
🏷️리스트 추상화1 - 인터페이스 도입
public interface MyList<E> {
int size();
void add(E e);
void add(int index, E e);
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E e);
E remove(int index);
int indexOf(E e);
}public class MyLinkedList<E> implements MyList<E> {
// ...
}public class MyArrayList<E> implements MyList<E> {
// ...
}🏷️리스트 추상화2 - 의존관계 주입
MyArrayList를 활용해서 많은 데이터를 처리하는 BatchProcessor 클래스를 개발한다고 가정하자. 막상 프로그램을 개발하고 보니 데이터를 앞에서 추가하는 일이 많은 상황이라고 가정하자. 데이터를 앞에서 추가하거나 삭제하는 일이 많다면 배열 리스트보다는 연결 리스트가 더 효율적이다.
public class BatchProcessor {
// final 키워드 사용 → 생성자로 한 번 초기화 후 변경X
private final MyList<Integer> myList;
// 생성자를 통한 의존관계 주입
public BatchProcessor(MyList<Integer> myList) {
this.myList = myList;
}
public void logic(int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
myList.add(0, i); // 앞쪽에서 데이터 추가가 일어나는 상황
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("크기 : " + size + ", 계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}✔️효율성 측면 확인 코드 - MyLinkedList
public class BatchProcessorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연결리스트의 경우 첫 번째 위치에 데이터 삽입시 데이터를 이동시킬 필요가 없음
MyLinkedList<Integer> list = new MyLinkedList<>();
BatchProcessor processor = new BatchProcessor(list);
processor.logic(100000); // 크기 : 100000, 계산 시간 : 9ms
}
}✔️효율성 측면 확인 코드 - MyArrayList
public class BatchProcessorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 배열리스트의 경우 첫 번째 위치에 데이터 삽입시 모든 데이터를 오른쪽으로 이동시켜야 함
MyArrayList<Integer> list = new MyArrayList<>();
_텍스트_
BatchProcessor processor = new BatchProcessor(list);
processor.logic(100000); // 크기 : 100000, 계산 시간 : 20110ms
}
}- ✔️정리
- 어떤
MyList list의 구현체를 선택할지는 실행 시점에 생성자를 통해서 결정된다. → 스프링의 의존관계 주입 - 생성자를 통해서
MyList구현체가 전달된다. MyArrayList인스턴스가 들어올 수도 있고,MyLinkedList인스턴스가 들어올 수 있다.- 생성자를 통해서 의존관계를 주입했기 때문에 생성자 의존관계 주입이라고 한다.
- 어떤
🏷️리스트 추상화3 - 컴파일 타임, 런타임 의존관계
의존관계는 크게 컴파일 타임 의존관계와 런타임 의존관계로 나눌 수 있다.
- 컴파일 타임 의존관계 : 코드 컴파일 시점을 뜻한다.
- 런타임 의존관계 : 프로그램 실행 시점을 뜻한다.
-
✔️컴파일 타임 의존관계
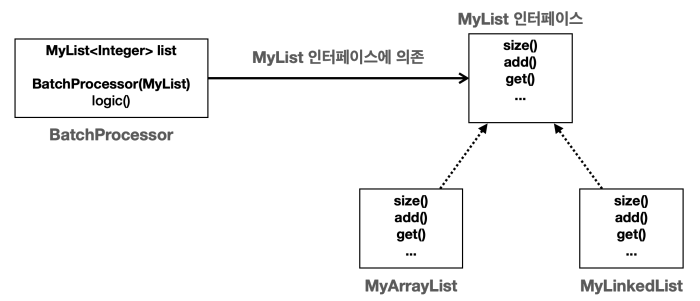
- 클래스에 바로 보이는 의존관계, 실행하지 않은 소스 코드에 정적으로 나타나는 의존관계
BatchProcessor클래스를 보면MyList인터페이스만 사용한다. 코드 어디에도MyArrayList나MyLinkedList와 같은 정보는 보이지 않는다.- 따라서
BatchProcessor는MyList인터페이스에만 의존한다.
-
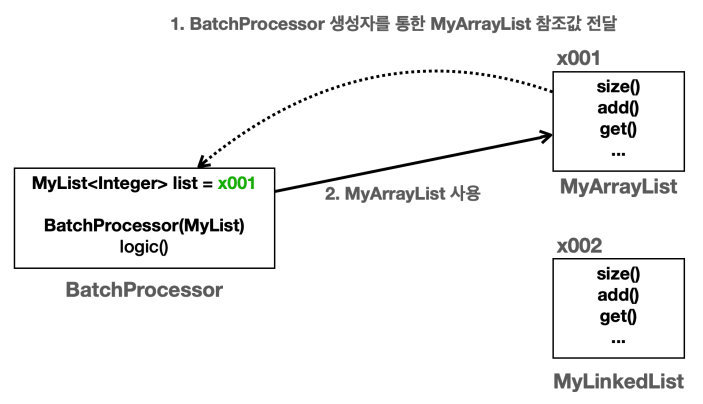
✔️런타임 의존관계
BatchProcessor인스턴스의MyList list는 생성자를 통해MyLinkedList인스턴스를 참조한다.BatchProcessor인스턴스에MyLinkedList의존관계를 주입한다.- 이후
logic()을 호출하면MyLinkedList인스턴스를 사용하게 된다.
