CPU Scheduling
-
CPU & I/O Bursts in Program Execution
: CPU burst(load store, add store, read...) -> I/O burst(wait for I/O) -> CPU burst(store increment, index, write to file) -> I/O burst -> CPU burst -> I/O burst ...여러 종류의 job(=process)이 섞여 있기 때문에
CPU Scheduling이 필요하다.CPU burst time : process 수행 중 I/O 등 다른 요청 없이 CPU만을 잡고 한 번에 지속적으로 쓰려고 하는 time interval
-
프로세스 특성
- I/O-bound process: CPU를 잡고 계산하는 시간보다 I/O에 많은 시간이 필요한 job (many short CPU bursts)
ex) TV 채널 전환
- CPU-bound process: 계산 위주의 job (few very long CPU bursts).
ex) TV Graphic -
CPU Scheduler & Dispatcher
- CPU Scheduler: Ready 상태의 process 중에서 이번에 CPU를 줄 process를 고름
- Dispatcher: CPU의 제어권을 CPU Scheduler에 의해 선택된 process에게 넘김. (context switch)CPU Scheduling이 필요한 경우
1) Running -> Blocked (ex. I/O 요청 system call) => nonpreemptive(비선점형: 강제X, 자진반납)
2) Running -> Ready (ex. 시간 만료 timer interrupt) => preemptive(선점형: 강제반납)
3) Blocked -> Ready (ex. I/O 완료 후 interrupt) => preemptive
4) Terminate => nonpreemptive -
Scheduling Criteria: Performance index(=measure) 성능 척도
1. CPU utilization(이용률): keep the CPU as busy as possible
전체 시간 중 CPU가 일한 시간의 비율 (시스템)
2. Throughput(처리량): # of processes that complete their execution per time unit
주어진 시간에 몇 개의 process 처리했는지 (시스템)
3. Turnaround time(소요시간, 반환시간): amount of time to execute a particular process
CPU 사용 시작부터 끝까지의 실행 시간. Waiting time + CPU 수행시간 (프로세스) => Average turnaround time (ATT)
4. Waiting time(대기시간): amount of time a process has been waiting in the ready queue
CPU를 얻기 전 ready queue에서 기다린 시간 (프로세스)
5. Response time(응답시간): amount of time it takes from when a request was submitted until the first response is produced, not output (for the time-sharing environment)
처음 들어가서 CPU를 얻기까지의 시간 (프로세스)CPU burst time 내부에서!!! Process 시작~종료까지가 아니라 Process가 CPU를 쓰러 들어와서 I/O execution 전까지의 시간
FCFS (First-Come-First-Service)
먼저 도착한 순서대로 처리
- Nonpreemtive
| Process | Burst Time |
|---|---|
| P1 | 24 |
| P2 | 3 |
| P3 | 3 |
프로세스 도착 순서: P1, P2, P3
Waiting time: P1 = 0, P2 = 27, P3 = 30
Average Waiting time: (0 + 27 + 30) / 3 = 17
프로세스 도착 순서: P2, P3, P1
Waiting time: P1 = 6, P2 = 0, P3 = 3
Average Waiting time: (6 + 0 + 3) / 3 = 3
=> 앞의 겨우보다 훨씬 better
Convoy Effect: short process behind long process
SJF (Shortest-Job-First)
CPU burst time이 짧은 순서대로 처리
- Nonpreemtpive : 일단 CPU를 한 번 잡으면 CPU burst가 완료될 때까지 CPU를 선점당하지 않음. CPU가 빈 경우에만 누가 더 짧은지 비교
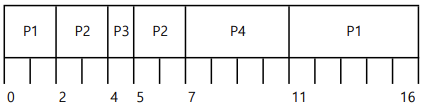
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.0 | 7 |
| P2 | 2.0 | 4 |
| P3 | 4.0 | 1 |
| P4 | 5.0 | 4 |
P1이 제일 먼저 들어왔으니 P2, P3, P4가 들어와도 일단 계속 수행
Waiting time: P1 = 0, P2 = 6, P3 = 3, P4 = 7
Average Waiting time: (0+6+3+7) / 4 = 4
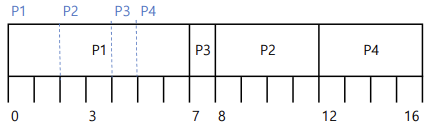
- Preemptive : 현재 수행 중인 프로세스의 남은 CPU burst time보다 더 짧은 CPU burst time을 가지는 새로운 프로세스가 도착하면 CPU를 선점당함 => Shortest-Remaining-Time-First(SRTF)
| Process | Arrival Time | Burst Time |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.0 | 7 |
| P2 | 2.0 | 4 |
| P3 | 4.0 | 1 |
| P4 | 5.0 | 4 |
Waiting time: P1 = 9, P2 = 1, P3 = 0, P4 = 2
Average Waiting time: (9+1+0+2) / 4 = 3
각 프로세스의 다음번 CPU burst time을 가지고 스케줄링에 활용
=> SJF is optimal: 주어진 프로세스들에 대해 minimum average waiting time 보장
BUT!!
(-) Starvation 발생: CPU burst time이 긴 process는 never execute
(-) CPU burst time을 알고있다는 예측 하에. 만약 예측X 라면?
