import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
static int N;
static int[] dr = {1,0,-1,0};
static int[] dc = {0,1,0,-1};
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int sum;
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T;
T=sc.nextInt();
for(int test_case = 1; test_case <= T; test_case++)
{
N = sc.nextInt();
sum = 0;
visited = new boolean[N][N];
map = new int[N][N];
for(int i = 0; i<N; i++){
String str = sc.next();
for(int j = 0; j<N; j++){
map[i][j] = str.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
if(N==1){
System.out.println("#"+test_case+" "+map[0][0]);
}
else{
bfs(N/2,N/2);
System.out.println("#"+test_case+" "+sum);
}
}
}
public static void bfs(int row, int col){
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(new int[] {row,col,0});
visited[row][col] = true;
sum += map[row][col];
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] current = que.poll();
int crow = current[0];
int ccol = current[1];
int count = current[2];
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++){
int nrow = crow + dr[i];
int ncol = ccol + dc[i];
int ncount = count + 1;
if(nrow<0||ncol<0||nrow>=N||ncol>=N)
continue;
if(!visited[nrow][ncol]&&ncount<N/2){
visited[nrow][ncol] = true;
sum += map[nrow][ncol];
que.add(new int[] {nrow,ncol,ncount});
}
else if (!visited[nrow][ncol]&&ncount==N/2){
visited[nrow][ncol] = true;
sum += map[nrow][ncol];
}
}
}
}
}문제조건
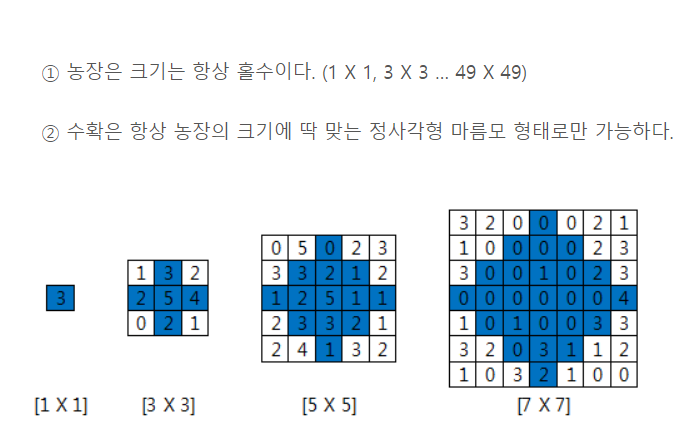
풀이방법
가운데 부터 bfs탐색을 시작해서 총 N/2번 수행하면 멈추도록 구현한다.
- que에 좌표와, count값을 넣는다.
- sum에 다음 좌표에 해당하는 값을 넣고, que에 다음 좌표와 count+1 값을 넣어준다.
- count가 N/2가 되면 더이상 que에는 값을 넣지 않고, 좌표에 해당하는 값만 sum에 넣어준다.
- N이 1일때는 map[0][0]을 출력하고, 나머지는 bfs탐색 후 sum값을 출력해 준다.
후기
bfs탐색을 사용해야 하는 것은 한눈에 보였지만, 유형은 처음 보는 유형이어서 신선했다.