OutputStream & InpuStream
public class Test190 { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\\...\\b.dat"); out.write( 100 ); out.write( 101 ); out.write( 102 ); out.close(); // InputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:\\...\\b.dat"); for( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ ) { int r = in.read(); System.out.println( r ); } in.close(); } catch( IOException e ) { } } }
Stream
- 단위는 byte
- 순서 개념이 있다.
- 사용이 끝나면 반드시 close() 호출
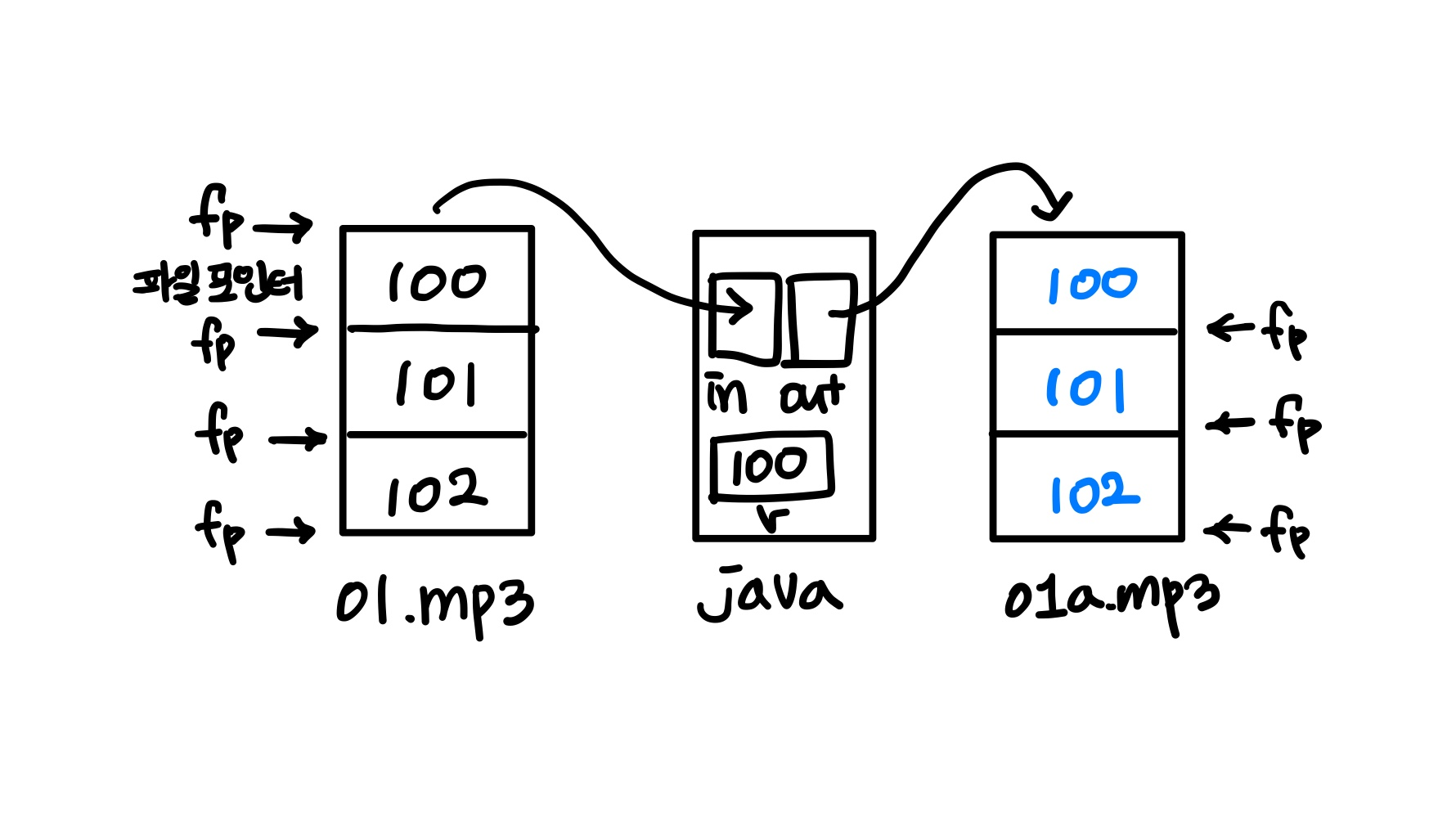
int read( )
// mp3 파일 복사 public class Test191 { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:\\...\\01.mp3"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\\...\\01a.mp3"); // 한바이트씩 읽어서 -1 이 나올때까지 wirte int r = 0; while( ( r = in.read() ) != -1 ) { out.write( r ); } out.close(); in.close(); } catch( IOException e ) {} } }
int read( byte[] )
public class Test192 { public static void main( String[] args ) { long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { InputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:\\...\\file.msi"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\\JavaWork\\a.msi"); // int len = 0; // buf 의 크기를 대략적으로 조정하다보면 최적의 속도가 나오는 구간이 있다. byte[] buf = new byte[1024*128]; // buf 의 크기가 한꺼번에 읽고 내보내는 크기 while( ( len = in.read( buf ) ) != -1 ) { out.write( buf, 0, len ); } out.close(); in.close(); } catch( IOException e ) {} System.out.println( System.currentTimeMillis() - time ); } }

read 에는 두가지 오버로딩된 함수가 있다.
