1. 구조 가상 클래스
-
특정 위치에 있는 요소를 선택할 수 있는 가상 클래스
-
부모 요소가 있어야 정상적으로 작동 합니다.
가상 클래스 종류
| 가상 클래스 child | 가상 클래스 type |
|---|---|
| first-child | first-of-type |
| last-child | last-of-type |
| nth-child() | nth-of-type() |
| nth-last-child() | nth-last-of-type() |
| only-child | |
| empty | 기타 |
| root | 기타 |
1.1 first-child
- 모든 자식 요소 중에서 첫 번째에 위치하는 요소들을 모두 선택한다.
<p> 텍스트 더미1 </p>
<p> 텍스트 더미2 </p>
<p> 텍스트 더미3 </p>
<section>
<p> 텍스트 더미4 </p>
</section>/* p 요소 중에서 첫 번째에 위치하는 자식 요소를 모두 선택 */
p:first-child {
color: red;
}
1.2 last-child
- 모든 자식 요소 중에서 마지막에 위치하는 요소를 선택한다.
<body>
<p> 텍스트 더미1 </p>
<p> 텍스트 더미2 </p>
<p> 텍스트 더미3 </p> <!-- 선택되지 않음 -->
<section>
<p> 텍스트 더미4 </p>
<p> 텍스트 더미5 </p>
</section>
</body>/* p 요소 중에서 마지막 요소만 선택 된다. */
p:last-child {
color: green;
}
1.3 nth-child(n) & nth-last-child(n)
-
모든 자식 요소 중에서 (n)번 째에 해당하는 요소들을 모두 선택
nth-last-child는 뒤에서부터 요소를 선택한다 -
n은 정수 0이다.
-
0과 음수는 생략된다. 2n+1과 2n-1, 3n+1과 3n-1은 같은 수열을 생성한다.
| nth-child(n) | 내용 |
|---|---|
| (n) | 모든 요소를 선택 한다 |
| (5) | 5 번째에 해당하는 요소를 선택 |
| (2n) | (0x2) (1x2) (2x2) (3x2) , 2의 배수에 해당하는 요소를 선택 (짝수) |
| (2n+1) | (0x2)+1 (1x2)+1 (2x2)+1 , 2의 배수+1에 해당하는 요소를 선택 (홀수) |
| (3n-2) | (0x3)-2 (1x3)-2 (2x3)-2 ~~~ 요소 선택(-2, 1, 4 ~~) |
| (n+6) | (0+6) (0+7) (0+8) (0+9), 6 번째와 그 이후에 모든 요소 선택 |
| (n-4) | (-0+4) (-1+4) (-2+4) (-3+4) 앞에서부터 4개의 까지 요소 선택 |
| (n+8):(-n+12) | 8 번째 부터 12 번째 까지의 요소를 선택 |
<body>
<ol>
<li>Espresso</li>
<li>Americano</li>
<li>Caffe Latte</li>
<li>Caffe Mocha</li>
<li>Caramel Latte</li>
<li>Cappuccino</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>Espresso</li>
<li>Americano</li>
<li>Caffe Latte</li>
<li>Caffe Mocha</li>
<li>Caramel Latte</li>
<li>Cappuccino</li>
</ul>
</body>/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 짝수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(2n) { color: orange; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 홀수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(2n+1) { color: green; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 첫번쨰 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:first-child { color: red; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 마지막 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:last-child { color: blue; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 4번째 요소 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(4) { background: brown; }
/* ul 요소의 모든 자식 요소 중에서 뒤에서부터 시작하여 홀수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ul > :nth-last-child(2n+1) { color: red; }
/* ul 요소의 모든 자식 요소 중에서 뒤에서부터 시작하여 짝수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ul > :nth-last-child(2n) { color: blue; }
1.4 first-of-type & last-of-type
- 형제 요소 중에서 자신의 유형과 일치하는 첫 번째 요소를 선택 합니다
last-of-type은 뒤에서 부터 요소를 선택한다.