- 다음 CPU Burst time 예측: 과거 CPU burst time 이용해서 추정 ( exponential averaging )
- = actual length of CPU burst (과거의 확인된 값. 실질값)
- = predicted value for the next CPU burst (이전단계 기반 예측값)
- (값⬇ 최근값 반영⬇ , 값⬆ 최근값 반영⬆)
- Define:
최근값 많이 반영. 과거값 적게 반영.
Priority Scheduling
우선 순위가 제일 높은 process 순서대로 처리
- Highest priority (=smallest integer) 가진 process에게 CPU 할당.
- Preemptive, Nonpreemtpive
- SJF: 일종의 priority scheduling (priority = predicted next CPU burst time)
(-) Starvation: low priority processes는 never execute
=> Solution: Aging (as time progresses, increase the priority of the process)
RR (Round Robin)
할당 시간이 지나면 프로세스는 선점당하고 ready queue의 제일 뒤에 가서 다시 줄을 선다
- 각 프로세스는 동일한 크기의 할당 시간 (time quantum)을 가짐: 일반적으로 10-100 ms
- n개의 process가 ready queue에 있고 할당 시간이 q time unit인 경우, 각 프로세스는 최대 q time unit 단위로 CPU 시간의 1/n을 얻는다.
=> 어떤 프로세스도 (n-1)q time unit 이상 기다리지 않는다. (waiting time이 CPU burst time에 가장 근접하게 비례하는 스케줄링)
-
Performance:
q time unit잘 조절해야함
- q large => FIFO 들어오는 순서대로 처리. q가 너무 크면 웬만해서 q 시간 안에 처리 가능
- q small => context switch 너무 잦음. 오버헤드 커짐. -
Preemptive
| Process | Burst Time |
|---|---|
| P1 | 53 |
| P2 | 17 |
| P3 | 68 |
| P4 | 24 |
일반적으로 SJF보다 average turnaround time (총 runtime)이 길지만 response time은 더 짧다.
일정 시간(q)이 지나면 average turnaround time이 일정해진다
Multilevel Queue
Ready queue를 여러 개로 분할하여 각 queue별로 scheduling
- Foreground(interative): RR. interative, 빠르게 blocked
- Background(batch - no human interaction): FCFS. 순서대로.
- Fixed priority scheduling : foreground 완료 후, backgrond.
(-) possibility of starvation - Time slice : 각 queue에 CPU time을 적절한 비율로 할당
(+) starvation 어느정도 해결 가능
ex) 80% to foreground in RR, 20% to background in FCFS
Multilevel Feedback Queue
프로세스가 다른 queue로 이동 가능 => aging 구현
- Multilevel-feedback-queue scheduler를 정의하는 parameters
- queue 수
- 각 queue의 scheduling algorithm
- process를 상위 queue로 보내는 기준
- process를 하위 queue로 내쫓는 기준
- process가 CPU 서비스를 받으려 할 때 들어갈 queue를 결정하는 기준
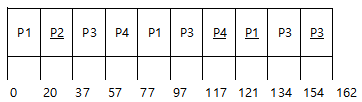
Three Queues
Q0: time quantum 8ms RR
Q1: time quantum 16ms RR
Q2: FCFS
Scheduling
1. new job이 queue Q0로 들어감
2. CPU를 잡아서 할당시간 8ms 동안 수행
3. 8ms 동안 다 끝내지 못했으면 queue Q1로 내려감
4. Q1에 줄서서 기다렸다가 CPU를 잡아서 16ms 동안 수행
5. 16ms에 끝내지 못한 경우 queue Q2로 내려감
Other Scheduling Methods
Multiple-Processor Scheduling
CPU가 여러 개인 경우 스케줄링
- Homogeneous processor: queue에 한 줄로 세워서 각 processor가 알아서 꺼내가게 할 수 있다.
(-) 반드시 특정 processor에서 수행되어야 하는 process가 있는 경우: 복잡 - Load Sharing: 일부 processor에 job이 몰리지 않도록 load를 적절히 공유하는 메커니즘 필요
별개의 queue를 두는 방법 VS 공동 queue를 사용하는 방법 - Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP): 각 processor가 각자 알아서 scheduling 결정
- Asymmetric Muliprocessing: 하나의 processor가 시스템 데이터의 접근과 공유를 책임지고 나머지 processor는 거기에 따른다.
Real-Time Scheduling
- Hard real-time systems: Hard real-time task는 정해진 시간 안에 반드시 끝내도록 스케줄링
- Soft real-time computing: Soft real-time task는 일반 process에 비해 높은 priority를 갖도록 스케줄링
Thread Scheduling
- Local Scheduling: User level thread의 경우 사용자 수준의 thread library에 의해 어떤 thread를 scheduling할지 결정
- Global Scheduling: Kernel level thread의 경우 일반 process와 마찬가지로 kernel의 단기 scheduler가 어떤 thread를 scheduling할지 결정
Algorithm Evalutation
- Queueing models: 확률 분포로 주어지는 arrival rate와 service rate 등을 통해 performance index 값 계산하여 결과 비교
- Implementation(구현) & Measurement(성능 측정): 실제 시스템에 알고리즘 구현. 실제 작업(worklaod)에 대해 성능 측정 비교
- Simulation(모의 실험): 알고리즘을 모의 프로그램으로 작성 후 trace를 입력으로 하여 결과 비교
운영체제 - 반효경
http://www.kocw.net/home/cview.do?cid=3646706b4347ef09