컬렉션
자바의 List, Map, Set 등을 Collection이라고 한다.
Generic으로 구현이 되어 다양한 타입과 함께 사용될 수 있으며,
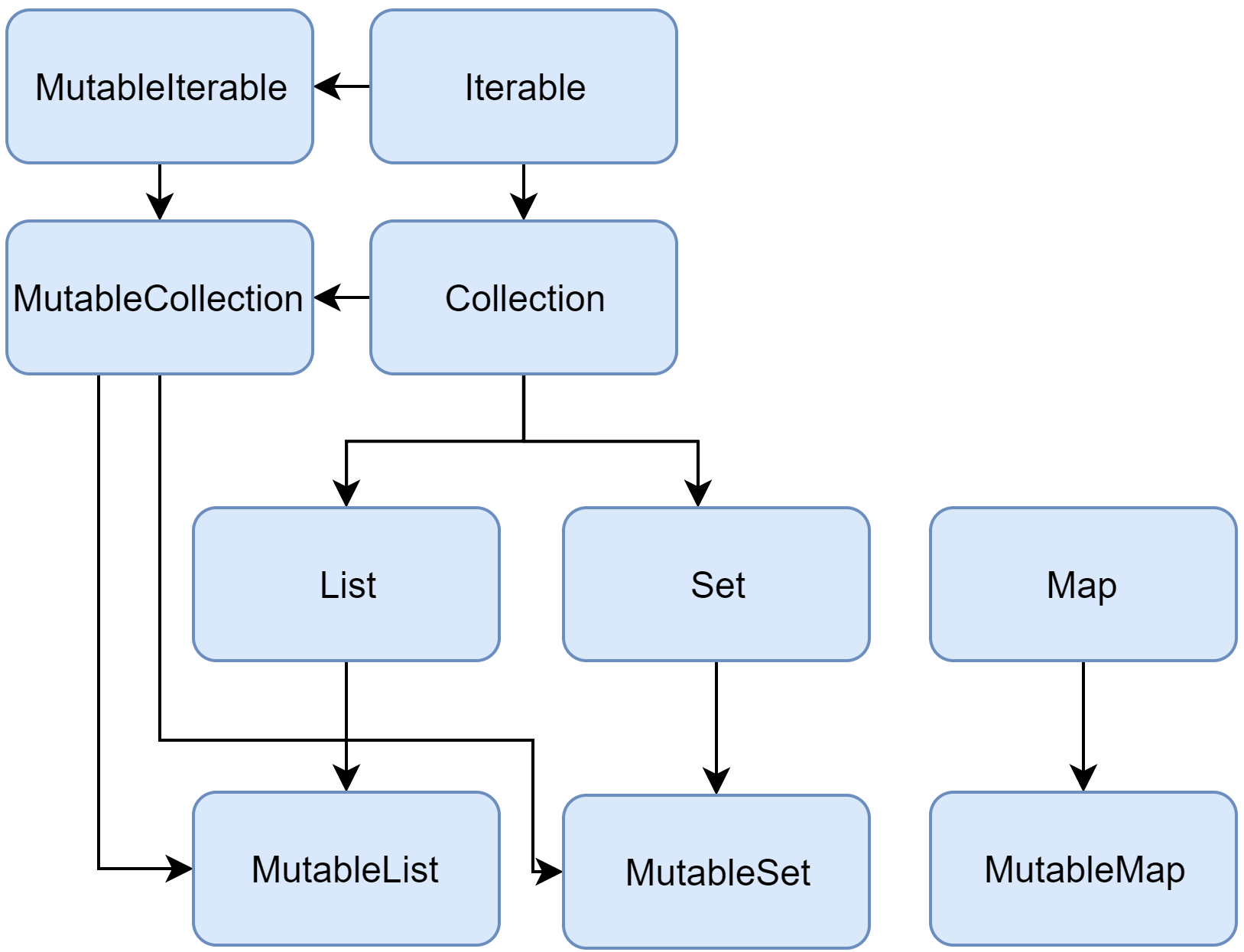
코틀린의 Collection은 Mutable(변할 수 있는)과 Immutable(불변)을 별개로 지원한다.
Mutable로 생성하면 추가, 삭제가 가능하지만, Immutable로 생성하면 수정이 안된다.
코틀린의 콜렉션들은 아래 그림과 같은 상속 구조 갖고 있다
List
- 순서가 있는 데이터 집합
- 가변과 불변 객체를 생성하는 함수
listOfmutableListOfarrayListOf제공- ArrayList 는 MutableList를 상속받는다
class ArrayList<E> : MutableList<E>, RandomAccess
둘의 유일한 차이점은 의도를 전달하는 것이다.
