Compiler 강의 노트 CH4
Finite automata : Abstract models of computing machines
and
Formal language : Formal representation of computing problems.
Regular Language for Finite Automata, Pushdown Automata fo CFG, Recursive Language for Turing Machines
Basic concept
- G =(V,T,P,S)
- V: set of variables
- T: set of terminals
- P: set of production rules
- S: The start variables.
ex: G = ({S, A, B}, {a, b}, {S->aA, A->bS, S->lambde}, S)
example1) Grammar for a^nb^n |n>=0
- {S->lambda , S->aSb}
example2) 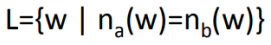
{S->lambda, S->aSb, S->bSa}
example3)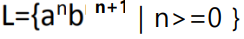
{S-> Ab, A->aAb, A->lambda}
Regular expression
- A notation of describing a language.

- If r1 and r2 are regular expression, so are below
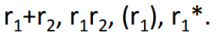
The Language L(r) denoted by r is
- Pi(empty set)
- lambda
- a (element of sigma)
- L(r1+r2)
- L(r1r2)
- L((r1))
- L(r1*)
RE for language
- L = {w (= {a,b} : w starts with a ends with b}
r: a (a+b) * b - L = {w (= {a,b} : w contains substring aba}
r: (a+b) * aba (a+b) * - L = {w (= {0,1} :w has no consecutive o}
r: (1 + 01) *(0 + lambda)
RE and RL
- Every RE r denotes a regular language.
- For every r, there is a NFA M for acceptiong L(r) - Every RL L is denoted by a RE r.
- For every DFA M, there is a RE r L(r) = L(M)