GRANT
-
SQL GRANT is a command used to provide access or privileges on the database objects to the users.
-
The Syntax for the GRANT command is:
GRANT privilege_name
ON object_name
TO {user_name |PUBLIC |role_name}
[WITH GRANT OPTION];
privilege_name is the access right or privilege granted to the user.
Some of the access rights are ALL, EXECUTE, and SELECT.
object_name is the name of an database object like TABLE, VIEW, STORED PROC and SEQUENCE.
user_name is the name of the user to whom an access right is being granted.
-
PUBLIC is used to grant access rights to all users.
-
ROLES are a set of privileges grouped together.
-
WITH GRANT OPTION - allows a user to grant access rights to other users.
GRANT SELECT ON employee TO user1;
REVOKE
The REVOKE command removes user access rights or privileges to the database objects.
The Syntax for the REVOKE command is:
REVOKE privilege_name
ON object_name
FROM {user_name |PUBLIC |role_name}
REVOKE SELECT ON employee FROM user1
Privileges and Roles
-
Privileges: Privileges defines the access rights provided to a user on a database object. There are two types of privileges.
1) System privileges - This allows the user to CREATE, ALTER, or DROP database objects.
2) Object privileges - This allows the user to EXECUTE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE data from database objects to which the privileges apply.
Few CREATE system privileges are listed below:
System Privileges
CREATE object allows users to create the specified object in their own schema.
CREATE ANY object allows users to create the specified object in any schema.
The above rules also apply for ALTER and DROP system privileges.
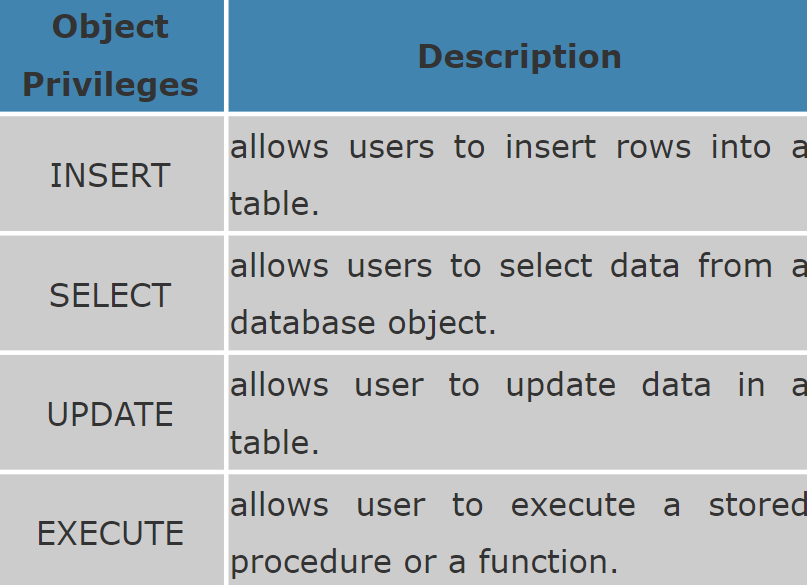
Few of the object privileges are listed below:

The above rules also apply for ALTER and DROP system privileges.
Some of the privileges granted to the system roles are as given below:
- Roles: Roles are a collection of privileges or access rights. When there are many users in a database it becomes difficult to grant or revoke privileges to users. Therefore, if you define roles, you can grant or revoke privileges to users, thereby automatically granting or revoking privileges. You can either create Roles or use the system roles pre-defined by oracle.
System Role Privileges Granted to the Role

Creating Roles:
The Syntax to create a role is:
CREATE ROLE role_name
[IDENTIFIED BY password];
- For Example: To create a role called "developer" with password as "pwd",the code will be as follows
CREATE ROLE testing
[IDENTIFIED BY pwd];
It's easier to GRANT or REVOKE privileges to the users through a role rather than assigning a privilege directly to every user. If a role is identified by a password, then, when you GRANT or REVOKE privileges to the role, you definitely have to identify it with the password.
We can GRANT or REVOKE privilege to a role as below.
- For example: To grant CREATE TABLE privilege to a user by creating a testing role:
- create a testing Role
CREATE ROLE testing
- grant a CREATE TABLE privilege to the ROLE testing. You can add more privileges to the ROLE.
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO testing;
- grant the role to a user.
GRANT testing TO user1;
To revoke a CREATE TABLE privilege from testing ROLE, you can write:
REVOKE CREATE TABLE FROM testing;
The Syntax to drop a role from the database is as below:
DROP ROLE role_name;
- For example: To drop a role called developer, you can write:
DROP ROLE testing;
