핵심 키워드
- callback
- Promise
- async, await
callback
동기 = synchronous : 순서대로 일을 처리하는 방식이다.
비동기 = asynchrounous : 순서대로 일 처리 X 빨리 처리할 수 있는 일 부터 처리한다.
콜백함수 : CallBack 함수란 이름 그대로 나중에 호출되는 함수를 말한다.
어떤 이벤트가 발생했거나 특정 시점에 도달했을 때
시스템에서 호출하는 함수이다.비동기 함수는 동기 함수가 모두 끝난 후 실행된다.
비동기 함수의 순서는 보장될 수 있다.
// 반대로 말하자면 동기함수가 끝나지 않으면 비동기 함수는 실행되지 않는다.
function fn_newCallBack(){
console.log("비동기적으로 호출되고 싶다.");
}
console.log("------- 호출 직전 -------");
setTimeout(fn_newCallBack, 0);
console.log("------- 호출 이후 -------");
// 무한로프
while(true){
console.log("Loading...");
}Loading....
// setTimeout 함수로 3초늦게 async찍기
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('Hello')
},40)
function syncFunc(syncCallback){
syncCallback();
}
function asyncFunc(asyncCallback){
setTimeout(asyncCallback, 3000);
}
syncFunc(() => console.log('sync'));
asyncFunc(() => console.log('async'));
// sync
// asyncSettimeout로 인해 3000 mils가 지나기 전까지는 함수가 호출 X
싱글쓰레드인 JS에서 어떻게 비동기처리를 하지??
JS는 콜백함수를 차례대로 Queue에 적재한다.
이 Queue는 현재 동작중인 메인스레드가 일을 다 끝내면, 다음으로 해야할 일들이 있는 Queue이다.
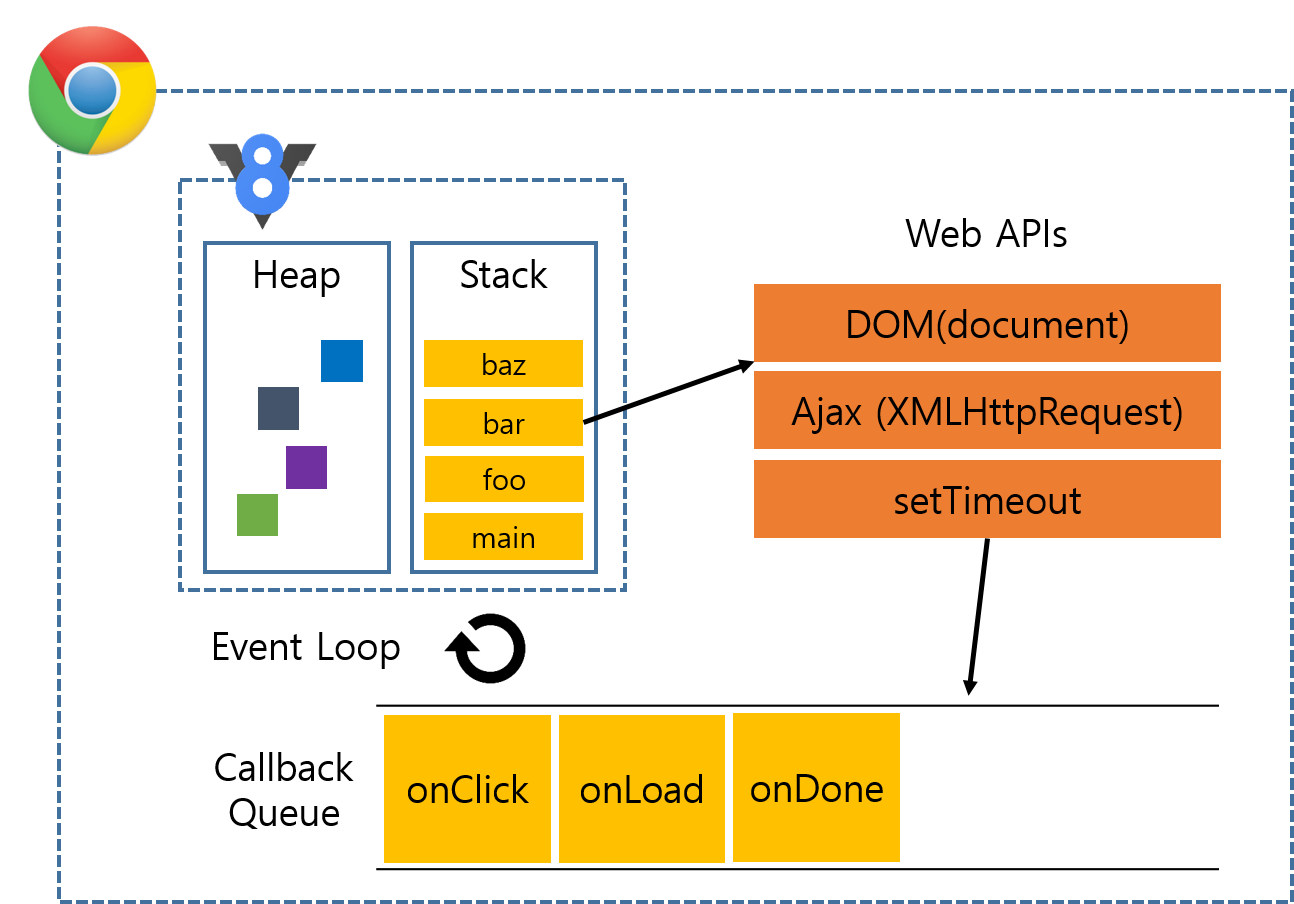
더 자세히 공부하고 싶으면 자바스크립트 런타임을 검색해보자
Callback 왜쓰는데?