- int read( ) : 한 바이트를 읽어서 그 내용을 리턴한다.
- int read( byte[] ) : 읽어서 byte[] 에 내용을 복사하고, 읽은 바이트수를 리턴한다.
write 에도 두가지 방법이 제공된다.
- void write( int i ) : 하위 8비트를 전송한다.
- void write( byte[] buf, int offset, int len )
: buf 안의 내용을 offset 부터시작해서 len 크기만큼을 전송한다.
ObjectOutputStream & ObjectInputStream
public class Test199 { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("e.dat") ); out.writeInt( 2323232 ); out.writeDouble( 3.141692 ); out.writeUTF("김수한무거북이와두루미"); out.close(); // ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream( new FileInputStream("e.dat") ) ; int r = in.readInt(); double d = in.readDouble(); String t = in.readUTF(); /* 더 이상 읽을것이 없을때 in.read() 는 에러를 발생치 않고 -1 을 리턴한다. 하지만 readInt() 함수의 경우에는 EOFException 이라는 에러를 발생시킨다. */ int j = in.readInt(); System.out.println( j ); in.close(); // System.out.println( r ); System.out.println( d ); System.out.println( t ); } catch( IOException e ) { e.printStackTrace(); // 발생한 에러의 스택정보를 추적할 수 있도록 해 줌 } } }
public ObjectOutputStream( OutputStream out ) throws IOException
- 매개변수 out 은 FileOutputStream 의 인스턴스를 가리킬 수 있기에 위의 코드가 가능하다.
writeInt / readInt - int 를 깨지 않고 주고 받을 수 있는 멤버함수
InputStream / OutputStream 에서는 write read 를 이용해서 byte 단위로 전송할 수 있었는데
ObjectInputStream / ObjectOutputStream 은 다양한 자료형과 문자열까지 주고 받을 수 있는 함수를 제공
순서대로 주고 받기때문에 순서는 바뀌면 절대 안됨!!
Socket
Server
public class Test194S { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { ServerSocket svr = new ServerSocket(7890); // 포트번호 ( 네트워크 통로의 고유번호 ) System.out.println( "before accept" ); Socket skt = svr.accept(); // 올때까지 계속 대기. 오게되면 Socket 생성 후 리턴 // byte[] buf = new byte[]{100,101,102,103}; OutputStream out = skt.getOutputStream(); // out.write( 100 ); out.write( buf, 0, buf.length ); out.flush(); // 네트워크 상의 전송은 보낸 다음 반드시 flush() 호출 out.close(); // skt.close(); svr.close(); } catch( Throwable e ) {} } }
svr.accept() 여기서 멈추어 대기하고 있는 상황이다
ipconfig 로 IP 주소 확인
Client
public class Test194C { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { Socket skt = new Socket("...",7890); // 찾아가서 접속시도 // InputStream in = skt.getInputStream(); // int r = in.read(); byte[] buf = new byte[4]; int len = in.read( buf ); in.close(); // for( int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++ ) { System.out.println( buf[i] ) ; } // System.out.println( r ); skt.close(); } catch( Throwable e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }

