController"에 매핑하여 요청을 처리합니다.
이때 "localhost:8080/Controller"에 Get 방식으로 요청했을 때 아래와 같은 결과가 나옵니다.
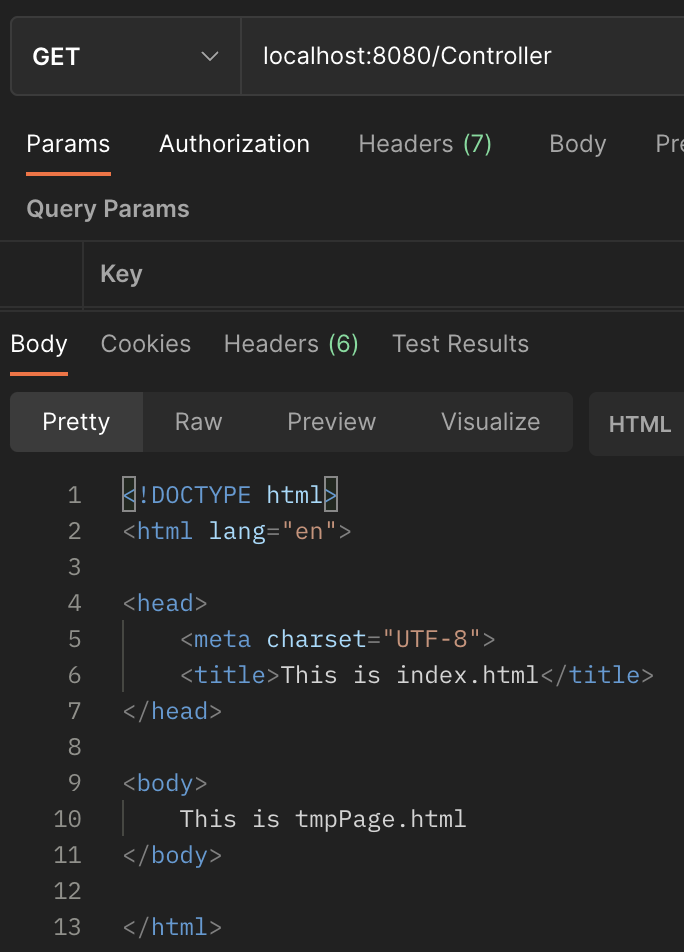
다음은 "/RestController" 에 Get 방식으로 요청했을 때의 결과입니다.
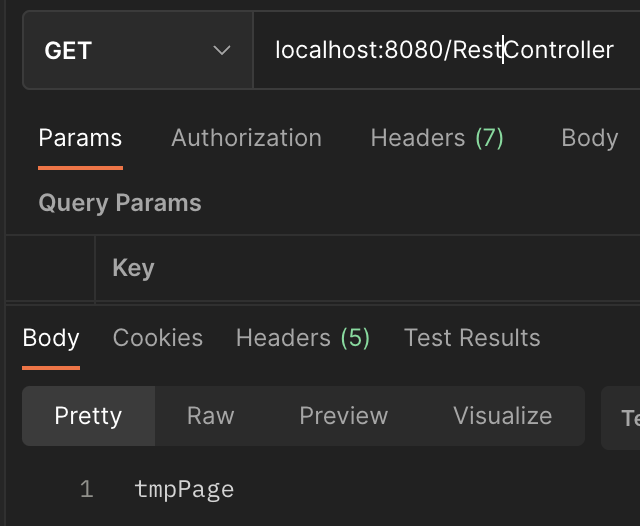
코드 상으로는 같은 "tmpPage" 를 반환합니다.
하지만 @ResponseBody 가 붙지 않은 메서드인, justController()의 경우 Spring 내의 ViewResolver에 의해 view로 변환이 됩니다.
반면 restController()의 경우 문자열 "tmpPage"이 그대로 Body에 반환되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
