
1. Intro
@OneToMany 연관관계 설정시에 HashSet 과 @OrderBy 를 사용할 경우 내부동작에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
2. 개발환경
- Spring Boot 2.6.5
- Java 11
- Kotlin 1.6.10
- Gradle 7.4.1
- Intellij IDEA 2021.3.3
build.gradle.kts
import org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.tasks.KotlinCompile
plugins {
val springBootVersion = "2.6.5"
val dependencyManagementVersion = "1.0.11.RELEASE"
val kotlinVersion = "1.6.10"
id("org.springframework.boot") version springBootVersion
id("io.spring.dependency-management") version dependencyManagementVersion
kotlin("jvm") version kotlinVersion
kotlin("kapt") version kotlinVersion
kotlin("plugin.spring") version kotlinVersion
kotlin("plugin.jpa") version kotlinVersion
}
group = "com.ask"
version = "0.0.1-SNAPSHOT"
java.sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa")
implementation("com.fasterxml.jackson.module:jackson-module-kotlin")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-reflect")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8")
runtimeOnly("com.h2database:h2")
developmentOnly("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools")
kapt("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-configuration-processor")
testImplementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test")
}
tasks.withType<KotlinCompile> {
kotlinOptions {
freeCompilerArgs = listOf("-Xjsr305=strict")
jvmTarget = "11"
}
}
tasks.withType<Test> {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
allOpen { // (1)
annotation("javax.persistence.Entity")
}(1) Hibernate 는 Lazy Loading 을 위해 Entity 를 상속받아 프록시 객체를 생성하므로 Entity 에 대하여 allOpen 을 설정합니다.
plugin.spring 은 plugin.allOpen 을 wrapping 하였기 때문에 allOpen 을 추가로 지정할 수 있습니다.
3. Property, Entity 설정
application.yml
spring:
sql:
init:
data-locations: classpath:sql/data.sql # (1)
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
username: sa
password:
jpa:
properties:
hibernate:
show_sql: false
format_sql: true
open-in-view: false
defer-datasource-initialization: true # (2)
logging:
level:
"[org.hibernate.SQL]": debug
"[org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder]": trace- (1) 서버 시작시에 실행할 data sql 파일 위치를 지정합니다.
- (2) hibernate 에 의해 schema 생성이 끝난후에 data.sql 파일을 실행하도록 설정합니다.
resources/sql/data.sql
insert into tb_company values('company01', 'cname');
insert into tb_user values ('user21', 'user21', 3, 'company01');
insert into tb_user values ('user22', 'user22', 2, 'company01');
insert into tb_user values ('user23', 'user23', 1, 'company01');Company Entity
@Entity
@Table(name = "tb_company")
class Company(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid")
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuid", strategy = "uuid2")
@Column(name = "company_id")
var id: String? = null,
@Column(nullable = false, length = 30)
var name: String,
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "company")
val users: Set<User> = hashSetOf() // (1)
) {
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (other == null || Hibernate.getClass(this) != Hibernate.getClass(other)) return false
other as Company
return id == other.id
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
return id.hashCode()
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Company(id=$id, name='$name')"
}
}(1) 순서를 보장하지 않는 타입으로 초기화 타입을 지정하였습니다. 하단과 같이 선언하여도 무관합니다.
val users: MutableSet<User> = mutableSetOf()User Entity
@Entity
@Table(name = "tb_user")
class User(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid")
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuid", strategy = "uuid2")
@Column(name = "user_id")
var id: String? = null,
@Column(nullable = false, length = 30)
var loginId: String,
@Column(nullable = false)
var priority: Long,
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, optional = false)
@JoinColumn(name = "company_id")
var company: Company
) {
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (other == null || Hibernate.getClass(this) != Hibernate.getClass(other)) return false
other as User
return id == other.id
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
return id.hashCode()
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "User(id='$id', loginId='$loginId', priority='$priority')"
}
}4. Test Code
테스트 1
@DataJpaTest
internal class CompanyTest(
@Autowired private val testEntityManager: TestEntityManager
) {
@DisplayName("HashSet 으로 선언한 컬렉션 타입 검증")
@Test
internal fun verifyType() {
// given
val companyId = "company01" // (1)
// when
val company = testEntityManager.find(Company::class.java, companyId)
val users = company.users
// then
assertThat(users).isInstanceOf(PersistentSet::class.java) // (2)
}
}- (1) data.sql 파일을 통해 insert 되어있는 company 의 id 를 사용합니다.