- ArrayList 는 MutableList를 상속받는다
- 널 값이 없는 리스트를 만들 땐
listOfNotNull함수를 사용.- 내부적으로 null을 필터링 해서 원소에 null이 있어도 제외함.
- 아무 원소도 없는 리스트는
emptyList함수로 만들 수 있음. - 가변, 불변에 따라서 컬렉션에 원소를 추가해주는 함수의 유무가 결정됨.
fun main() {
// init
val mulist1: MutableList<Int> = mutableListOf(10, 20, 11, 23, 55)
val mulist2 = mutableListOf(10, 20, 30);
val mulist3 = (1..50).toMutableList()
val mulist4 = mutableListOf<Int>()
val mulist5 = MutableList<Int>(5, { i -> i}) // 0..4로 초기화
// use
val countryList = listOf<String>("한국","미국","일본")
val minusCountryList = countryList - "일본" // ["한국", "미국"]
val plusCountryList = countryList + "중국" // ["한국","미국","일본","중국"]
newlistData.addAll(plusList) // List 합치기
val newlistData2 = plusList1 + plusList2 // + 기호로 합치기
val newListData3 = plusList1.plus(plusList2) // plus함수로 합치기
val newListData4 = plusList1.union(plusList2) // 중복제거 한 후 합치기
}Set
- 집합은 순서가 없고 모든 원소는 유일한 값을 가짐.
fun main() {
val set1 = mutableSetOf(1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1)
println(set1) // [1,2,3,4,5]
// 1 2 3 4 5
for(elem in set1){
println(elem)
}
set1.add(1)
set1.add(2)
set1.add(3)
set1.add(4)
println(set1) // [1,2,3,4,5]
}Map
- Key, Value로 구성된 쌍 형태의 자료형
- Key는 고유값이어야 한다
fun main() {
val map1 = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3)
println(map1) // {key1=1, key2=2, key3=3}
println(map1["key1"]) // 1
println(map1.get("key2")) // 2
println(map1.containsKey("key1")) // true
println(map1.containsKey("key4")) // false
println(map1.containsValue(1)) // true
println(map1.containsValue(4)) // false
}컬렉션 사용
컬렉션 기본 메서드
컬렉션 인터페이스에서 정의된 함수에는 다음이 있다.
public interface Collection<out E> : Iterable<E> {
public val size: Int // 크기
public fun isEmpty(): Boolean // 비어있는지 확인
public operator fun contains(element: @UnsafeVariance E): Boolean // 하나 이상 포함
override fun iterator(): Iterator<E> // iterator 형태로 변환
public fun containsAll(elements: Collection<@UnsafeVariance E>): Boolean // 모두 포함
}원소 조회 메서드
[index]get(index: Int): 해당 인덱스 원소 접근first()last(): 처음, 마지막 조회indexOf(element: T)lastIndexOf(element: T): 앞, 뒤에서 부터 비교해 같은 데이터의 인덱스 반환find(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)findLast(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
람다로 들어온 조건을 앞, 뒤에서 부터 조회
조건 검사
all(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): 람다 식 내의 반환 조건이 모두 참none(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): 람다 식 내의 반환 조건이 모두 거짓any(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): 람다 식 내의 반환 조건이 하나라도 만족하는 경우 참
컬렉션 처리 함수
map: 컬렉션을 순회해서 내부 원소를 변환filter: 컬렉션을 순회해서 조건이 true 인 원소만 추출reduce: 컬렉션을 순회해서 조건을 누적하며 결과를 단일 값으로 반환fold: reduce와 동일하지만, 초깃값 부터 연산을 시작함.
// map
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val doubled = numbers.map { it * 2 } // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
// filter
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val evens = numbers.filter { it % 2 == 0 } // [2, 4]
// reduce
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val sum = numbers.reduce { acc, n -> acc + n } // 15
// fold
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val sum = numbers.fold(0) { acc, n -> acc + n } // 15그룹화
data class Person(val name: String, val age: Int)
fun main() {
val words = listOf("apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry")
val groups = words.groupBy { it.length }
println(groups) // {5=[apple], 6=[banana, cherry], 4=[date], 10=[elderberry]}시퀀스
- 지연계산(Lazy Evaluation)으로 수행한다.
map이나filter같은 함수는 컬렉션을 즉시(eagerly)생성한다.
