파일 쓰기
file = open('hello.txt', 'w') # hello.txt 파일을 쓰기모드로 열기
file.write('Hello, world!') # 파일에 문자열 저장
file.close() # 파일 객체 닫기파일 읽기
file = open('hello.txt', 'r') # hello.txt 파일을 읽기모드로 열기
s = file.read()
print(s) # Hello, world!
file.close()자동으로 파일 객체 닫기
with open('hello.txt', 'r') as file:
s = file.read()
print(s)문자열 여러 줄을 파일에 쓰기
with open('hello.txt', 'w') as file:
for i in range(3):
file.write('Hello, world! {0}\n'.format(i))리스트에 들어있는 문자열을 파일에 쓰기 - writelines
lines = ['안녕하세요\n', 'heyrin입니다.\n']
with open('hello.txt', 'w') as file:
file.writelines(lines)파일의 내용을 한 줄씩 리스트로 가져오기
with open('hello.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
print(lines) # ['안녕하세요\n', 'heyrin입니다.\n']파일의 내용을 한 줄씩 읽기
with open('hello.txt', 'r') as file:
line = None
while line != '': # 빈 문자열이 나올 때까지 == 내용이 없을 때까지
line = file.readline()
print(line.strip('\n'))readline() 은 더 이상 읽을 줄이 없을 때는 빈 문자열을 반환한다는 특성을 이용해 조건식을 만든다.
with open('hello.txt', 'r') as file:
for line in file: # 파일의 내용을 한 줄씩 읽어서 변수에 저장
print(line.strip('\n')) # 문자열에서 \n 삭제하여 출력 파일 객체는 이터레이터(반복가능객체)이므로, 언패킹도 가능하다.
with open('hello.txt', 'r') as file:
a, b = file
print(a.strip('\n'))
print(b.strip('\n'))
# 안녕하세요
# heyrin입니다.파이썬 객체를 파일에 저장하고 가져오기
피클링 : 객체를 파일에 저장하는 것 pickle.dump()
언피클링 : 파일에서 객체를 읽어오는 것 pickle.load()
import pickle
name = 'heyrin'
age = 26
address = '서울시'
scores = {'korean':100, 'english': 90, 'mathmatics': 99, 'science': 93}
with open('heyrin.p', 'wb') as file:
pickle.dump(name, file)
pickle.dump(age, file)
pickle.dump(address, file)
pickle.dump(scores, file)with open('heyrin.p', 'wb') as file: 바이너리 쓰기 모드로 파일 열기
heyrin.p 의 .p 는 확장자이며, 다른 확장자도 상관 없음
import pickle
with open('heyrin.p', 'rb') as file:
name = pickle.load(file)
age = pickle.load(file)
address = pickle.load(file)
scores = pickle.load(file)
print(name)
print(age)
print(address)
print(scores)name, age, address, scores 순으로 저장했으므로, 불러올 때도 같은 순서로 불러온다.
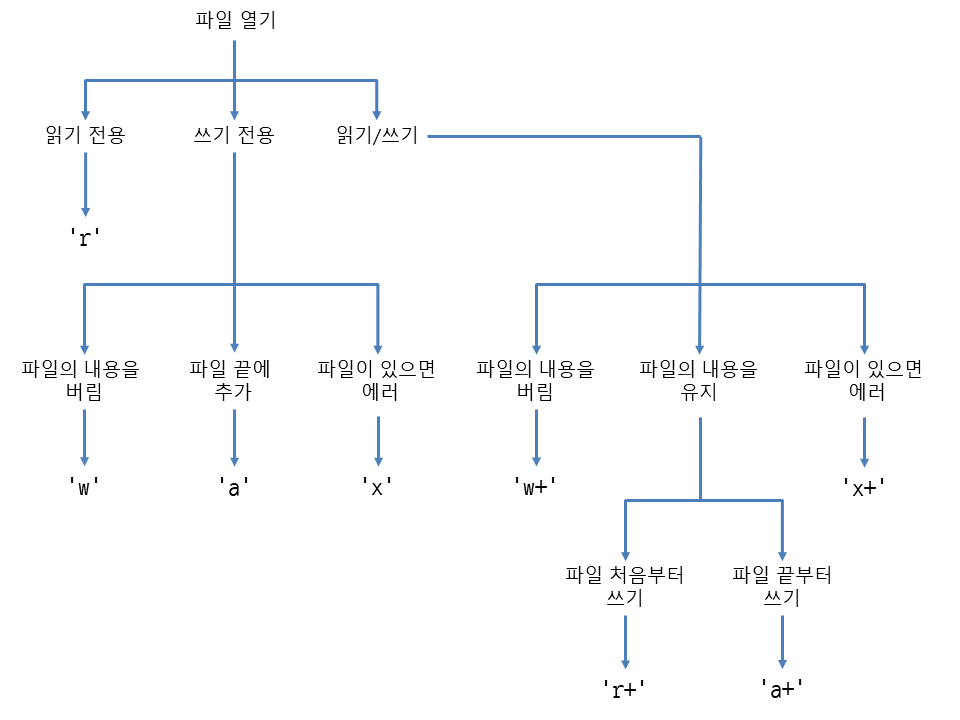
파일 모드