- (2) hibernate 에 의해 Set 컬렉션은
PersistentSet으로 wrapping 되는것을 검증합니다.
테스트 1, 실행 결과 - 성공
- 테스트가 정상 동작하는것을 확인 가능합니다.
테스트 2
@DataJpaTest
internal class CompanyTest(
@Autowired private val testEntityManager: TestEntityManager
) {
@DisplayName("HashSet 사용시 순서 검증")
@Test
internal fun verifySetOrder() {
// given
val companyId = "company01"
// when
val company = testEntityManager.find(Company::class.java, companyId)
val users = company.users
// then
assertAll(
{ assertThat(users).isInstanceOf(PersistentSet::class.java) },
{ assertThat(users).flatMap(User::priority).containsSequence(1L, 2L, 3L) }
)
}
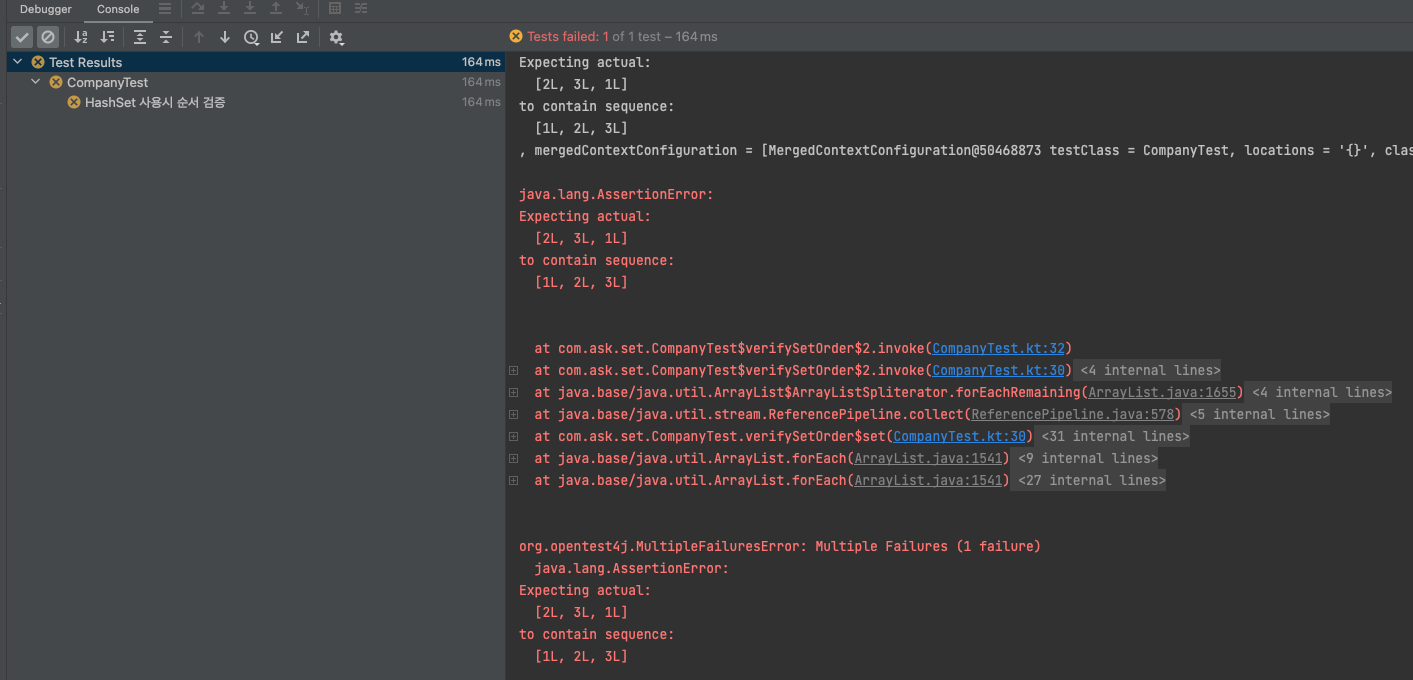
}테스트 2, 실행 결과 - 실패
- priority 필드값의 순서가 일치하지 않아 테스트가 실패합니다.
