IPC methods
- Pipe : parent - child b/w process
- FIFO : named pipe
- Message queue
- Shared Memory
FIFO(named Pipe)
Pipe
- IPC 중 가장 오래되고 기본적인 방법
- r/w system call
- blocking 기능이 존재(automatic)
- 한계점
- 양방향 소통을 하려면 2개를 사용해야한다.
- 공통 조상일 때만 사용이 가능하다.
- 외부에 전달이 되지 않는다.
FIFO
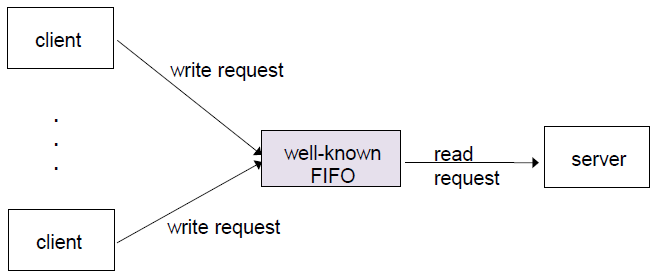
- 서로 관련 없는 process끼리도 공유가 가능하다.
- file처럼 활용이 가능하다.(open, close..)
- server - client 관계에서도 주로 사용
- well-known FIFO : 이름을 만들어놓고 접근하도록 한다.
mkfifo
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
- FIFO를 create하는 함수
- pathname : file name
- mode : permission ← open() 함수와 동일
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
System V IPC methods
- Message Queues
- mailbox와 유사하게 작동하며 message를 보낸다.
- Asynchronous IPC이다. 즉, 시간을 꼭 맞출 필요가 없다.
- "message" data를 주고받는데, sender는 message에 type을 붙여서 보낸다.
- Shared memory
- memory를 공유한다.
- data race가 발생할 수 있어 주의해야한다.
Identifiers & Keys
Identifier
- 각 IPC 구조체는 음이 아닌 정수를 가진다.
- OS가 IPC 구조에 부여한 고유 번호이다.
- 실제 생성된 객체에 부여한다.
Key
- programmer가 정의한 값
- id = xxxget(key, ...)
IPC object에 접근하는 법

- ipc_perm 구조체에 key 값이 존재한다.
- key값을 정의한다.
- client/server : key를 확인하고 agree
- server가 key를 이용하여 IPC를 create
- client는 open / 같은 key를 가지고 IPC를 사용한다.
- create할 때 이미 key값이 존재한다면? → error
- 존재하던 key를 delete하고 다시 새 것으로 create
Message Queues
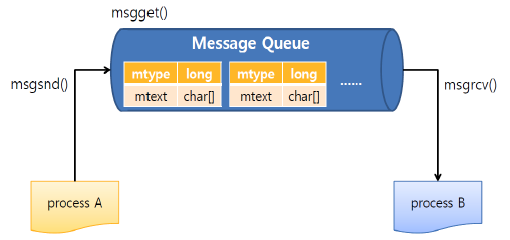
- kernel에 massage가 linked list 형태로 존재한다.
- OS는 identifier로 구분한다.
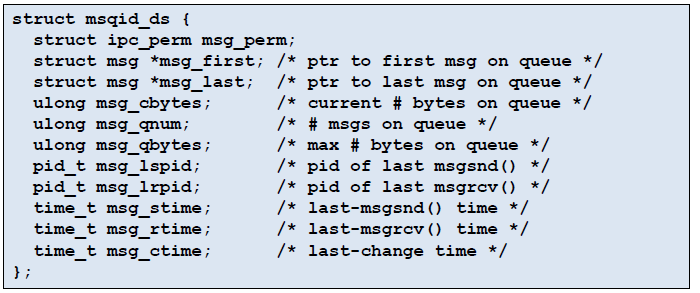
- 각 queue는 msqid 구조체가 존재하고, msgctl() 함수로 확인할 수 있다.
- message structure는 user가 정의하는 mtype과 mtext로 구성된다.
- message를 보낸다는 것은 message structure를 보낸다는 의미이다.
