SCC
SCC(Strongly Connected Component)는 방향 그래프에서 모든 정점이 서로 연결된 부분 그래프를 의미합니다. 즉, 한 SCC 안의 모든 정점 u,v에 대해
u→v (u에서 v로 가는 경로 존재)
v→u (v에서 u로 가는 경로 존재)
이 두 조건을 만족해야 합니다.
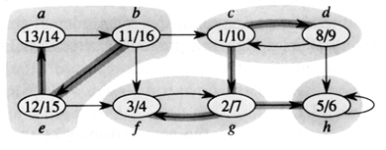
타잔 알고리즘
깊이 우선 탐색 알고리즘(DFS)을 활용해 SCC(Strongly Connected Component, 강한 연결 요소)를 찾는 알고리즘
동작 방식
- 각 정점을 방문하며 id와 low-link 값을 계산한다.
low-link란 현재 정점이 속한 SCC에서 가장 낮은 DFS 방문 순서이다. - 현재 정점의 id와 low-link 값이 같다면 해당 정점은 SCC의 시작점이다.
- 스택에서 정점을 꺼내며 SCC를 구성한다.
문제로 확인하기
전체 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BaekJoon2150 {
static int V, E, id;
static boolean[] finished;
static int[] ids, low;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] arr;
static Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> sccList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
initialize(); // 그래프 초기화 및 입력 처리
findSCCs(); // SCC 찾기
printResult(); // 결과 출력
}
private static void initialize() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 수
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 수
finished = new boolean[V + 1]; // SCC 완료 여부
ids = new int[V + 1]; // 각 정점의 DFS 방문 순서
low = new int[V + 1]; // 각 정점의 Low-Link 값
arr = new ArrayList[V + 1]; // 그래프 인접 리스트 초기화
id = 0; // DFS 방문 순서 초기화
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
arr[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
while (E-- > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr[A].add(B);
}
}
private static void findSCCs() {
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
if (ids[i] == 0) { // 아직 방문하지 않은 정점이면 DFS 수행
DFS(i);
}
}
}
private static void printResult() {
for (ArrayList<Integer> scc : sccList) {
scc.sort(null);
}
sccList.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.get(0) - o2.get(0));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(sccList.size()).append("\n");
for (ArrayList<Integer> scc : sccList) {
for (int node : scc) {
sb.append(node).append(" ");
}
sb.append("-1\n");
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
private static void DFS(int at) {
ids[at] = low[at] = ++id; // 현재 정점의 방문 순서와 Low-Link 값 초기화
stack.push(at); // 스택에 현재 정점 추가
for (int to : arr[at]) { // 인접 정점 탐색
if (ids[to] == 0) { // 방문하지 않은 정점이면 DFS 수행
DFS(to);
low[at] = Math.min(low[at], low[to]); // DFS 후 Low-Link 값 갱신
} else if (!finished[to]) { // 방문했지만 아직 SCC로 분리되지 않은 정점
low[at] = Math.min(low[at], low[to]); // 역방향 간선이므로 Low-Link 값 갱신
}
}
// SCC의 루트 노드인지 확인
if (ids[at] == low[at]) {
extractSCC(at); // SCC 추출
}
}
private static void extractSCC(int at) {
ArrayList<Integer> scc = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
int node = stack.pop(); // 스택에서 정점 추출
finished[node] = true; // 해당 정점을 SCC 완료 상태로 설정
scc.add(node); // SCC 리스트에 추가
if (node == at) break; // 루트 노드까지 추출하면 종료
}
sccList.add(scc); // SCC 결과 리스트에 추가
}
}

