boolean
public class Test015 { public static void main( String[] args ) { boolean i = true; i = false; // i = ( 100 > 50 ); System.out.println( i ); // true } }
java 는 boolean 이라는 별도의 자료형이 존재한다.
boolean 값은 다른 자료형의 값으로 형변환이 불가능하다 ( 자동 강제 모두 )
100 > 50 이러한 종류의 연산의 결과는 true / false 로 나타나고 그 값을 담는 변수는 boolean 으로 선언된다.
if-else 문
public class Test016 { public static void main( String[] args ) { boolean i = true; int j = 5; // if( i ) { System.out.println("Orange"); } // if( j > 10 ) { System.out.println("Apple"); } else if( j > 0 ) { System.out.println("Kiwi"); } else { System.out.println("Banana"); } } }
if( .. ) 의 .. 안에는 반드시 boolean 값만 와야 한다.
if( false ) 면
else if 로 이동하고 else if( false ) 면
else 로 이동한다.
j 는 정수형 변수이지만 j > 10 의 결과는 boolean 이라서
if( j ) 는 불가능하고, if ( j > 10 ) 는 가능하다.
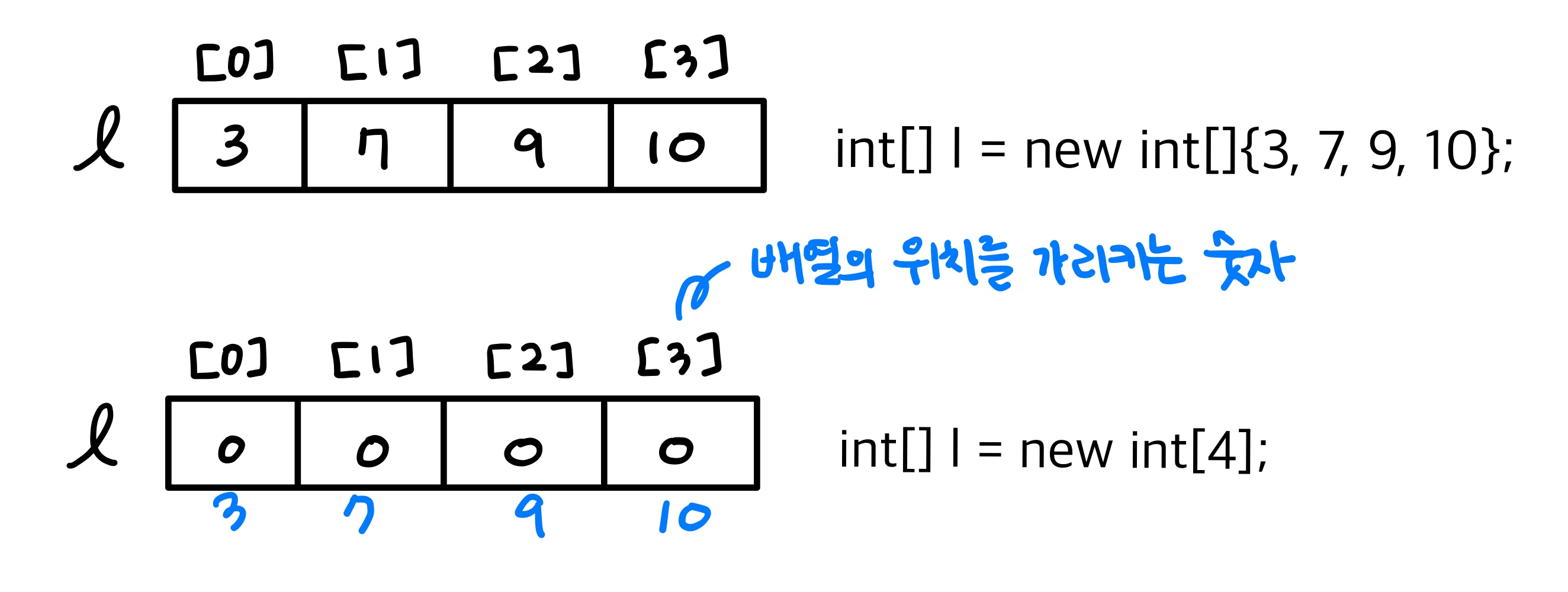
배열
public class Test017 { public static void main( String[] args ) { // int[] l = new int[]{ 3, 7, 9, 10 }; // 아래의 코드는 위와 동일한 구조의 배열을 만든다. int[] l = new int[4]; l[0] = 3; l[1] = 7; l[2] = 9; l[3] = 10; // System.out.println( l[0] ); System.out.println( l[1] ); System.out.println( l[2] ); System.out.println( l[3] ); } }
배열
- 동일한 자료형의 변수가 연속으로 확보된 기억공간
( int, double 혼합 불가)
- 위의 경우에는 l 이라는 변수명으로 4개의 기억공간이 확보되어 있다
각각은 l[0] ~ l[3] 으로 구분되고 값을 대입할 수 있고, 이용할 수 있다. - 배열은 자동으로 초기값을 부여한다 ( 0 또는 0.0 , false )
public class Test018 { public static void main( String[] args ) { int[] l = { 3, 7, 9, 10 }; // System.out.println( l[2] ); System.out.println( l.length ); // 배열이 가진 크기 // // 외우자!! for 와 배열의 연동 for( int i = 0 ; i < l.length ; i++ ) { System.out.println( l[i] ); } } }
int[] l = { 3, 7, 9, 10 }; 이렇게도 가능하다
for 반복문과 연동해서 사용하는 경우는 굉장히 흔하다.