비동기 처리를 위해 Callback함수를 사용한다.
데이터(글목록)을 서버로부터 받아와서 화면에 뿌려주는 웹을 생각해보자.
맨 처음 서버로부터 데이터를 받아온다.
동기적으로 실행한다면 서버로부터 데이터를
받아올 때 동안 클라이언트는 대기한다.
비동기로 실행한다면 데이터를 수신하는 코드를 비동기적으로
실행하며 화면을 표시하는 코드먼저 실행하여 보다 빠르고 효율적으로 실행한다.이러한 예제 외에도
1. 사용자의 이벤트 처리
2. 네트워크의 응답 처리
3. 파일을 읽고 쓰는 등 파일 시스템 작업
4. 알람 기능같은 의도적 시간 지연 기능네트워크가 있다고 가정하고 JS소스를 만들어보자.
// 포스트 목록
const posts = [
{post_id : 1, post_title: '첫번째 글'},
{post_id : 2, post_title: '두번째 글'},
{post_id : 3, post_title: '세번째 글'}
];
// 코멘트 목록
const comments = [
{post_id : 1, comment_id : 1, comment : "첫번째 글 첫번째 코멘트"},
{post_id : 2, comment_id : 1, comment : "두번째 글 첫번째 코멘트"},
{post_id : 2, comment_id : 2, comment : "두번째 글 두번째 코멘트"},
{post_id : 3, comment_id : 1, comment : "두번째 글 첫번째 코멘트"},
{post_id : 3, comment_id : 2, comment : "세번째 글 두번째 코멘트"},
];
const postNum = 3;
// Post를 가져오는 Callback 함수
const getPost = (id, onSuccess, onError) =>{
setTimeout(() => {
const post = posts.find(post=>post.post_id === id);
if(post){
onSuccess(post.post_id);
}else{
onError("No post");
}
}, 1000)
}
// Comments 가져오는 Callback 함수
const getComments = (post_id, onSuccess, onError) =>{
setTimeout(() => {
const result = comments.filter(comments=>comments.post_id === post_id);
if(result.length>0){
onSuccess(result);
}else{
onError("No Comments");
}
}, 2000)
}
// 콜백함수 내 콜백함수 사용시
// 가독성이 좋지않고, 실수 위험도 커진다.
getPost(postNum,
(postId)=>{
console.log('Post',postId);
getComments(postId,
(result)=>{
console.log(result)
}),
(msg)=>{
console.log(msg)
}
},
(msg)=>{
console.log(msg)
}
)
// Result
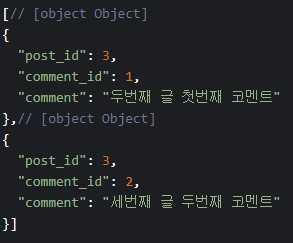
Promise
Promise MDN
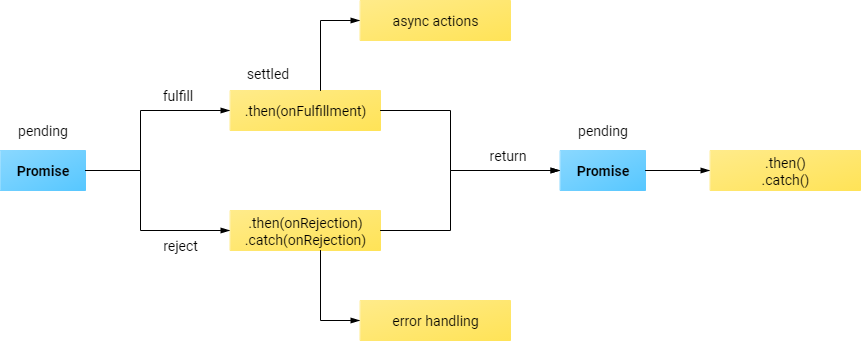
Promise 객체는 비동기 작업이 맞이할 미래의 완료 또는 실패와 그 결과 값을 나타냅니다.
