Theory
Context - In a nutshell, a Context is a web application.
<Context docBase="Driver:/locationOfWebApp/webManager" path="WebAppUrl"/>CATALINA_HOME and CATALINA_BASE
CATALINA_HOME: Represents the root of your Tomcat installation, for example /home/tomcat/apache-tomcat-9.0.10 or C:\Program Files\apache-tomcat-9.0.10.
CATALINA_BASE: Represents the root of a runtime configuration of a specific Tomcat instance. If you want to have multiple Tomcat instances on one machine, use the CATALINA_BASE property.
Contents of CATALINA_BASE
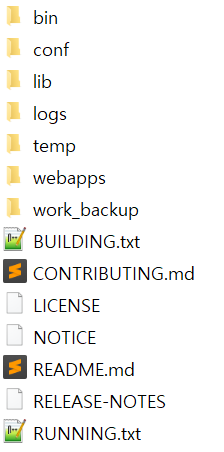
Before you start using CATALINA_BASE, first consider and create the directory tree used by CATALINA_BASE. Note that if you do not create all the recommended directories, Tomcat creates the directories automatically. If it fails to create the necessary directory, for example due to permission issues, Tomcat will either fail to start, or may not function correctly.
Consider the following list of directories:
The bin directory with the setenv.sh, setenv.bat, and tomcat-juli.jar files.
Recommended: No.
Order of lookup: CATALINA_BASE is checked first; fallback is provided to CATALINA_HOME.
The lib directory with further resources to be added on classpath.
Recommended: Yes, if your application depends on external libraries.
Order of lookup: CATALINA_BASE is checked first; CATALINA_HOME is loaded second.
The logs directory for instance-specific log files.
Recommended: Yes.
The webapps directory for automatically loaded web applications.
Recommended: Yes, if you want to deploy applications.
Order of lookup: CATALINA_BASE only.
The work directory that contains temporary working directories for the deployed web applications.
Recommended: Yes.
The temp directory used by the JVM for temporary files.
Recommended: Yes.
Standard DIR layout
.html, .jsp, etc. - The HTML and JSP pages, along with other files that must be visible to the client browser (such as JavaScript, stylesheet files, and images) for your application. In larger applications you may choose to divide these files into a subdirectory hierarchy, but for smaller apps, it is generally much simpler to maintain only a single directory for these files.
/WEB-INF/web.xml - The Web Application Deployment Descriptor for your application. This is an XML file describing the servlets and other components that make up your application, along with any initialization parameters and container-managed security constraints that you want the server to enforce for you. This file is discussed in more detail in the following subsection.
/WEB-INF/classes/ - This directory contains any Java class files (and associated resources) required for your application, including both servlet and non-servlet classes, that are not combined into JAR files. If your classes are organized into Java packages, you must reflect this in the directory hierarchy under /WEB-INF/classes/. For example, a Java class named com.mycompany.mypackage.MyServlet would need to be stored in a file named /WEB-INF/classes/com/mycompany/mypackage/MyServlet.class.
/WEB-INF/lib/ - This directory contains JAR files that contain Java class files (and associated resources) required for your application, such as third party class libraries or JDBC drivers.
JDBC Pool
<Resource name="jdbc/TestDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory"
testWhileIdle="true"
testOnBorrow="true"
testOnReturn="false"
validationQuery="SELECT 1"
validationInterval="30000"
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis="30000"
maxActive="100"
minIdle="10"
maxWait="10000"
initialSize="10"
removeAbandonedTimeout="60"
removeAbandoned="true"
logAbandoned="true"
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis="30000"
jmxEnabled="true"
jdbcInterceptors="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.ConnectionState;
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.interceptor.StatementFinalizer"
username="root"
password="password"
driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql"/>LOGGING
Empty catalina.out
cat /dev/null > catalina.out로깅 정책
/etc/logrotate.d/tomcat
/var/log/tomcat/catalina.out { copytruncate daily rotate 7 compress missingok size 5M }
/usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf설명
copytruncate : 기존 파일을 백업해서 다른 파일로 이동하고 기존 파일은 지워버리는 옵션
daily : 로그파일을 날짜별로 변환
compress : 지나간 로그파일들을 gzip으로 압축
dateext : 순환된 로그파일의 날짜확장자
missingok : 로그파일이 없더라도 오류를 발생시키지 않음
rotate 30 : 로그 파일은 30개만큼 저장된 다음 제거되거나 메일로 보내짐
notifempty : 파일의 내용이 없으면 새로운 로그 파일을 생성 안함
postrotate-endscript : 로그파일 처리 후에 해당 명령어를 실행
size 100M : 사이즈가 100M가 되면 로테이트 됨
extension ext : logrotate 실행후에 순환되어 생성되는 파일의 이름뒤에 확장자로 붙일 확장자명을 지정한다.
create 0664 root utmp : 로그파일을 새로 생성할 때, 0644 권한, root 사용자, utmp 그룹으로 생성한다.
REF
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/jdbc-pool.html
https://www.linux.co.kr/linux/logrotate/page04.htm
https://m.blog.naver.com/PostView.naver?isHttpsRedirect=true&blogId=sory1008&logNo=221124291927
