/ 큐
한쪽 끝으로 자료를 넣고, 반대쪽에서는 자료를 뺄 수 있는 선형 구조
(FIFO, First In First Out)
/ 큐의 구현
enqueue(data) : 맨 뒤에 데이터 추가하기
dequeue() : 맨 앞의 데이터 뽑기
peek() : 맨 앞의 데이터 보기
isEmpty(): 큐가 비었는지 안 비었는지 여부 반환해주기
-
데이터 넣고 뽑는 걸 자주하는 자료 구조입니다
-
스택과 마찬가지로 링크드 리스트와 유사하게 구현할 수 있습니다
-
스택과 다르게 큐는 끝과 시작의 노드를 전부 가지고 있어야 하므로,
self.head 와 self.tail 을 가지고 시작
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def enqueue(self, value):
# 제일 뒤에 넣어줌 tail에
new_node = Node(value)
if self.is_empty(): # 비어있을때 예외처리
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
return
def dequeue(self):
# 제일 앞에꺼 반환 head반환
if self.is_empty():
return "Queue is Empty"
delete_head = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
return delete_head.data
def peek(self):
# 제일 앞에꺼 조회
if self.is_empty():
return "Queue is Empty"
return self.head.data
def is_empty(self):
# 큐가 비엇는가?
return self.head is None
queue = Queue()
queue.enqueue(3)
print(queue.peek())
queue.enqueue(4)
print(queue.peek())
queue.enqueue(5)
print(queue.dequeue()) # 맨앞꺼 빼서 반환, 3반환
print(queue.peek()) # 맨앞꺼 조회, 4
print(queue.dequeue()) # 맨앞꺼 빼서 반환, 4반환
print(queue.dequeue()) # 맨앞꺼 빼서 반환, 5반환
print(queue.dequeue()) # Queue is Empty
print(queue.is_empty()) # True/ 해쉬
/ 해쉬 테이블이란?
컴퓨팅에서 키를 값에 매핑할 수 있는 구조인 연관 배열 추가에 사용되는 구조이다. 해시 테이블은
해시 함수를 사용하여 색인(index)을 버킷(bucket)이나 슬롯(slot)의 배열로 계산한다. 데이터를 다루는 기법 중에 하나로 데이터의 검색과 저장이 아주 빠르게 진행된다
- 딕셔너리 = 해쉬테이블
딕셔너리 내부적으로는 배열을 사용한다는 사실
- 해쉬 함수(Hash Function)는 임의의 길이를 갖는 메시지를 입력하여 고정된 길이의 해쉬값을 출력하는 함수이다
class Dict:
def __init__(self):
self.items = [None] * 8
def put(self, key, value):
# 구현해보세요!
index = hash(key) % len(self.items)
self.items[index] = value
return
def get(self, key):
# 구현해보세요!
index = hash(key) % len(self.items)
return self.items[index]
my_dict = Dict()
my_dict.put("test", 3)
print(my_dict.get("test")) # 3이 반환되어야 합니다!만약 인덱스 값이 같아져 버리면 충돌발생! 데이터를 덮어 써버리는 결과발생한다
해결방법 =>
- 링크드 리스트 이용
( 이 방식을 연결지어서 해결한다고 해서 체이닝(Chaining) 이라고 합니다 )
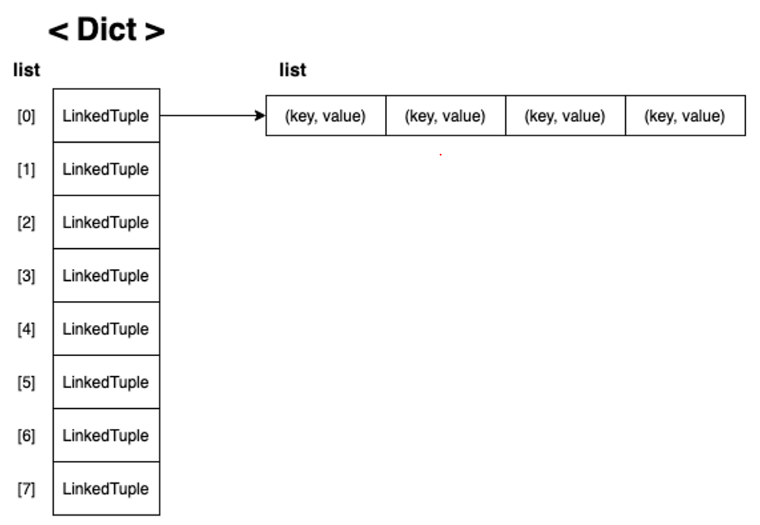
class LinkedTuple:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def add(self, key, value):
self.items.append((key, value))
def get(self, key):
for k, v in self.items:
if k == key:
return v
class LinkedDict:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
for i in range(8):
self.items.append(LinkedTuple())
def put(self, key, value):
index = hash(key)%len(self.items)
self.items[index].add(key,value)
return
def get(self, key):
index = hash(key) % len(self.items)