Server와 Client 간 파일 공유
public class Test195S { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { ServerSocket svr = new ServerSocket(7890); System.out.println( "before accept" ); Socket skt = svr.accept(); // OutputStream out = skt.getOutputStream(); InputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:\\...\\01.mp3"); // int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024*128]; while( ( len = in.read( buf ) ) != -1 ) { out.write( buf, 0, len ); out.flush(); } in.close(); out.close(); // skt.close(); svr.close(); } catch( Throwable e ) {} } }
public class Test195C { public static void main( String[] args ) { try { Socket skt = new Socket("192.168.31.100",7890); // 찾아가서 접속시도 // InputStream in = skt.getInputStream(); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("C:\\...\\down.mp3"); // int len = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[1024*128]; while( ( len = in.read( buf ) ) != -1 ) { out.write( buf, 0, len ); } out.close(); in.close(); // skt.close(); } catch( Throwable e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
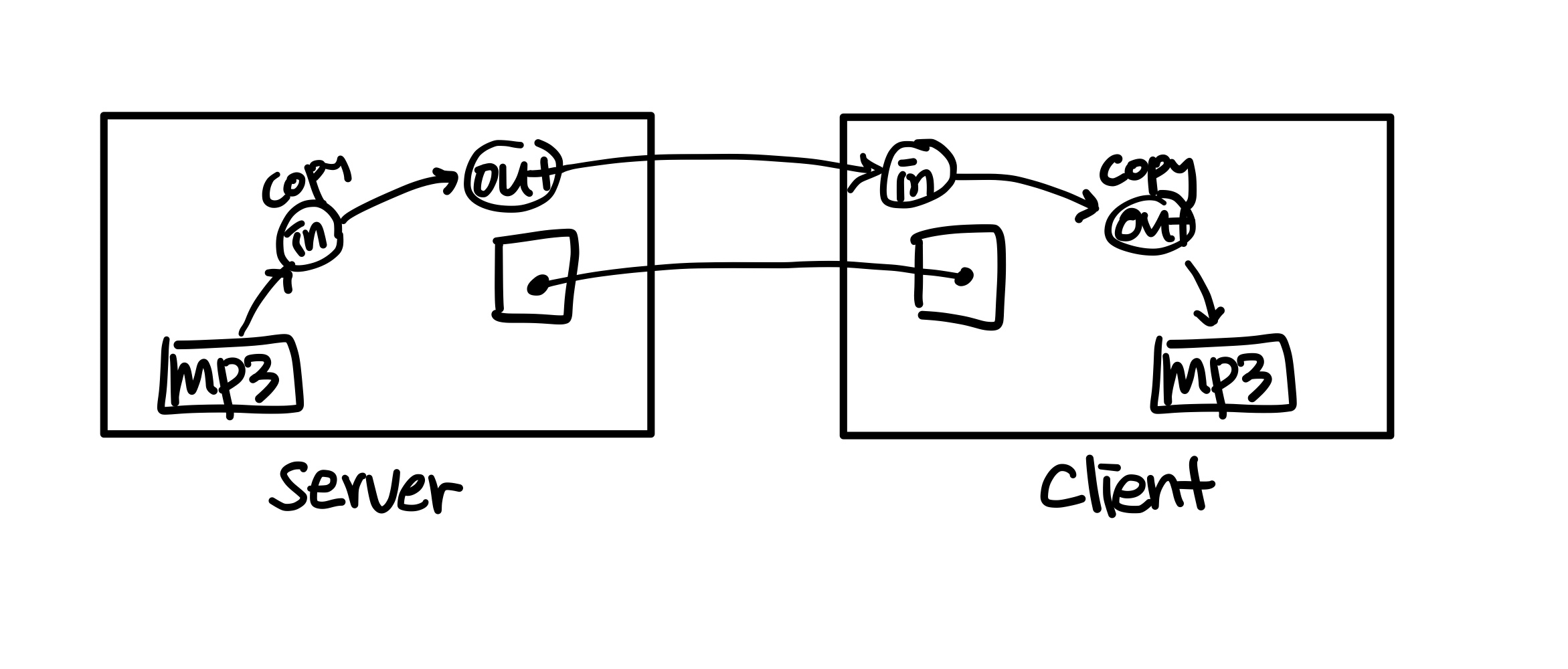
서버가 보내는 파일을 클라이언트에서 불러들여와 복사하는 코드
시프트 연산자
public class Test196 { public static void main( String[] args ) { int i = 10; System.out.println( i << 2 ) ; System.out.println( i >> 2 ) ; } }
왼쪽으로 밀때마다 * 2 를 한 효과
00001010 : 10
00010100 : 10 << 1 -> 20
00101000 : 10 << 2 -> 40오른쪽으로 밀때마다 /2 를 한 효과
00001010
00000101 : 10 >> 1 -> 5
00000010 : 10 >> 2 -> 22의 보수
public class Test197 { public static void main( String[] args ) { System.out.println( -5 >> 2 ); System.out.println( -1 >>> 1 ); // 2147483647 ... 대단히 큰 숫자가 얻어짐 } }
'-5 는 2진수로 어떻게 표기될까??' : 5에서 0 과 1 을 바꾸고 + 1 을 더해준다
0000 0101 -> +5
1111 1011 -> -5
----------------
0000 0000 -> 0 '이런식으로 음의 정수를 만들어 내는 것을 2의 보수법 ( 2's complement ) 라고 한다.'
signbit
2의 보수법에 의하면 맨 앞자리 bit 가 0이면 양수, 1 이면 음수가 된다. 맨 앞자리 bit 를 signbit 라고 한다.
>> 으로 밀때는 밀어주고 빈 공간에 signbit 를 채운다.
11111011 : -5
11111101 : -3 ( -5 >> 1 )
11111110 : -2 ( -5 >> 2 )unsigned shift
1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 : -1 >>> 1 의 결과. 즉 >>> 은 밀어낸 공간에 무조건 0 채운다.
2147483647 은 int 가 표현가능한 가장 큰 숫자가 된다.
>>> 은 부호에 상관없이 무조건 밀고 난 다음 0으로 채운다고 하여 unsigned shift 라고 한다.