1. 머신러닝과 딥러닝의 차이
미프 2차를 통해, 머신러닝과 딥러닝을 실습해보았다.
x주제에 대한 df을 받아서, 데이터 전처리를 거치고, 머신러닝과 딥러닝을 각각 돌려보면서 더 우수한 성능을 나타내는지 비교분석했다.
신기하게도, 머신러닝 모델에서 더 좋은 mae와 mape 값을 얻을 수 있었다.
이를 통해, 알 수 있는 사실은 다음과 같다.
- 데이터 전처리가 가능하며, df와 같이 정형 데이터를 다룰 때는 머신러닝이 더 좋다.
- 이미지, 텍스트, 음성 데이터와 같이 비정형 데이터를 다룰 때는 딥러닝이 더 좋다.
2. CNN
- 이미지 데이터를 사용하여 딥러닝하는 방법이다.
- 전에 했던 딥러닝은 Functional API를 사용하는 방법이지만, CNN의 경우에는 Sequential API 방식을 사용한다.
- suquential API은 Convolutional Layer를 사용한다.
- Convolutional은 1. Conv2D /// 2. Maxpool2D를 사용한다.
- Conv2D는 1) filters 2) kernel_size, 3) strides, 4) padding, 5) activation를 매개변수로 사용한다.
- Maxpool2D는 1) pool_size, 2) strides를 매개변수로 사용한다.
-
1) 원래 하던 functional 방식을 사용하기 전에, 전처리를 한다고 생각하면 된다.
-
2) functional은 flatten을 사용하는 것처럼, 2차원으로 만들어서 쫙 핀 다음, 학습을 하기 때문에, 위치 정보의 소실이 발생한다.
-
3) sequential은 convolutional layer를 거쳐서 위치 정보가 보존된 서로 다른 feature을 갖는 feature map을 만든다.
-
333) filters는 depth/hidden layer와 유사하다. 값 설정은 우리가 hidden layer 값 정한는 것과 같이 우리가 정한다.
-
4) Conv2D 방법은 kernel_size가 strides 보폭만큼 이동하면서 kernel 크기에서 random 값이 들어있는 컴퓨터가 생성한 filter map와의 연산을 통해 새로운 값을 도출하고 activation을 거친 다음에, 해당 값을 새로운 map에 입력하며, feaure map의 크기는 작아진다.
-
4-1) 필요에 따라, padding을 할 수 있다. padding은 이전 feautre map의 size를 유지시킨다.
-
5) Maxpool 방법은 pool_size가 stride 보폭만큼 이동하는데 pool_size에서 가장 큰 값을 도출하고 해당 값을 갖는 map을 형성하며 크기가 작아진다.
-
5-1) 보통 pool_size와 stride는 같은 값을 갖는다.
- 이미지 데이터의 x_train shape을 보면 (60000, 28, 28)을 나타내는 경우, 그냥 사용했었지만 흑백(1) or 색의 이미지 데이터(3)의 경우 (60000, 28, 28, 1(흑백), 3(색))의 shape을 사용해야 한다.
- 이미지 데이터의 y_train의 경우 원래 (60000,)였는데, (60000, 10)과 같이 원핫인코딩을 통해서 1차원에서 2차원으로 바꿔줘야한다.
- 주의할 점이 하나 있는데, class_n이 100과 같이 너무 크다면,
- 원핫인코딩을 하지 않고 model.compile(loss = 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy')로 두는 것이 더 좋다.
- 4차원의 데이터에 대해서 MinMax 스케일링을 하게 된다면, 기존에 알던 방식이 아닌 공식을 사용해서 작성해야 한다.
- 원핫인코딩의 경우, 어떤 관측치에 대해서 할지 모른다. 그래서 get_dummies가 아닌 to_categorical 라이브러리를 사용해야 한다.
- MinMax 스케일링 # x_train으로 fit해준다. max_n = x_train.max() min_n = x_train.min() x_train = (x_train - max_n) / (max_n - min_n) x_test = (x_test - max_n) / (max_n - min_n) ======================================================= - 원핫인코딩 from tf.keras.utils import to_categorical # 만약에 안된다면 keras.utils import to_categorical 해보셈 class_n = len(np.unique(y_train)) y_train = to_categorical(y_train, class_n) y_test = to_categorical(y_test, class_n) x_train.shape, y_train.shape <출력> ((14979, 28, 28, 1), (14979, 10))
2-1. MinMax scaling 방법 2가지
-
standard scaling의 경우는 train = (train-mean)/std의 식이다.
-
xtrain.shape을 보면 (40000,28,28,3)이 출력된다면 (,,,3)을 통해서 색 이미지임을 알 수 있다.
-
색은 R,G,B를 통해서 표현된다.
-
그래서 스케일링 방법이 2가지가 존재한다.