- ✔️정리
BatchProcessor클래스는 구체적인MyArrayList나MyLinkedList에 의존하는 것이 아니라 추상적인MyList에 의존한다. 따라서 런타임에MyList의 구현체를 얼마든지 선택할 수 있다.BatchProcessor에서 사용하는 리스트의 의존관계를 클래스에서 미리 결정하는 것이 아니라 런타임에 객체를 생성하는 시점으로 미룬다. 따라서 런타임에MyList의 구현체를 변경해도BatchProcessor의 코드는 전혀 변경하지 않아도 된다.- 이렇게 생성자를 통해 런타임 의존관계를 주입하는 것을 생성자 의존관계 주입 또는 줄여서 생성자 주입이라고 한다.
- 클라이언트 클래스는 컴파일 타임에 추상적인 것에 의존하고 런타임에 의존관계 주입을 통한 구현체를 주입받아 사용함으로써 이런 이점을 얻을 수 있다.
❗전략 패턴(Strategy Pattern)
전략 패턴은 알고리즘을 클라이언트 코드 변경없이 쉽게 교체할 수 있다. 위의BatchProcessor에서 사용한 코드가 바로 전략 패턴을 사용한 코드이다.MyList인터페이스가 전략을 정의하는 인터페이스가 되고, 각각의 구현체인MyArrayList,MyLinkedList가 전략의 구체적인 구현이 된다. 전략을 클라이언트 코드(BatchProcessor)의 변경없이 손쉽게 교체할 수 있다.
🏷️직접 구현한 리스트의 성능 비교
public class MyListPerformanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 50000;
System.out.println("==MyLinkedList 추가==");
addFirst(new MyLinkedList<Integer>(), size);
addMid(new MyLinkedList<Integer>(), size);
addLast(new MyLinkedList<Integer>(), size);
System.out.println("==MyArrayList 추가==");
addFirst(new MyArrayList<Integer>(), size);
addMid(new MyArrayList<Integer>(), size);
addLast(new MyArrayList<Integer>(), size);
int loop = 10000;
System.out.println("==MyArrayList 조회==");
MyArrayList<Integer> myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
addLast(myArrayList, size);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, 0);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==MyLinkedList 조회==");
MyLinkedList<Integer> myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList<>();
addFirst(myLinkedList, size);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, 0);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==MyArrayList 검색==");
search(myArrayList, loop, 0);
search(myArrayList, loop, size / 2);
search(myArrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==MyLinkedList 검색==");
search(myLinkedList, loop, 0);
search(myLinkedList, loop, size / 2);
search(myLinkedList, loop, size - 1);
}
private static void addFirst(MyList<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(0, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void addMid(MyList<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i / 2, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void addLast(MyList<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void getIndex(MyList<Integer> list, int loop, int index) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.get(index);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("index: " + index + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " +
(endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void search(MyList<Integer> list, int loop, int findValue) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.indexOf(findValue);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("findValue: " + findValue + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}실행 결과
==MyLinkedList 추가==
계산 시간 : 7ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 3276ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 5166ms, 크기 : 50000
==MyArrayList 추가==
계산 시간 : 5333ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 2732ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 4ms, 크기 : 50000
==MyArrayList 조회==
계산 시간 : 1ms, 크기 : 50000
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
==MyLinkedList 조회==
계산 시간 : 1ms, 크기 : 50000
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1113ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 2400ms
==MyArrayList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 280ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 287ms
==MyLinkedList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 2659ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1245ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms- ✔️정리
- 앞쪽에서 추가(삭제) : 배열리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(1), 추가(삭제)하고 데이터의 이동이 필요하므로O(N) - 앞쪽에서 추가(삭제) : 연결리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(N), 추가(삭제)한 이후 데이터의 이동이 불필요하므로O(1) - 중간에서 추가(삭제) : 배열리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(1), 추가(삭제)하고 데이터의 이동이 필요하므로O(N/2), 따라서O(N) - 중간에서 추가(삭제) : 연결리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(N/2), 추가(삭제)한 이후 데이터의 이동이 불필요하므로O(1), 따라서O(N) - 뒤쪽에서 추가(삭제) : 배열리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(1), 추가(삭제)하고 데이터의 이동이 불필요하므로O(1) - 뒤쪽에서 추가(삭제) : 연결리스트의 경우 찾는데
O(N), 추가(삭제)하고 데이터의 이동이 불필요하므로O(1), 따라서O(N)
- 앞쪽에서 추가(삭제) : 배열리스트의 경우 찾는데
- ✔️시간 복잡도와 실제 성능
- 이론적으로
MyLinkedList가 평균 추가에 있어 더 효율적일 수 있으나 현대 컴퓨터 시스템의 메모리 접근 패턴, CPU 캐시 최적화 등을 고려할 때MyArrayList가 실제 사용 환경에서 더 나은 성능을 보여주는 경우가 많다. 대부분의 경우 배열 리스트가 성능상 유리하다. 이런 이유로 실무에서는 주로 배열 리스트를 기본으로 사용한다. 만약 데이터를 앞쪽에서 자주 추가하거나 삭제하는 일이 잦다면 연결 리스트를 고려하자.