비동기 연산이 종료된 이후에 결과 값과 실패 사유를 처리하기 위해 사용.
프로미스를 사용하면 비동기 메서드에서 마치 동기 메서드처럼 값을 반환할 수 있다.Promise는 3가지의 상태를 가진다.
대기(pending): 이행하지도, 거부하지도 않은 초기 상태.
이행(fulfilled): 연산이 성공적으로 완료됨.
거부(rejected): 연산이 실패함.
// Promise
// 성공했을때 수행할 함수 resolve, 실패했을 때 reject
// state를 가지며, 각 state에 따라 다른 함수실행
// pending : 진행 중, fulfilled : 성공적으로 끝난 상태, rejected : 실패로 끝난 상태
// 생성법 new Promise(resolve, reject)
const getPost = (id) =>{
// 전에 onScuccess, onError을 추가해준 것과는 달리
// Promise객체에 resolve, reject로 처리 가능
// new Promise(...) 하는 순간 여기에 할당된 비동기 작업은 바로 시작
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const post = posts.find(post=>post.post_id === id);
if(post){
resolve(post.post_id);
}else{
reject("No post");
}
}, 1000)
})
}
const getComments = (post_id) =>{
return new Promise ((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const result = comments.filter(comments=>comments.post_id === post_id);
if(result.length>0){
resolve(result);
}else{
reject("No Comments");
}
}, 2000)
})
}
const postNum = 2;
// .then 성공했을 때
// .catch 실패했을 때 -> 다른 함수가 실패했을 때도 실행 or .catch()
getPost(postNum)
.then(postId => {
console.log('PostId : ',postId)
// return을 실행하여야 getCommtents가 리턴되어 new Promise를 만들 수 있음
return getComments(postId)
})
.then(result => console.log("Comments",result))
.catch(msg => console.log(msg))Promise의 다른 예
function getData(callback) {
// new Promise() 추가
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
$.get('url 주소/products/1', function(response) {
// 데이터를 받으면 resolve() 호출
resolve(response);
});
});
}
async, await
Promise와 함께 사용되며
async await 사용
await
await 문은 Promise가 fulfill되거나 reject 될 때까지 async 함수의 실행을 일시 정지하고, Promise가 fulfill되면 async 함수를 일시 정지한 부분부터 실행합니다. 이때 await 문의 반환값은 Promise 에서 fulfill된 값이 됩니다.
async를 함수앞에 붙임으로 비동기 함수라는 것을 선언하고 비동기 함수 내에서만 await 사용가능
// async await 사용
// async를 함수앞에 붙임으로 비동기 함수라는 것을 선언
async function getResult(){
// 비동기 실행될 때 await으로 호출된 값을 기다린 후에 postId_result에 넣어준다.
const postId_result = await getPost(postNum);
console.log("Post Id : ",postId_result);
const commemts_result = await getComments(postId_result);
console.log("Comments : ",commemts_result)
}
getResult();await를 사용하지 않았다면 데이터를 받아온 시점에 콘솔을 출력할 수 있게 콜백 함수나 .then()등을 사용해야 했을 것.
하지만 async await 문법 덕택에 비동기에 대한 사고를 대비하지 않아도 된다.
// try catch로 비동기함수에 대한 에러처리를 할 수있다.
async function getResult(){
try{
const postId_result = await getPost(postNum);
console.log("Post Id : ",postId_result);
const commemts_result = await getComments(postId_result);
console.log("Comments : ",commemts_result)
}catch(error){
console.log(error)
}
}논의해보면 좋은 것들
- 왜 Callback 함수를 안쓰고 promise와 async, await를 사용하는지 토론해보기
-> 소스의 가독성이 좋아지고 구조를 설계하는데 있어 얻는 이득이 많다.
- Promise와 async, await를 어느 기능에서 활용하면 좋을지 토의해보기
네트워킹 처리, 사용자 이벤트처리, 애니메이션 처리 등등...