테스트 3
- 테스트에 앞서 Company Entity
@OneToMany선언 부분에@OrderBy("priority ASC")를 추가합니다.
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "company")
@javax.persistence.OrderBy("priority ASC")
val users: Set<User> = hashSetOf()- @OrderBy 어노테이션 추가후에
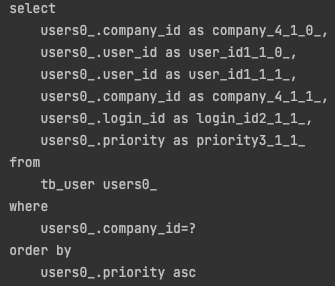
테스트 2에 실행한 테스트를 다시 실행시 성공하는것이 확인 가능합니다. - 추가로 Lazy Loading 된 컬렉션을 touch 할때 발생하는 sql 에
order by가 추가된 부분도 확인 가능합니다.

5. Debugging
HashSet 은 순서를 보장하지 않는데 어떻게 Hibernate 에서는 순서를 유지 시킬수 있을까요?
결론 먼저 정리하면 PersistentSet 은 Set 을 wrapping 하였기 때문에 내부에 Set 을 생성하여 가지고있는데
이때 객체 생성에 사용하는것이 org.hibernate.type.CollectionType 이며 @OrderBy 사용했는지 안했는지에 따라 달라집니다.
따라서 위의 테스트 1 과 같이 생각해보면 필드 초기화 타입이 어떤 타입인지는 영향을 끼치지 않으며 선언 타입이 Set 일 경우
PersistentSet 으로 wrapping 되며 @OrderBy 를 사용하면 내부에 LinkedHashSet 을 사용하기 때문에 순서가 보장되는것을 알 수 있습니다.
Set 에 @OrderBy 를 사용했을 경우
org.hibernate.type.OrderedSetType 사용
public class OrderedSetType extends CollectionType {
// ...
@Override
public Object instantiate(int anticipatedSize) {
return anticipatedSize > 0
? new LinkedHashSet( anticipatedSize )
: new LinkedHashSet();
}
}Set 에 @OrderBy 를 사용하지 않았을 경우
org.hibernate.type.SetType 사용
public class SetType extends CollectionType {
// ...
@Override
public Object instantiate(int anticipatedSize) {
return anticipatedSize <= 0
? new HashSet()
: new HashSet(anticipatedSize + (int) (anticipatedSize * .75f), .75f);
}
}CollectionType Setting
CollectionType 이 세팅되는 메서드 입니다.
package org.hibernate.type;
public class Set extends Collection {
// ...
public CollectionType getDefaultCollectionType() {
if (isSorted()) { // (1)
return getMetadata().getTypeResolver()
.getTypeFactory()
.sortedSet(getRole(), getReferencedPropertyName(), getComparator());
} else if (hasOrder()) { // (2)
return getMetadata().getTypeResolver()
.getTypeFactory()
.orderedSet(getRole(), getReferencedPropertyName());
} else {
return getMetadata().getTypeResolver()
.getTypeFactory()
.set(getRole(), getReferencedPropertyName());
}
}
// ...
}- (1) 연관관계 맵핑시 선언 타입에
SortedSet을 사용할 경우 true 를 반환합니다. - (2)
@OrderBy를 사용할 경우true를 반환합니다.