- RGB를 한번에 스케일
- R/G/B 따로 스케일을 진행하고 합치기(np.stack)
- 1번 방법 해당 방법은 위에서 정리했다. - 2번 방법 # min, max fit tr_r_max, tr_r_min = train_x[:,:,:,0].max(), train_x[:,:,:,0].min() tr_g_max, tr_g_min = train_x[:,:,:,1].max(), train_x[:,:,:,1].min() tr_b_max, tr_b_min = train_x[:,:,:,2].max(), train_x[:,:,:,2].min() # train_x train_r_mm = (train_x[:,:,:,0] - tr_r_min) / (tr_r_max - tr_r_min) train_g_mm = (train_x[:,:,:,1] - tr_g_min) / (tr_g_max - tr_g_min) train_b_mm = (train_x[:,:,:,2] - tr_b_min) / (tr_b_max - tr_b_min) # test_x test_r_mm = (test_x[:,:,:,0] - tr_r_min) / (tr_r_max - tr_r_min) test_g_mm = (test_x[:,:,:,1] - tr_g_min) / (tr_g_max - tr_g_min) test_b_mm = (test_x[:,:,:,2] - tr_b_min) / (tr_b_max - tr_b_min) # R/G/B 분할된거 하나로 합치기 train_x_mm = np.stack((train_r_mm, train_g_mm, train_b_mm), axis=3) # shape, (max 값) 확인 train_x_mm.shape <출력> (40000, 32, 32, 3)
3. Functional API 예제
----------------------------------------------------------- # 1. 세션 클리어 : 메모리에 기존 모델 구조가 남아있으면 정리해줘. keras.backend.clear_session() ----------------------------------------------------------- # 2. 레이어 사슬처럼 엮기 il = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[28, 28, 1]) # x_train shape임 h = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(il) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu')(h) h = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2)(h) ol = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(h) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 3. 모델의 시작과 끝 지정 model = tf.keras.models.Model(il, ol) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 4. 컴파일 model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics='accuracy') model.summary() ----------------------------------------------------------------------- # 5. Early stop from tf.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping es = EarlyStopping(es = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=5, verbose = 1, # 어느 epoch에서 얼리스토핑이 적용되었는지 보여줌 restore_best_weights=True,) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- # 6. model 학습 model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=100000, verbose=1, validation_split=0.2, callbacks=[es],) # callbacks에 여러개 쓸 수 있어서 [es]로 넣어준거래 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
3-1. model 평가
-
평가 방법은 1. evaluate 2. accuracy / classification_report 있다.
-
원핫 인코딩 한 것을 다시 묶어주는 코드 argmax
-
평가 지표 및 실제 데이터 확인을 위해 필요