val sequence = sequenceOf(1,2,3)
println(sequence.elementAt(0)) // 1
println(sequence.elementAt(1)) // 2iterator vs Sequence
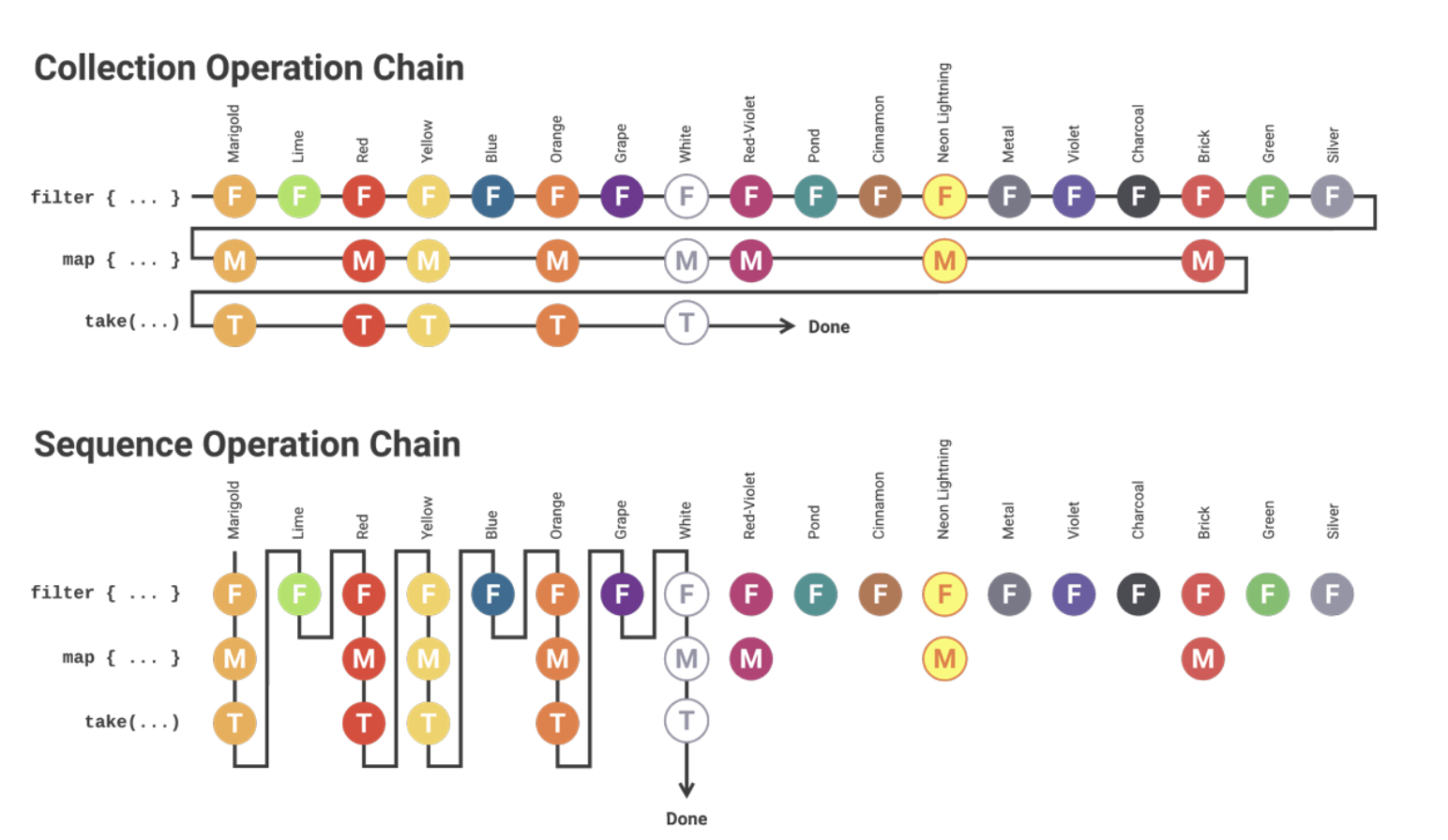
시퀀스의 경우 중간 처리 연산이 수행될 때마다 값을 생성해서 지연 계산을 처리하기에 성능적으로 이점을 볼 수 있지만
단순한 연산에서는 불필요한 오버헤드 때문에 Sequence가 더 느리게 동작하는 경우도 있다.
val list = 1..6
list.filter {
println("iterator filter: $it")
it%2 == 0
}.also {
println("iterator filter done : $it")
}.map {
println("iterator map: $it")
it * it
}.also {
println("iterator map done : $it")
}.take(2)
.also {
println("iterator done : $it")
}
println()
println()
list.asSequence().filter {
println("sequence filter: $it")
it%2 == 0
}.map {
println("sequence map: $it")
it * it
}.take(2)
.toList()
.also {
println("sequence done : $it")
}print:
iterator filter: 1
iterator filter: 2
iterator filter: 3
iterator filter: 4
iterator filter: 5
iterator filter: 6
iterator filter done : [2, 4, 6]
iterator map: 2
iterator map: 4
iterator map: 6
iterator map done : [4, 16, 36]
iterator done : [4, 16]
sequence filter: 1
sequence filter: 2
sequence map: 2
sequence filter: 3
sequence filter: 4
sequence map: 4
sequence done : [4, 16]