- 이론적으로
🏷️자바 리스트
List 자료구조
순서가 있고, 중복을 허용하는 자료구조를 리스트라 한다.
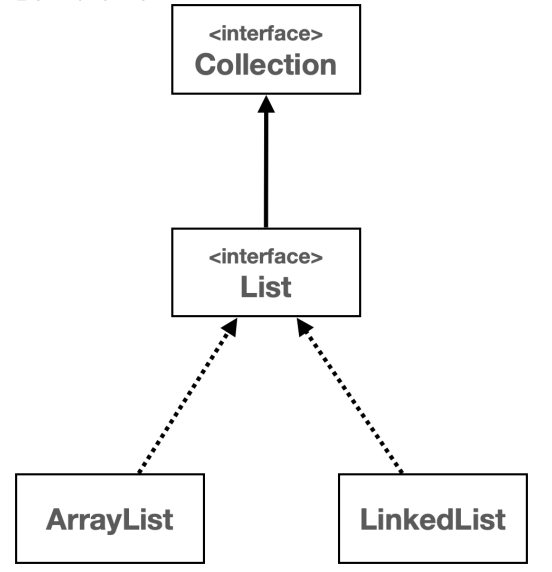
List 인터페이스
List 인터페이스는 객체들의 순서가 있는 컬렉션을 나타내며, 같은 객체의 중복 저장을 허용한다. 이 리스트는 배열과 비슷하지만, 크기가 동적으로 변화하는 컬렉션을 다룰 때 유연하게 사용할 수 있다.
자바 ArrayList
- 배열을 사용해서 데이터를 관리한다.
- 기본
CAPACITY는 10이다.CAPACITY를 넘어가면 배열을 50% 증가한다. - 시스템 레벨에서 배열을 한 번에 아주 빠르게 복사한다.
자바 LinkedList
- 이중 연결 리스트 구조
- 첫 번째 노드와 마지막 노드 둘 다 참조
🏷️자바 리스트의 성능 비교
public class JavaListPerformanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 50000;
System.out.println("==LinkedList 추가==");
addFirst(new LinkedList<Integer>(), size);
addMid(new LinkedList<Integer>(), size);
addLast(new LinkedList<Integer>(), size);
System.out.println("==ArrayList 추가==");
addFirst(new ArrayList<Integer>(), size);
addMid(new ArrayList<Integer>(), size);
addLast(new ArrayList<Integer>(), size);
int loop = 10000;
System.out.println("==ArrayList 조회==");
ArrayList<Integer> myArrayList = new ArrayList();
addLast(myArrayList, size);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, 0);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(myArrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==LinkedList 조회==");
LinkedList<Integer> myLinkedList = new LinkedList<>();
addFirst(myLinkedList, size);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, 0);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, size / 2);
getIndex(myLinkedList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==ArrayList 검색==");
search(myArrayList, loop, 0);
search(myArrayList, loop, size / 2);
search(myArrayList, loop, size - 1);
System.out.println("==LinkedList 검색==");
search(myLinkedList, loop, 0);
search(myLinkedList, loop, size / 2);
search(myLinkedList, loop, size - 1);
}
private static void addFirst(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(0, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void addMid(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i / 2, i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void addLast(List<Integer> list, int size) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("계산 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms, 크기 : " + size);
}
private static void getIndex(List<Integer> list, int loop, int index) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.get(index);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("index: " + index + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " +
(endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
private static void search(List<Integer> list, int loop, int findValue) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
list.indexOf(findValue);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("findValue: " + findValue + ", 반복: " + loop + ", 계산 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}실행 결과
==LinkedList 추가==
계산 시간 : 8ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 2948ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 5ms, 크기 : 50000
==ArrayList 추가==
계산 시간 : 166ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 84ms, 크기 : 50000
계산 시간 : 6ms, 크기 : 50000
==ArrayList 조회==
계산 시간 : 2ms, 크기 : 50000
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 0ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
==LinkedList 조회==
계산 시간 : 4ms, 크기 : 50000
index: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
index: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 762ms
index: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms
==ArrayList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 2ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 394ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 671ms
==LinkedList 검색==
findValue: 0, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 2665ms
findValue: 25000, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1248ms
findValue: 49999, 반복: 10000, 계산 시간: 1ms