# 7. model 평가 model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) <출력> 118/118 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3140 - accuracy: 0.9076 [0.3139810562133789, 0.9076101183891296] ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- # 7-1 model 평가 y_pred = model.predict(x_test) y_pred_arg = np.argmax(y_pred, axis = 1) test_y_arg = np.argmax(y_test, axis = 1) from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report # 1 accuracy_score(test_y_arg, y_pred_arg) # 2 print(classification_report(test_y_arg, y_pred_arg)) <출력> 0.9076101468624833 precision recall f1-score support 0 0.93 0.89 0.91 357 1 0.85 0.91 0.88 365 2 0.93 0.94 0.93 374 3 0.93 0.91 0.92 392 4 0.97 0.85 0.91 406 5 0.95 0.96 0.96 377 6 0.86 0.92 0.89 372 7 0.89 0.93 0.91 374 8 0.86 0.86 0.86 385 9 0.91 0.94 0.92 343 accuracy 0.91 3745 macro avg 0.91 0.91 0.91 3745 weighted avg 0.91 0.91 0.91 3745
3-2. 시각화
3-2-1. 실제 데이터 확인
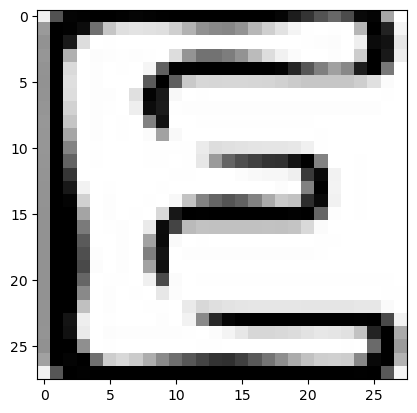
letters_str = "ABCDEFGHIJ" rand_idx = np.random.randint(0, len(y_pred_arg)) test_idx = test_y_arg[rand_idx] pred_idx = y_pred_arg[rand_idx] class_prob = np.floor( y_pred[rand_idx]*100 ) print(f'idx = {rand_idx}') print(f'해당 인덱스의 이미지는 {letters_str[test_idx]}') print(f'모델의 예측 : {letters_str[pred_idx]}') print(f'모델의 클래스별 확률 : ') print('-------------------') for idx, val in enumerate(letters_str) : print(val, class_prob[idx]) print('=================================================') if test_y_arg[rand_idx] == y_pred_arg[rand_idx] : print('정답') else : print('땡') plt.imshow(x_test[rand_idx], cmap='Greys') plt.show() <출력> idx = 2016 해당 인덱스의 이미지는 E 모델의 예측 : E 모델의 클래스별 확률 : ------------------- A 4.0 B 15.0 C 2.0 D 0.0 E 69.0 F 0.0 G 4.0 H 0.0 I 1.0 J 0.0 =================================================
3-2-2. 틀린 이미지 확인
# 1 temp = (test_y_arg == y_pred_arg) false_idx = np.where(temp==False)[0] false_len = len(false_idx) false_len # 2 letters_str = "ABCDEFGHIJ" rand_idx = false_idx[np.random.randint(0, false_len)] test_idx = test_y_arg[rand_idx] pred_idx = y_pred_arg[rand_idx] class_prob = np.floor( y_pred[rand_idx]*100 ) print(f'idx = {rand_idx}') print(f'해당 인덱스의 이미지는 {letters_str[test_idx]}') print(f'모델의 예측 : {letters_str[pred_idx]}') print(f'모델의 클래스별 확률 : ') print('-------------------') for idx, val in enumerate(letters_str) : print(val, class_prob[idx]) print('=================================================') if test_y_arg[rand_idx] == y_pred_arg[rand_idx] : print('정답') else : print('땡') plt.imshow(x_test[rand_idx], cmap='Greys') plt.show() <출력> idx = 1359 해당 인덱스의 이미지는 I 모델의 예측 : C 모델의 클래스별 확률 : ------------------- A 1.0 B 0.0 C 30.0 D 2.0 E 6.0 F 9.0 G 27.0 H 6.0 I 5.0 J 8.0 ================================================
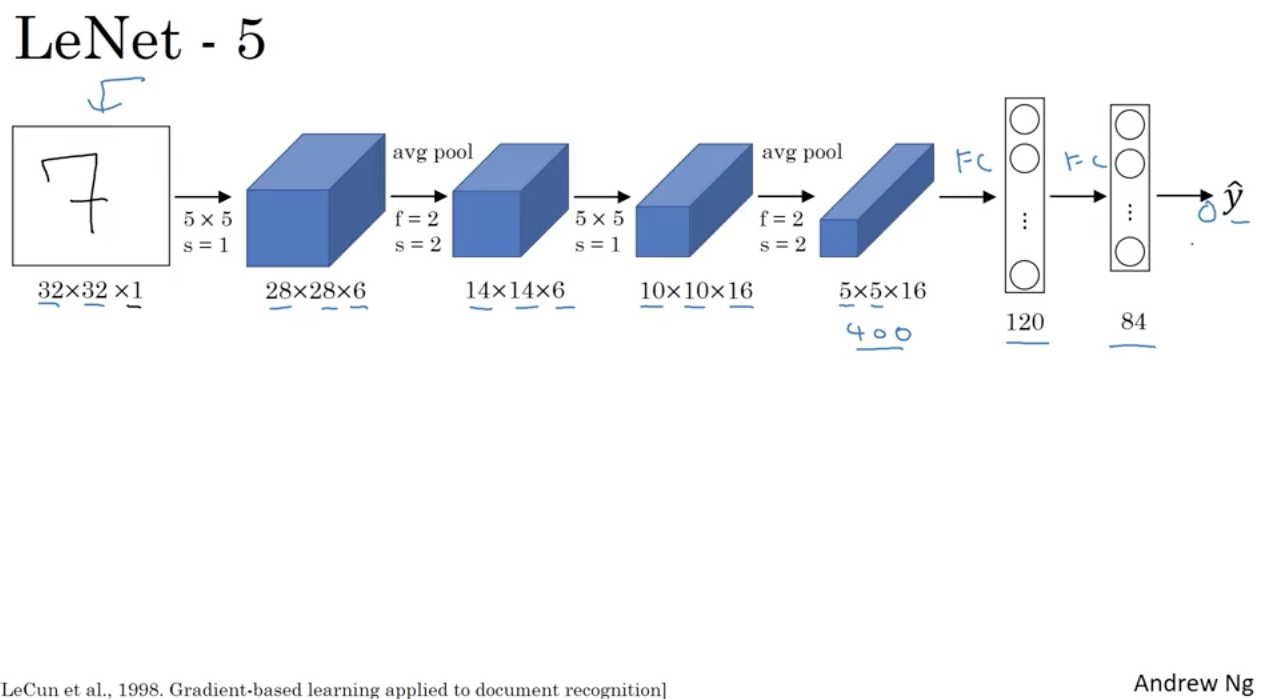
4. convolutional layer
- 1) 32 x 32 x 1의 input layer를 받는다.