배열이 가지는 크기는 굳이 숫자를 명시하지 않고 l.length 로 사용이 가능하다.
// 배열의 합 구하기
public class Test019 {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] l = new int[]{ 3,7,9,10 };
int sum = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < l.length ; i++ ) {
sum = sum + l[i];
}
System.out.println( sum );
}
}// 최대값, 최소값 구하기
public class Test020 {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] l = new int[]{ 3, 7, 9, 10 };
int max = l[0];
for( int i = 1 ; i < l.length ; i++ ) {
if( l[i] > max ) {
max = l[i];
}
}
System.out.println( max );
}
}break 와 continue
public class Test021 { public static void main( String[] args ) { // break 는 반복문 안에서 써야 한다. for( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ ) { System.out.println("Apple " + i ); if( i == 3 ) { System.out.println("Kiwi"); continue; // break; } System.out.println("Banana " + i ); } System.out.println("Orange"); } }
문자열의 뒤에 이어붙일때는 + 기호를 쓴다.
= 대입 : 변수에 값을 넣을때
== 비교 : 두개의 값을 비교할 때 : 양쪽의 값이 일치하면 true / 일치 안하면 false

위의 Test021 코드에서 i == 3 일때
break 인 경우 반복문을 종료하고
continue 인 경우 하위 코드는 실행하지 않고 i = 4 로 넘어간다.
// 배열 안에 8이라는 값이 존재하면 true 아니면 false 를 출력하는 코드를 짜기
public class Test022{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] l = {3, 7, 9, 10};
int find = 8;
boolean exist = false;
for(int i = 0; i < l.length; i++){
if(l[i] == find){
exist = true;
break; // 있는지 확인만 하면 되니까 빠져나감!!
}
}
System.out.println(exist);
}
}char
public class Test023 { public static void main( String[] args ) { char i = '한'; int j = i; System.out.println( i ); System.out.println( j ); // 65 } }
char : 문자 하나를 ' ' 로 감싼 값을 대입할 수 있는 변수를 생성하는 자료형
char 는 int 형으로 자동 형변환 가능하다. char < int
ASCII 코드 : 문자 하나를 어떤 숫자에 매핑시킬 것인가를 정한 표준
char형 변수에 저장되는건 문자 그 자체가 아니라 아스키 코드에 근거한 문자에 해당하는 숫자값이다. ( 그러니 int로 자동형변환 가능 )