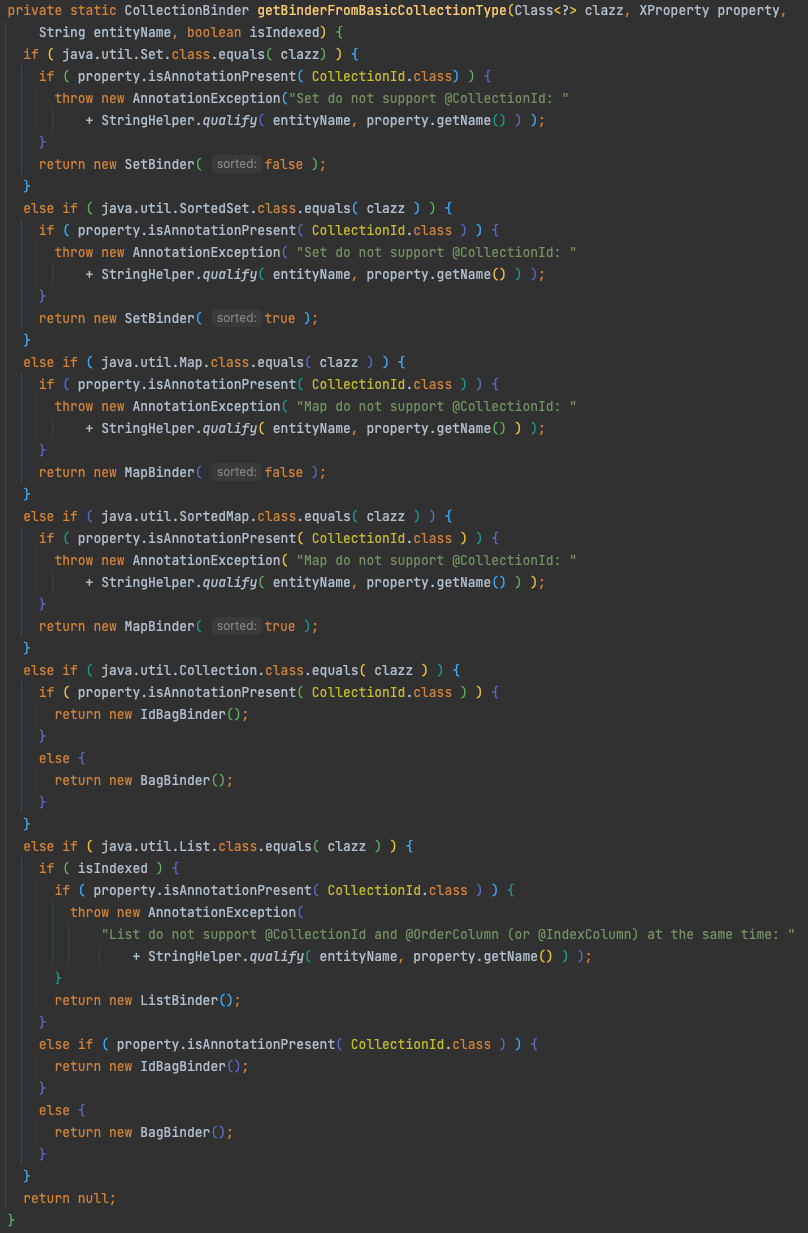
CollectionBinder
추가적으로 Hibernate 에서 지원하는 컬렉션 타입에 따른 분기 처리를 하단 메서드에서 확인 가능합니다.
지원하지 않는 타입으로 선언하여 null 을 리턴할 경우 예외가 발생합니다.
org.hibernate.cfg.annotations.CollectionBinder
6. 마무리
이로서 연관관계 맵핑시에 Set 과 @OrderBy 를 사용할 경우 어떻게 순서를 보장하는지 알아 보았습니다.
Intro 에는 HashSet 과 @OrderBy 를 사용할 경우 내부동작에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 라고 했었지만
확인 결과 초기화 타입은 영향이 없으며 선언 타입과 @OrderBy 어노테이션의 조합으로 동작이 달라지는것을 알 수 있었습니다.
이상으로 이번 포스팅은 마무리 하도록 하겠습니다.
블로그에서 사용된 코드는 GitHub 에서 확인 하실 수 있습니다.