- message를 수용할 수 있는 최대 숫자만큼 수용했거나, message의 byte가 최대일 때 message queue가 제한된다.
msgget
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgget(key_t key, int flag);
- key : message queue key(id)
- flag : open/create flag와 동일
- return : 성공 시 message queue id / 실패 시 -1
msgsnd
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *ptr, size_t nbytes, int flag);
- msqid : message queue id
- ptr : message structure pointer
- nbytes : mtype을 제외하고, user가 define한 buffer 크기
- flag : blocking / non-blocking
- 0(default) : blocking
- IPC_NOWAIT : nonblocking
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
msgrcv(1)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgrcv(int msqid, void *ptr, size_t nbytes, long msgtype, int flag);
- msqid : message queue id
- ptr : recieve buffer address
- nbytes : buffer의 size
- msgtype :
- == 0 : 가장 첫 message(type에 관계 없이)
- > 0 : msgtype 값과 동일한 message
- < 0 : 값에 절대값을 적용한 뒤 이 값과 같거나 작은 값
- flag : blocking / non-blocking
- 0(default) : blocking
- IPC_NOWAIT : nonblocking
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
msgctl
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
int msgctl(int msqid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf);
- message queue miqid structure 관리
- Kernel에 있기 때문에 사용이 끝나면 꼭 제거해야한다.
- msqid : message queue id
- cmd : queue control
- IPC_STAT : read
- IPC_SET : update
- IPC_RMID : remove
- buf : msqid_ds structure pointer
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
Shared memory
왜 shared memory를 사용하는가?
- 각 process는 자신의 adress space를 보호받는다. (process protection)
- 즉, OS가 반드시 지원하는 memory 영역이 존재한다.
- thread를 사용할 때 의도하지 않게 쉬운 변수 공유라는 문제점이 발생한다.
- 이를 방지하기 위해 공유 영역을 정해두고 나머지는 개인 영역으로 지정한다.
Shared memory
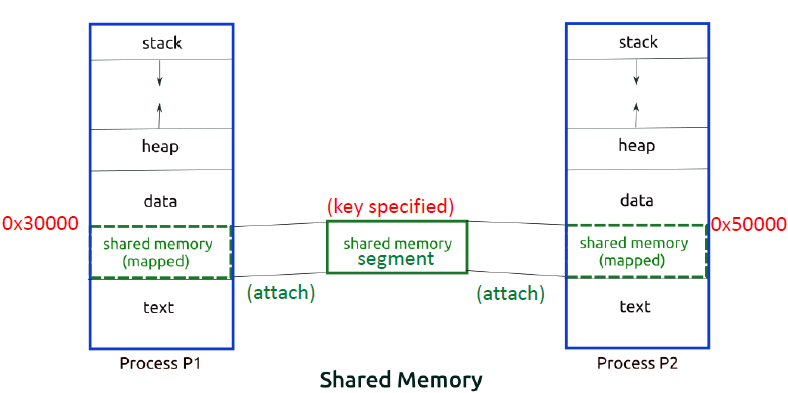
- OS가 제공하는 memory 공유 방식으로 IPC중 빠른 편이다.
- shared region을 OS에 요청한다.(s-m segment)
- s-m segment를 process에 연결한다.(attached)
- synchronize가 발생할 수 있기 때문에 mutex/semaphore로 순서를 정해야한다.
- programmer는 segment에 key를 할당하고, OS는 shared memory id를 부여한다.
- attach 되는 주소는 항상 동일하지 않다.
- shmid_ds structure가 존재하며, shmctl() 함수를 통해 확인할 수 있다.
shmget
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, int size, int flag);
- key : shared memory id
- size : shared memory size
- flag : open/create와 동일한 option
- return : 성공 시 shared memory id / 실패 시 -1
shmat
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, void *addr, int flag);
- OS의 도움으로 shared memory를 attach하는 함수
- key : shared memory id
- addr : shared memory address
- == 0 : kernel이 적당한 위치를 정해준다.
- != 0 : 지정된 주소로 정한다.
- flag :
- 0(default) : read/write 가능
- SHM_RDONLY : read만 가능
- return : 성공 시 OS가 mapping한 address / 실패 시 -1
shmdt
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void shmdt(void *addr);
- attach 되어있는 shared memory를 detach하는 함수
- addr : detach할 shared memory의 주소
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
shmctl
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
- shmid_ds structure를 관리하는 함수
- shmid : shared memory id
- cmd : queue control
- IPC_STAT : read
- IPC_SET : update
- IPC_RMID : remove
- buf : shmid_ds structure pointer
- return : 성공 시 0 / 실패 시 -1
ipcs command
ipcs
- System V IPC resource 상태를 확인
- $ ipcs : IPC 정보를확인(q, m, s 모두)
- $ ipcs–q : Message Queue 정보를확인
- $ ipcs–m : Shared Memory 정보를확인
- $ ipcs–s : Semaphore 정보를확인
ipcrm
- 생성된 IPC resource를 제거
- $ ipcrm–q id : Message Queue를제거
- $ ipcrm–m id : Shared Memory를제거
- $ ipcrm–s id : Semaphore를제거





