import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class RGB_Distance {
static int N;
static int[][] cost;
static int[][] dp;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
cost = new int[N][3];
dp = new int[N][3];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cost[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
dp[0][0] = cost[0][0];
dp[0][1] = cost[0][1];
dp[0][2] = cost[0][2];
System.out.println(Math.min(Math.min(dfs(N-1,0),dfs(N-1,1)),dfs(N-1,2)));
}
public static int dfs(int N,int color){
if(dp[N][color]==0){
if(color==0){
dp[N][0] = Math.min(dfs(N-1,1),dfs(N-1,2))+cost[N][0];
}
else if(color==1){
dp[N][1] = Math.min(dfs(N-1,0),dfs(N-1,2))+cost[N][1];
}
else if(color==2){
dp[N][2] = Math.min(dfs(N-1,1),dfs(N-1,0))+cost[N][2];
}
}
return dp[N][color];
}
}
풀이방법
이 문제는 dp문제로 dfs로 모든 경우의수를 탐색하면 안된다.
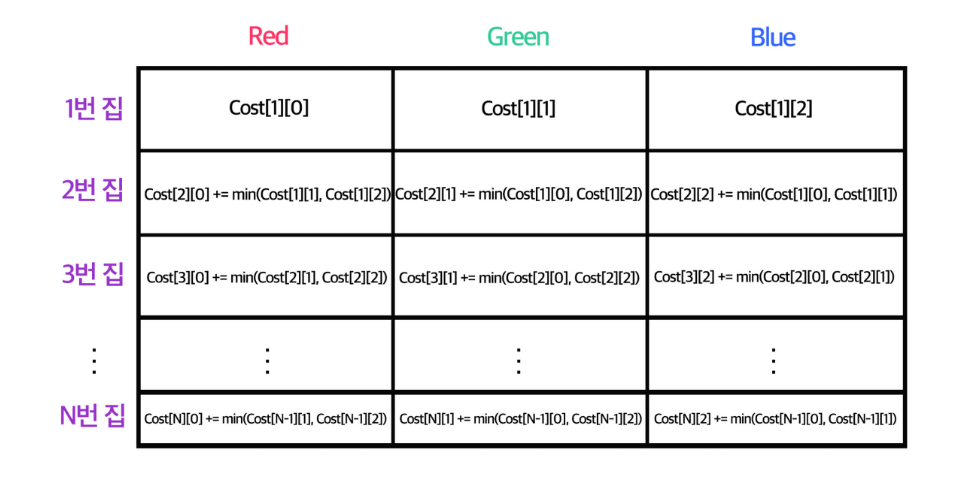
이런 구조를 떠올린 후, 배열의 맨 아래부터 재귀함수를 호출해서 맨위까지 올라가는 설계를 해야한다.
- 첫번째 배열에 색깔별 초깃값을 넣어준다.
- 맨마지막 배열을 색깔별로 dfs호출한다.
- 재귀함수를 처음 도는 배열이라면, 내 색깔과는 다른 두칸의 cost중 작은수와 내 cost값을 더한다.
- 그 값을 return하고 최종적으로는 맨 마지막 배열의 최소값이 답이 된다.
후기
처음 해보는 dp 알고리즘이었고, 알고리즘 자체도 처음 봤다.
아직 정확하게 이해도 안되고 떠올릴 자신도 없어서 다음에 다시한번 풀어봐야겠다.