return self.items[index].get(key)
- 배열의 다음 남는 공간에 넣어서
개방 주소법(Open Addressing) - 구현 x
해쉬 퀴즈 (출석체크)
all_students = ["나연", "정연", "모모", "사나", "지효", "미나", "다현", "채영", "쯔위"]
present_students = ["정연", "모모", "채영", "쯔위", "사나", "나연", "미나", "다현"]
def get_absent_student(all_array, present_array):
# 구현해보세요!
student_dict = {}
for key in all_array:
student_dict[key] = True
for key in present_array:
del student_dict[key]
for key in student_dict:
return key
print(get_absent_student(all_students, present_students))
print("정답 = 예지 / 현재 풀이 값 = ",get_absent_student(["류진","예지","채령","리아","유나"],["리아","류진","채령","유나"]))
print("정답 = RM / 현재 풀이 값 = ",get_absent_student(["정국","진","뷔","슈가","지민","RM"],["뷔","정국","지민","진","슈가"]))2주차 퀴즈
최대할인 적용
shop_prices = [30000, 2000, 1500000]
user_coupons = [20, 40]
def get_max_discounted_price(prices, coupons):
# 이 곳을 채워보세요!
prices.sort(reverse=True)
coupons.sort(reverse=True)
price_index=0
coupons_index = 0
max_discounted_price = 0
while price_index < len(prices) and coupons_index < len(coupons):
max_discounted_price += prices[price_index] * (100 -coupons[coupons_index]) /100
price_index += 1
coupons_index += 1
while price_index < len(prices):
max_discounted_price += prices[price_index]
price_index += 1
return max_discounted_price
print("정답 = 926000 / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_max_discounted_price([30000, 2000, 1500000], [20, 40]))
print("정답 = 485000 / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_max_discounted_price([50000, 1500000], [10, 70, 30, 20]))
print("정답 = 1550000 / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_max_discounted_price([50000, 1500000], []))
print("정답 = 1458000 / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_max_discounted_price([20000, 100000, 1500000], [10, 10, 10]))올바른 괄호
def is_correct_parenthesis(string):
# 구현해보세요!
stack =[]
for i in range(len(string)):
if string[i] == "(":
stack.append(i)
elif string[i] == ")":
if len(stack) == 0:
return False
else:
stack.pop()
if len(stack) ==0:
return True
else:
return False
return
print("정답 = True / 현재 풀이 값 = ", is_correct_parenthesis("(())"))
print("정답 = False / 현재 풀이 값 = ", is_correct_parenthesis(")"))
print("정답 = False / 현재 풀이 값 = ", is_correct_parenthesis("((())))"))
print("정답 = False / 현재 풀이 값 = ", is_correct_parenthesis("())()"))
print("정답 = False / 현재 풀이 값 = ", is_correct_parenthesis("((())"))베스트 앨범 뽑기
1. 속한 노래가 많이 재생된 장르를 먼저 수록한다.(단, 각 장르에 속한 노래의재생 수 총합은 모두 다르다.)