String 과 char배열
public class Test024 { public static void main( String[] args ) { String t = "Helloworld"; System.out.println(t); // // "" 안에 있는 문자 하나하나를 요소로 갖는 배열을 생성하는것 char[] j = "Helloworld".toCharArray(); for(int k = 0; k < j.length; k++){ System.out.println(j[k]); } } }
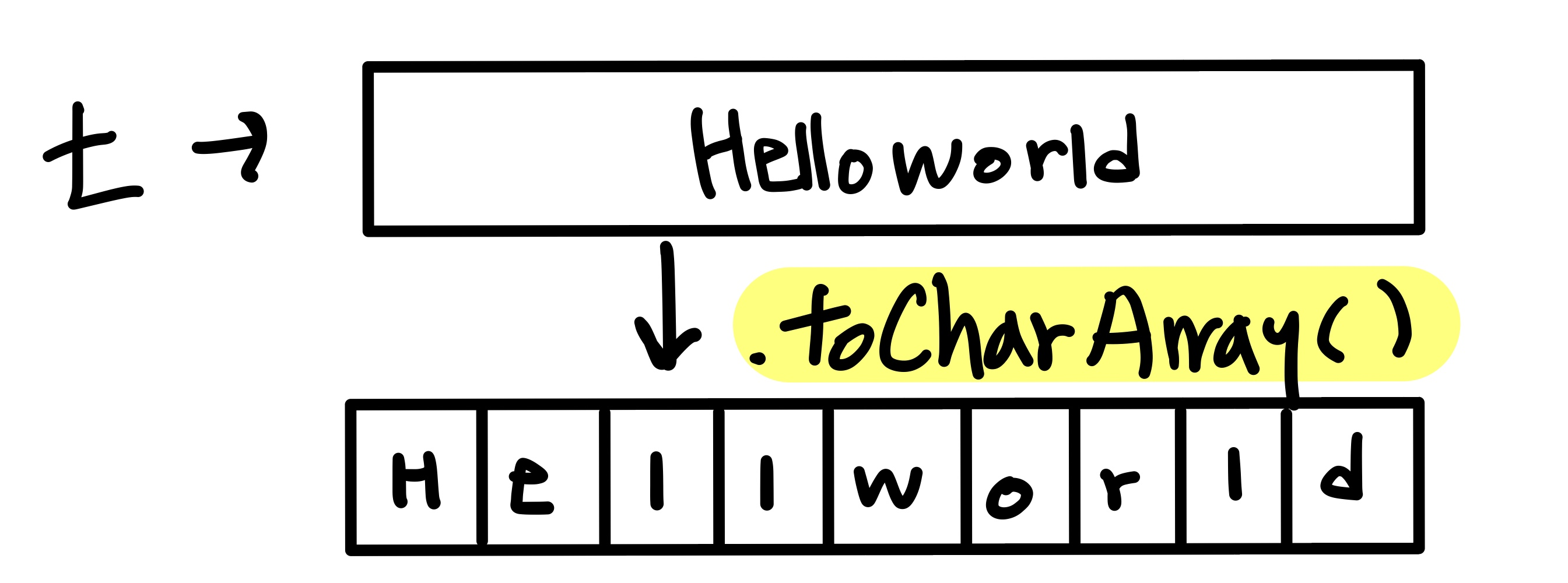
"Helloworld" - char 아님
- String 과 char 비교
1. char는 자료형이다. String 은 자료형이 아니다. (클래스)
2. char는 1개의 문자에 해당하는 코드값을 저장할 수 있는 변수 선언이 가능하다.
3. String은 " "로 감싼 문자열(0개 이상의 문자의 나열)을 대입할 수 있는 변수선언이 가능하다. (t 는 실은 포인터)
// a와 b 배열에 들어있는 문자열이 동알하면 true 아니면 false 출력 public class Test025{ public static void main(String[] args){ char[] a = "apple".toCharArray(); char[] b = "Banana".toCharArray(); boolean same = true; // 배열의 길이가 다르면 비교할 필요가 없다 if(a.length != b.length){ same = false; } else{ // 배열의 길이가 같으므로 a, b 둘 중 아무 길이나 사용가능 for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){ if(a[i] != b[i]){ same = false; break; } } } System.out.println(same); } }
public class Test027{ public static void main(String[] args){ char[] a = "Helloworld".toCharArray(); char[] b = "lrd".toCharArray(); // int idx = -1; int len = a.length - b.length + 1; // for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){ boolean match = true; for(int j = 0; j < b.length; j++){ if(a[ i + j ] != b[j]){ match = false; break; } } if(match == true){ idx = i; break; } } System.out.println(idx); } }
word에 있는 문자열 ptn의 위치를 출력하는 코드를 짜기. 패턴이 없으면 -1이 출력된다.
- "ll" 일 경우 2 출력
"llo" 일 경우 2 출력
"lloW" 일 경우 2 출력
"xyz" : -1 출력
[ H ][ e ][ l ][ l ][ o ][ w ][ o ][ r ][ l ][ d ]
[ r ][ l ][ d ]배열 a의 길이 : 10
배열 b의 길이 : 3
배열 a에서 b[0]의 인덱스는 7이 되고 a[i + j] 와 b[j] 를 비교하기 때문에
a[7] == b[0]
a[8] == b[1]
a[9] == b[2]
i는 7 이상의 값을 가져서는 안된다. 따라서 전체 길이에서 배열 b의 길이를 빼줘야한다.