Record Lock
Concurrent-Readers / Exclusive-Writers
- writer / reader process가 동시에 공유 자원에 접근하려고 할 때 기존의 Mutex는 한 번에 1개의 process만 접근하도록 하기 때문에 성능이 안좋은 상황이 생긴다.
- 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 reader와 writer의 상황을 따로 적용한다.
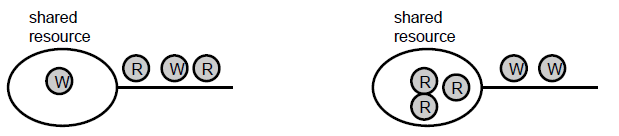
writer process
- 한 번에 1개의 writer만 접근하도록 한다.
- writer가 접근중일 때는 writer와 reader 모두 block
- exclusive lock → Mutex와 동일하다.
- ex.) 은행의 withdraw / deposit ...
reader process
- reader가 접근하고 있을 때 다른 reader도 접근을 허용한다.
- 단, writer는 접근을 허용하지 않는다. 읽고있던 process가 전부 종료되면 writer의 접근을 허용한다.
- Shared lock 형태
- 은행의 inquiry..
File Record Lock
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fildes, int cmd, struct flock *lock);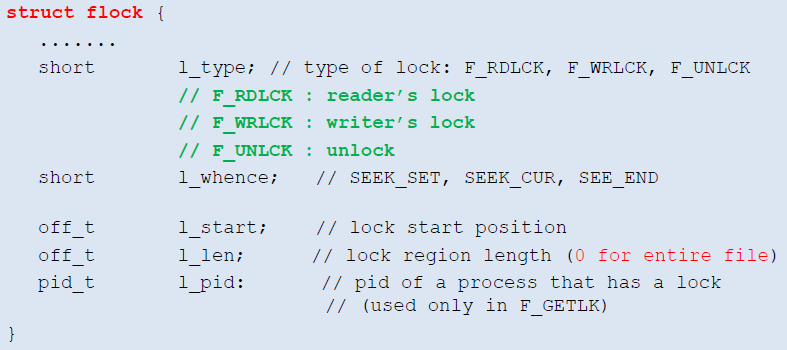
- fildes : file descriptor
- cmd : F_GETLK / F_SETLK / F_SETLKW
- F_GETLK : lock을 얻을 수 있나 check → 다른 누군가 lock하고 있으면 구조체에 그 정보를 전달한다. 가능하다면 F_UNLCK를 return
- F_SETLK : lock 설정을 시도 → R/W lock이 이미 되어 있으면 즉시 -1을 return
- F_SETLKW : lock 설정을 시도 → lock이 될 때까지 wait(blocking version)
File Lock
#include <fcntl.h>
int flock(int fd, int operation);- 전체 file을 lock한다.
- fd : open file descriptor
- operation : LOCK_SH(reader) / LOCK_EX(writer) / LOCK_UN
Lock inheritance & release
Inheritance
- fork()로 parent의 lock이 child에게 상속되지 않는다.
- exec() 시에는 process의 lock이 그대로 상속된다.
Release
- process가 종료할 때, process에 있는 모든 lock은 사라진다.
- file descriptor가 close되면 file의 모든 lock은 종료된다.
Lock의 정보는 HDD의 inode 내부에 존재한다.
Advisory / Mandatory Lock
Advisory locking
- kernel에 의해 강제된 lock이 아님 → kernel은 lock을 한 지 모른다.
- 문제가 생긴다면 programmer의 책임이다.
Mandatory locking
ex.)
$ chmod2644 lockfile
chmod g+s, g-x lockfile- OS가 lock을 관리한다.(kernel)
- set-group-ID를 ON / group-execute bit를 OFF하면 mandatory lock을 할 수 있다.
