○ 상속의 정의와 장점
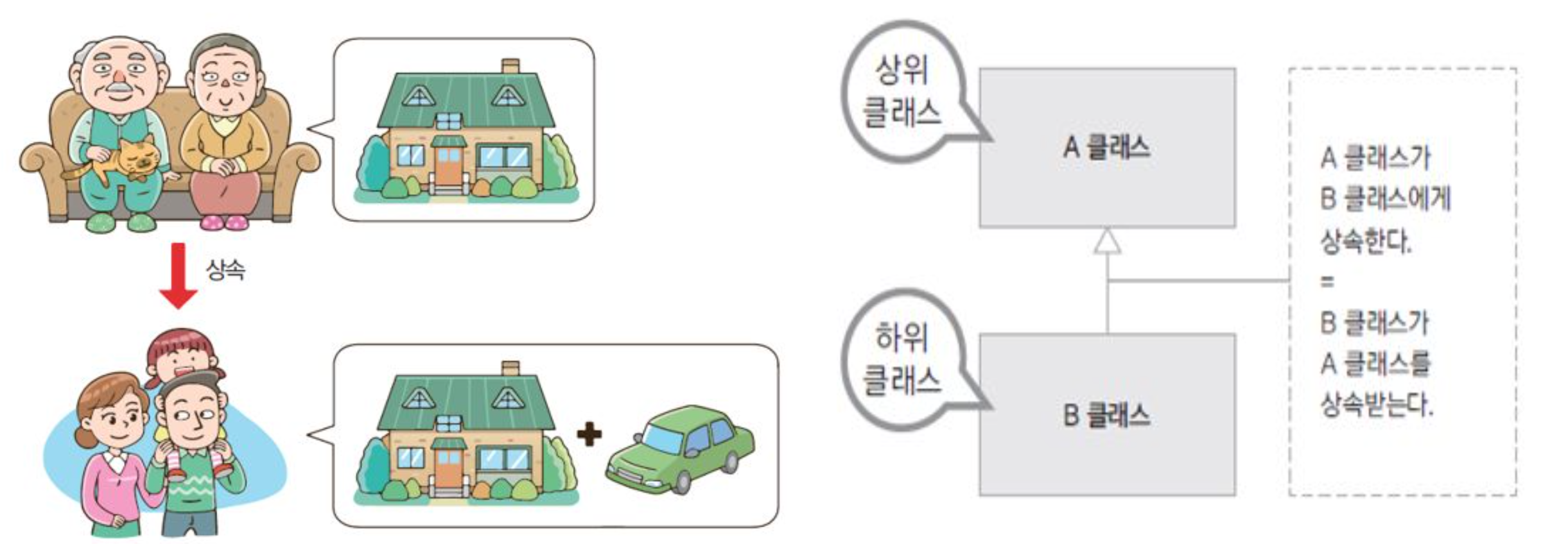
- 정의 :
상속이란, 기존의 클래스를 재사요하여 새로운 클래스를 작성하는 것이다. - 장점 :
- 재사용, 중복 제거 : 적은 양의 코드로 새로운 클래스를 작성
- 코드를 공통적으로 관리할 수 있어 유지/보수가 편하다.
class Child extends Parents {
}조상 클래스 = 부모클래스, 상위클래스, 기반클래스
자손 클래스 = 자식클래스, 하위클래스, 파생된 클래스
자손 클래스는 조상 클래스의 모든 멤버를 상속 받으므로 항상 조상 클래스보다 같거나 많은 멤버를 갖는다.
○ 메모리 그리기

부모가 먼저, 자식이 아래에 메모리가 할당된다. 인스턴스 주소는 부모 인스턴스가 시작되는 주소이다.
○ 생성자 호출
- (부모 클래스 생성자) > (자식 클래스 생성자) 순으로 호출된다.
- 상속이 되어 있으면 부모를 찾고 부모부터 생성자가 호출된다. 이후 메모리에 부모의 객체부터 올린다.
- 자식클래스 객체 안에는 부모 클래스에서 상속된 부분이 들어 있다.
- 따라서 자식 클래스 안의 부모 클래스 부분을 초기화하기 위하여 부모 클래스의 생성자도 호출되는 것이다.
○ super()
- 명시적인 생성자 호출 : 부모 클래스의 생성자를 호출
- 묵시적인 생성자 호출 : 개발자가
super()를 넣지 않으면 컴파일러가 부모 클래스 기본 생성자 자동 호출
💡 Object 클래스를 제외한 모든 클래스의 생성자는 첫 줄에 반드시 자신의 다른 생성자 또는 조상의 생성자를 호출해야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 컴파일러는 생성자의 첫 줄에
super();를 자동적으로 추가할 것이다.
- 자손 클래스의 멤버가 조상 클래스의 멤버를 사용할 수 있으므로 조상의 멤버들이 먼저 초기화되어 있어야 하기 때문이다.
- 자식클래스에서 부모클래스의 생성자를 선택할 때 인수 형태에 따라 적절한 생성자가 선택된다.
⭐️⭐️⭐️ 부모 클래스에 기본 생성자가 없으면, 나중에 자식에서 에러날 수 있으므로 보통 새로운 생성자를 만들면, 기본 생성자도 넣어준다.
- 프레임 워크에서 호출하는 기준이 기본생성자라서 프레임워크 사용 시에도 에러가 날 수 있다.
○ super
부모 클래스의 필드를 사용할 때는 아래 세 가지 방법이 있다.
1. 그냥 호출
2. super.변수 : 부모 클래스 소속을 나타내기 위해 가장 많이 이용
3. this.변수
class A {
int a = 10;
}
class B extends A {
B () {
//1번
System.out.println(a);
//2번
System.out.println(super.a);
//3번
System.out.println(this.a);
}
}- 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스에 같은 이름의 변수가 있을 때
super.x와this.x는 서로 다른 값을 참조하게 된다.
class Parent {
int x = 10;
}
class Child extends Parent {
int x = 20;
void method() {
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("this.x = " + this.x);
System.out.println("super.x = " + super.x);
}
}
//result
x=20
this.x=20
super.x=10super를 이용하여 메서드를 호출할 수도 있다. 보통 조상 클래스의 메서드를 자손 클래스에서 오버라이딩한 경우에super를 사용한다.
○ protected
default는 다른 패키지에서 사용할 수 없지만, protected는 다른 패키지더라도 상속한 클래스에서는 접근 가능하다.
자식 클래스는 부모 클래스의 private를 제외한 모든 멤버들을 상속 받는다.
○ 상속예제
class TV {
private int size;
public TV(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
protected int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
class ColorTV extends TV {
private int pixel;
ColorTV(int size, int pixel) {
super(size);
this.pixel = pixel;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.println(this.getSize() + "인치 " + pixel + "컬러");
}
protected int getPixel (){
return pixel;
}
}
class IPTV extends ColorTV {
private String ip;
IPTV (String ip, int size, int pixel) {
super(size, pixel);
this.ip = ip;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.print("나의 IPTV는 "+ ip +" 주소의 ");
super.printProperty();
}
}
public class InheritanceTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTV = new ColorTV(32, 1024);
myTV.printProperty();
IPTV iptv = new IPTV ("192.1.1.2", 32, 2048);
iptv.printProperty();
}
}💡 자손 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하면 조상 클래스의 멤버와 자손 클래스의 멤버가 합쳐진 하나의 인스턴스로 생성된다.
