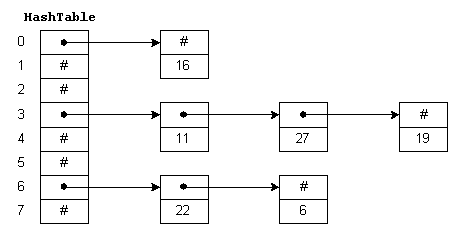
해시맵(HashMap)의 일반적인 개념
해시맵(HashMap)은 키(key)와 값(value)의 쌍으로 이루어진 데이터를 저장하고 검색하는 자료구조입니다. 해시맵은 효율적인 데이터 검색을 위해 해시 함수를 사용하여 키를 배열 인덱스로 변환하여 저장하고 검색합니다. 해시 함수를 통해 생성된 인덱스에 데이터가 충돌이 일어날 경우, 연결 리스트(LinkedList)나 균형 이진 탐색 트리(balanced binary search tree) 등을 사용하여 충돌 해결을 합니다.
해시맵의 구현 방법을 알아야 하는 이유
js개발자의 경우 new Map() 이나, 리터럴객체 (object literal) 를 이용하여 해시맵처럼 이용할 수 있습니다. 하지만 기본적인 자료구조의 동작 원리를 모르면서 개발자로서 커리어를 단단하게 쌓을수는 없다고 생각합니다. 해시맵은 기본적인 자료구조이지만, 각 언어마다 구현체가 다를 수 있고, 해시 알고리즘과 충돌 알고리즘이 달라서 퍼포먼스나 출력결과가 조금 씩 다를 수 있음을 이해하는것이 장기적인 커리어를 쌓는데 도움이 될것이라 생각해서 구현체를 만들어보았습니다.
해시맵 구현하기
저는 LinkedList를 이용해 HashMap 구조체를 구현해보았습니다. 성능최적화를 위하여 linkedList 대신 균형이진트리를 이용할 수 있습니다.
// LinkedList.js
class Node {
#key
#value
#next
constructor(key, value) {
this.#key = key
this.#value = value
}
hasNext() {
return !!this.#next
}
isEqual(node) {
return node instanceof Node && node.getKey() === this.#key
}
next() {
return this.#next
}
setNext(node) {
this.#next = node
}
toObj() {
return {key: this.getKey(), value: this.getValue()}
}
getValue() {
return this.#value
}
hasKey(key) {
return this.#key === key
}
getKey() {
return this.#key
}
}
class LinkedList {
#root = null
constructor() {
}
size(){
return this.getAll().length
}
getAll() {
const res = []
let current = this.#root
while (current){
res.push(current.toObj())
current = current.next()
}
return res
}
/**
* key를 기준으로 찾고 없으면 null을 반환
* */
search(key) {
let current = this.#root
while (current) {
if (current.hasKey(key)) {
return current
}
current = current.next()
}
return null
}
delete(key) {
if (!this.#root) return
if (this.#root.hasKey(key)) {
this.#root = this.#root.next()
return;
}
let current = this.#root
while (current.hasNext()) {
const nextNode = current.next()
if (nextNode.hasKey(key)) {
current.setNext(nextNode.next())
return;
}
current = nextNode
}
}
append(key, value) {
const newNode = new Node(key, value)
if (!this.#root) {
this.#root = newNode
return
}
if(this.#root.isEqual(newNode)){
this.#root = newNode
return;
}
let current = this.#root
while (current.hasNext() && !current.isEqual(newNode)) {
current = current.next()
}
current.setNext(newNode)
}
}
module.exports = {
LinkedList
}
// HashMap.js
const {LinkedList} = require("./LinkedList.js");
class HashMap {
#size = 100
#bucket
constructor(size) {
if (size) {
this.#size = size
}
this.#bucket = Array(this.#size).fill(null)
}
values() {
return this.#flatten().map(obj => obj.value)
}
forEach(callback) {
this.entries().forEach(callback)
}
entries() {
return this.#flatten().map(obj => [obj.key, obj.value])
}
keys() {
return this.#flatten().map(obj => obj.key)
}
set(key, value) {
const index = this.#getIdxByKey(key)
if (!this.#bucket[index]) {
this.#bucket[index] = new LinkedList()
}
const linkedList = this.#bucket[index]
linkedList.append(key, value)
}
size() {
return this.#bucket.filter(item => !!item).reduce((total, linkedList) => total + linkedList.size(), 0)
}
get(key) {
const linkedList = this.#getLinkedListByKey(key)
if (!linkedList) return null
const node = linkedList.search(key)
if (!node) return null
return node.getValue()
}
has(key) {
return !!this.get(key)
}
delete(key) {
const linkedList = this.#getLinkedListByKey(key)
linkedList.delete(key)
}
#flatten() {
return this.#bucket.filter(item => item).reduce((arr, linkedList) => arr.concat(linkedList.getAll()), [])
}
// return linkedList
#getLinkedListByKey(key) {
const idx = this.#getIdxByKey(key)
const node = this.#bucket[idx]
return node
}
#getIdxByKey(key) {
return this.#hash(key) % this.#size
}
/**
* key는 string으로만 받도록 구현
* */
#hash(key) {
if (!(typeof key === "string")) throw new Error("key should be a string");
let code = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
code += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return code;
}
}
module.exports = {
HashMap
}주요 부분은 다음과 같습니다.
해시 함수: 키를 해시 값으로 변환하는 함수입니다. 이 예시에서는 문자열 키의 각 문자의 유니코드 값을 합하여 해시 값을 계산합니다. 이번 구현에서는 간단하게 유니코드의 합을 이용하여 해시값을 계산했지만, 다양한 해시함수를 이용하여 구현할 수 있습니다. 해시함수를 구현하기 위해서 지켜야 할 규칙은 두가지입니다.
- 동일한 인풋이라면 항상 동일한 아웃풋을 반환해야 한다.
- 서로다른 두 인풋이 같은 아웃풋을 반환할 수 있다.
위의 두가지 성질로 인해 해시 충돌 현상이 발생하는 것이고, 이를 해결하기 위해 저는 링크드리스트 구현체를 사용하였습니다.
#hash(key) {
if (!(typeof key === "string")) throw new Error('key should be a string')
let code = 0
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
code += key.charCodeAt(i)
}
return code
}해시 값으로 인덱스 계산: 해시 값을 배열 인덱스로 변환합니다. 배열의 크기에 맞게 해시 값을 나머지 연산을 통해 인덱스로 변환합니다. 이 과정으로 인해 해시충돌 이 발생합니다. 이 함수로 인해 기본적으로 set, delete, get 메서드의 시간복잡도는 O(1)에 가깝습니다.(가깝다고 표현한 이유는 해시충돌 때문입니다.)
#getIdxByKey(key) {
return this.#hash(key) % this.#size
}마무리
코드로 직접 짜보니 오히려 링크드리스트나, 이진탐색트리 등의 자료구조의 필요성을 느끼게 되었습니다. 다음 포스팅은 시간이 허락한다면 bst를 다루고, 이를 응용한 업그레이드 hashMap을 구현해보도록 하겠습니다.(미래의 나에게 맡긴다.)