- 2) filters은 안나왔지만 우리가 원하는 값으로 설정한다.
- 2-1) kernal_size인 filter의 크기는 5x5이고 strides=1임으로 한칸 씩 이동하면서 값을 연산하고 저장한다.
- 2-2) 32에서 28로 줄어든것으로 보아 padding은 없고, 32x1에서 28x6이 된것으로 보아 filters는 6임을 알 수 있다.
- 3) pool이 진행됐으며, pool_size는 2이고 2칸씩 이동한다. 2칸의 값중 큰값만 14개가 저장된다. filters의 크기는 변하지 않는다.
- 4) kernal_size는 5이고 1칸씩 이동하면서 값을 저장한다. 계산해보면 5에서 출발해서 1칸씩이니까 14-5+1 = 10의 크기를 갖는 map이 만들어진다.
- 4-1) 14 x 6에서 10 x 16이 된것으로 보아 filters는 16임을 알 수 있다.
- 5) pool의 크기는 2이고 2칸씩이동하니까 10의 절반인 5의 크기를 갖는 map이 만들어지고 filterts는 변하지 않는다.
- 6) 만약 padding이 있다면, 이전 feature map의 사이즈가 유지된다.
- 000) 400개의 픽셀을 이제 flatten 시킨다음 hidden layer를 두고 out layer(y_train의 shape만큼)를 받는다.
5. Sequential API 예제 1.
- 데이터 분할됐다고 가정. # 1. x-reshape x_train.shape <출력> (60000, 28, 28) _, r, w = x_train.shape x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.reshape[0], r, w, -1) x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.reshape[0], r, w, -1) * -1은 앞에 3개에 데이터를 넣고 4번째에 남은 데이터 넣겠다 의미임. * 여기서는 1이랑 같음 x_train.shape, x_test.shape <출력> ((60000, 28, 28, 1), (10000, 28, 28, 1)) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 2. Min-Max scaling max_n, min_n = x_train.max(), x_train.min() x_train = (x_train - min_n) / (max_n - min_n) x_test = (x_test - min_n) / (max_n - min_n) x_train.max(), x_train.min() <출력> (1.0, 0.0) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 3. 원핫인코딩 from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical class_n = len(np.unique(y_train)) y_train = to_categorical(y_train, class_n) y_test = to_categorical(y_test, class_n) y_train.shape <출력> (60000, 10) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 4. Sequential API 작성 - 1) 라이브러리 불러오기 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras.backend import clear_session from tensorflow.keras.models import Model, Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Flatten, BatchNormalization, Dropout - 2) Sequential API ## Sequential API # 1번. 세션 클리어 keras.backend.clear_session() # 2번. 레이어 조립 il = Input(shape=(28,28,1)) h = Conv2D(filters=128, # Conv2D를 통해 제작하려는 Feature map의 수 kernel_size=(3,3), # filter의 가로세로 size strides=(1,1), # convolutional filter의 이동 보폭 padding='same', # filter가 훑기 전에 상하좌우로 픽셀을 덧붙임 activation='relu')(il) # activation 주의!!! h = Conv2D(filters=128, # Conv2D를 통해 제작하려는 Feature map의 수 kernel_size=(3,3), # filter의 가로세로 size strides=(1,1), # convolutional filter의 이동 보폭 padding='same', # filter가 훑기 전에 상하좌우로 픽셀을 덧붙임 activation='relu')(h) # activation 주의!!! h = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), # pooling filter의 가로세로 사이즈 strides=(2,2))(h) # pooling filter의 이동보폭 h = Flatten()(h) h = Dense(128, activation='relu')(h) ol = Dense(10, activation='softmax')(h) # 3번. 모델 컴파일 model = Model(il, ol) model.compile(loss = 'categorical_crossentropy', metrics='accuracy', optimizer = 'adam') model.summary() <출력> _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 28, 28, 1)] 0 > > conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 128) 1280 > > conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 128) 147584 > > max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2 (None, 14, 14, 128) 0 > D) > > flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0 > > dense (Dense) (None, 128) 3211392 > dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290 > > ================================================================= Total params: 3361546 (12.82 MB) Trainable params: 3361546 (12.82 MB) Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte) _________________________________________________________________
# 5. Early stopping from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping es = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=5, verbose=1, restore_best_weights=True) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epoches = 100, verbose = 1, validation_size=0.2, callbacks = [es]) ----------------------------------------------------------- # 6. model 평가 - 1번 평가 model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) - 2번 평가 y_pred = model.predict(test_x) y_pred_arg = np.argmax(y_pred, axis =1) test_y_arg = np.argmax(test_y, axis = 1) accuracy_score(test_y_arg, y_pred_arg) print( classification_report(test_y_arg, y_pred_arg) -----------------------------------------------------------