<body>
<h2>Heading</h2>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<section>
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
<p>Paragraph 4</p>
<p>Paragraph 5</p>
</section>
</body>/* 형제 요소 중에서 p 요소의 첫 번째 요소를 선택 */
p:first-of-type {
color: red;
font-style: italic;
}
/* 형제 요소 중에서 p 요소의 마지막 요소를 선택 */
p:last-of-type {
color: blue;
font-style: italic;
}
1.5 nth-of-type() & nth-of-last-type()
- 형제 요소 중에서 n번째 요소를 선택
nth-of-last-type()은 뒤에서 부터 요소를 선택
<div>
<div>This element isn't counted.</div>
<p>1st paragraph.</p>
<p class="fancy">2nd paragraph.</p> <!-- 2번째에 해당하는 요소이므로 밑줄은 안됨 -->
<div>This element isn't counted.</div>
<p class="fancy">3rd paragraph.</p>
<p>4th paragraph.</p>
</div>/* 홀수 odd (1,3,5~~) */
p:nth-of-type(2n + 1) {
color: red;
}
/* 짝수 even (2,4,5~~~) */
p:nth-of-type(2n) {
color: blue;
}
/* 형제 요소 중에 첫 번째 p 요소 선택 */
p:nth-of-type(1) {
font-weight: bold;
}
/* p 형제 요소 중에 클래스가 fancy 이며 홀수에 해당하는 요소 선택 */
p.fancy:nth-of-type(2n + 1) {
text-decoration: underline;
}

1.9 only-child
- 부모 요소를 갖는 자식 요소 중에서 형제 요소가 없는 요소만 선택 된다.
<div>
<div>I am an only child.</div> <!-- 형제 요소 X 선택됨 -->
</div>
<div>
<div>I am the 1st sibling.</div>
<div>I am the 2nd sibling.</div>
<div>
I am the 3rd sibling,
<div>but this is an only child.</div> <!-- 형제 요소 X 선택됨 -->
</div>
</div>div:only-child {
color: red;
}
div {
display: inline-block;
margin: 6px;
outline: 1px solid;
}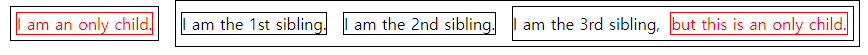
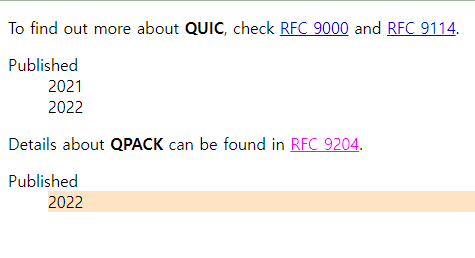
1.10 only-of-type
-
부모 요소를 갖는 자식 요소 중에서 같은 타입에 형제 요소가 없는 요소만 선택 된다.
-
형제 요소가 있어도 같은 타입만 아니라면 선택 된다.
<body>
<p>To find out more about <b>QUIC</b>, check <a href="#">RFC 9000</a> and <a href="#">RFC 9114</a>.</p>
<dl>
<dt>Published</dt>
<dd>2021</dd>
<dd>2022</dd>
</dl>
<p>Details about <b>QPACK</b> can be found in <a href="#">RFC 9204</a>.</p>
<!-- 같은 타입의 형제요소가 없기에 a 태그가 선택 됨 -->
<dl>
<dt>Published</dt>
<dd>2022</dd> <!-- 같은 타입의 형제 요소가 없기에 선택 됨 -->
</dl>
</body>a:only-of-type {
color: fuchsia;
}
dd:only-of-type {
background-color: bisque;
}
1.11 empty
-
자식이 없는 요소들을 선택합니다.
-
자식에는 공백, 요소, 텍스트 등이 포함될 수 있습니다. (주석은 예외)
<p>Element with no content:</p>
<div></div>
<p>Element with comment:</p>
<div><!-- Simple Comment --></div>
<p>Element with whitespace:</p>
<div> </div>
<p>Element with nested empty element:</p>
<div><p></p></div>div:empty {
outline: 2px solid deeppink;
height: 1em;
}
1.12 root
-
html의 최상위의 문서를 지정함 (우선 순위가 가장 높음) -
html에서 사용하는 모든 요소들에 대한 스타일을 정의할 수 있음
<body>
<p>Element with no content:</p>
<div></div>
<p>Element with comment:</p>
<div><!-- Simple Comment --></div>
<p>Element with whitespace:</p>
<div> </div>
<p>Element with nested empty element:</p>
<div>
<p></p>
</div>
</body>:root {
background: yellow;
color: white;
}