2. 장르 내에서 많이 재생된 노래를 먼저 수록한다.
3. 장르 내에서 재생 횟수가 같은 노래 중에서는 고유 번호가 낮은 노래를 먼저 수록한다.
가장 많이 → 정렬을 해야 한다! 라는 의미로 보시면 됩니다.
우선, 속한 노래가 가장 많이 재생된 장르를 찾아보겠습니다.
그걸 알기 위해서는 장르별 재생 수를 더해야 하는데,
장르별(Key) 로 재생 수(Value)를 더하고 관리하기 위해서는
딕셔너리를 쓰시면 됩니다!genres = ["classic", "pop", "classic", "classic", "pop"]
plays = [500, 600, 150, 800, 2500]
def get_melon_best_album(genre_array, play_array):
# 1. 속한 노래가 많이 재생된 장르를 먼저 수록한다
# 2. 장르 내에서 많이 재생된 노래를 먼저 수록한다
# 3. 장르 내에서 재생 횟수가 같다면 고유 번호가 낮은 노래 먼저 수록한다
# 장르(키) 별로 우선 재생된 횟수(벨류)를 저장해야 합니다
# 장르별로 곡의 정보(인덱스, 재생횟수) 배열로 묶어 저장한다
genre_total_play_dict = {}
genre_index_play_array_dict = {} # 2
n = len(genre_array)
for i in range(n):
genre = genre_array[i]
play = play_array[i]
if genre not in genre_total_play_dict:
genre_total_play_dict[genre] = play
genre_index_play_array_dict[genre] = [[i, play]]
# 2 배열로 만든다, 장르별 여러곡 쌓인걸 저장하기위해, 인덱스와 플레이횟수
else:
genre_total_play_dict[genre] += play
genre_index_play_array_dict[genre].append([i,play])
# print(genre_total_play_dict) # 장르(키) 별로 우선 재생된 횟수(벨류)를 저장해야 합니다
# {'classic': 1450, 'pop': 3100}
#print(genre_index_play_array_dict) # 장르별로 곡의 정보(인덱스, 재생횟수) 배열로 묶어 저장한다
# {'classic': [[0, 500], [2, 150], [3, 800]], 'pop': [[1, 600], [4, 2500]]}
# dict.items() => 튜플이 배열로감싸서 나옴 => 인덱스 이용 해서 정렬 [1] (딕셔너리의 벨류값)
# 함수 sorted(배열,key=람다) => sorted(a.items(), key lamda item : item[1],reverse=True)
# reverse=True 내림차순
# .items() 로 딕셔너리 튜플을 감싼 배열로 => sorted() 람다, 인덱스 이용해서 정렬 + 내림차순)
# 장르를 paly순으로 정렬된 값
sorted_genre_play_array = sorted(genre_total_play_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True)
# print(sorted_genre_play_array)
# [('pop', 3100), ('classic', 1450)]
# genre_index_play_array_dict 와 sorted_genre_play_array 이용해서
result =[]
for genre,value in sorted_genre_play_array:
index_play_array = genre_index_play_array_dict[genre] # 정렬 되어있지 않음
sorted_index_play_array = sorted(index_play_array, key=lambda item: item[1],reverse=True)
#print(sorted_index_play_array)
#[[4, 2500], [1, 600]] <- 총합 큰 pop먼저
#[[3, 800], [0, 500], [2, 150]] <- classic
for i in range(len(sorted_index_play_array)):
if i>1: # 두개씩만 호출
break
result.append(sorted_index_play_array[i][0]) # 곡의 인덱스 0번째
return result
print("정답 = [4, 1, 3, 0] / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_melon_best_album(["classic", "pop", "classic", "classic", "pop"], [500, 600, 150, 800, 2500]))
print("정답 = [0, 6, 5, 2, 4, 1] / 현재 풀이 값 = ", get_melon_best_album(["hiphop", "classic", "pop", "classic", "classic", "pop", "hiphop"], [2000, 500, 600, 150, 800, 2500, 2000]))