[TypeScript 문법] TypeScript의 인터페이스

📘 TypeScript 인터페이스
- 일반적으로 타입체크를 위해 사용된다
- 변수, 함수, 클래스에 사용할 수 있음
- 인터페이스에 선언된 프로퍼티 또는 메서드의 구현을 강제하여 일관성을 유지하도록 함
- Javascript에서는 지원하지 않음
- TypeScript의 예약어인
interface를 사용하여 생성할 수 있음
변수와 인터페이스
TypeScript에서 변수를 선언할 때 아래와 같이 사용할 수 있음
➡️ 주로 객체(Object)의 구조를 정의하기 위해 사용되는 예약어
// interface를 선언할 때에는 ,가 아닌 ; 사용
interface User {
name : string;
age: number;
}
// 정상선언
const user: User = {
name : "Dave",
age: 20
}
// 프로퍼티의 순서를 지키지 않아도 정상선언
const user: User = {
age: 20,
name : "Dave"
}
// 정의된 프로퍼티보다 적게 작성했기 때문에 에러발생
const user: User = {
name: "anna"
}
// 정의된 프로퍼티보다 많이 작성했기 때문에 에러발생
const user: User = {
name: "anna",
age: 20,
job: "developer"
}
위 코드는 사용자 정보를 정의하기 위해 interface 예약어를 사용하여 User 인터페이스를 만들었음 인터페이스를 만들 때 예약어를 작성하고, 인터페이스의 이름을 "대문자"로 작성
➡️ 이렇게 인터페이스의 이름을 대문자로 시작하는 것을 *네이밍 컨벤션
💡 네이밍 컨벤션 ?
: 이름을 짓는 일종의 관례, TypeScript로 개발할 때 대부분의 개발자는 인터페이스의 이름을 대문자로 시작하도록 작성, 인터페이스는 객체의 타입을 정의하고, 객체가 대문자로 시작하는 것과 유사 ➡️ 일관성 있는 코드 작성을 위해 따르는 관례
인터페이스 내에는 `name`과 `age`가 정의되어 있기 때문에, `User` 인터페이스를 사용하여 변수를 선언할 때는 반드시 정의된 프로퍼티를 추가로 작성하고자 해도 인터페이스 내에 정의되어 있지 않기 때문에 추가로 프로퍼티를 더 작성하여 선언할 수 없음
💡 그럼 어떻게 추가해야 할까?
그러나 인터페이스 안의 모든 프로퍼티가 필요한 것은 아니며,
어떤 조건에서만 존재하거나 아예 없는 경우도 발생할 수 있음
➡️ ? 연산자를 사용하여 "선택적 프로퍼티"를 작성할 수 있음
interface User {
name:string;
// ? 연산자를 이용하여 선택적 프로퍼티 작성
age?:number;
}
// age를 선언하지 않아도 정상선언
const user:User = {
name: "Dave"
}◎ 함수와 인터페이스
인터페이스를 사용하여 객체의 프로퍼티 이름과 타입을 정의하고, 함수의 매개변수 타입과 반환타입도 정의할 수 있음
interface User {
name: string;
age: number;
job: string;
}
// 함수의 매개변수타입, 반환타입
interface Greeting {
(user:User, greeting: string): string;
}
const greet: Greeting = (user, greeting) => {
return `${greeting}, ${user.name}! Your job : ${user.job}.`;
}
const user: User = {
nema : "Dave",
age:24,
job: "developer"
};
const message = greet(user, "Hi");
console.log(message)- 위 코드는
User인터페이스 외에도Greeting인터페이스를 추가로 작성하여 함수타입을 정의 Greeting인터페이스는User타입과 문자열 타입을 매개변수로 받아 문자열 타입을 반환greet함수는Greeting을 사용하야 구현되었으며,user객체와 문자열Hi를 전달인자로 전달받아 문자열을 반환했음
◎ 클래스와 인터페이스
클래스 내에서도 아래와 같이 인터페이스를 사용할 수 있다.
interface Calculator {
add(x:number, y: number) : number;
substract( x: number, y: number): number;
}
class SimpleCalculator implements Calculator {
add( x: number, y: number) {
return x + y;
}
substract(x: number, y: number) {
return x - y;
}
}
const calculator = new SimpleCalculator();
console.log(calculator.add(4,9)); // 13
console.log(calculator.substract(10,5)); // 5- 위 코드에서는
Calculator인터페이스는add와substract매서드를 정의 SimpleCalculator클래스는Calculator인터페이스를 사용하여 작성Calculator인터페이스를 사용하고 있기 때문에SimpleCalculator클래스 내에는Calculator인터페이스 내에 정의된 두 매서드를 반드시 작성해야함
🚨 주의할 점
- 클래스를 구현할 때 인터페이스에서 정의된 함수를 사용할 때, 클래서 내부에서 해당 메서드의 매개변수 타입을 다시한번 더 명시해 주지 않으면 컴파일 에러가 발생한다!!
◎ 실습 (JavaScript를 TypeScript로 포팅 하기 - 인터페이스)
포팅하기 전
// Todo 인터페이스를 작성합니다.
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 todos를 완성합니다.
let todos = [];
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 addTodo를 완성합니다.
function addTodo(todo) {
todos = [...todos, todo];
}
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 newTodo를 완성합니다.
const newTodo = {
id: 1,
content: 'learn typescript',
isDone: false,
};
addTodo(newTodo);
console.log(todos);포팅 후
// Todo 인터페이스를 작성합니다.
interface Todo {
id: number;
content: string;
isDone: boolean;
}
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 todos를 완성합니다.
let todos: Todo[] = [];
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 addTodo를 완성합니다.
function addTodo(todo: Todo) {
todos = [...todos, todo];
}
// Todo 인터페이스를 타입으로 받는 newTodo를 완성합니다.
const newTodo: Todo = {
id: 1,
content: 'learn typescript',
isDone: false,
};
const secondTodo: Todo = {
id: 2,
content: 'typescript',
isDone: true,
};
addTodo(newTodo);
addTodo(secondTodo);
console.log(todos);결과
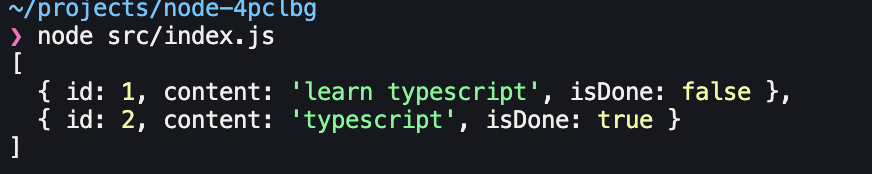
📘 인터페이스와 상속
Javascript에서 클래스를 확장할 때 extends라는 키워드를 사용해 기존에 존재하던 클래스를 상속해 새로운 클래스를 정의할 수 있음
Class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I'm ${this.age} years old.`);
}
}
// Person 클래스를 extends 키워드를 사용해 상속하여 새로운 클래스인 Student 정의
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, grade) {
super(name, age);
this.grade = grade;
}
study() {
console.log(`${this.name} is styding hard for the grade ${this.grade}.`);
}
}- 인터페이스도
extends라는 키워드를 사용하여 기존에 존재하던 인터페이스를 상속해 확장 가능
➡️ 기존에 존재하던 인터페이스의 프로퍼티를 다른 인터페이스에 복사 가능 ( 재사용성 ↑ )
interface Person {
name : string;
age: number;
}
interface Developer extends Person {
language: string;
}
const person: Developer = {
language: "Typescript",
age:20,
name: "Anna",
}
- 기존에 존재하던
Person인터페이스를extends키워드로 상속해 새로운 인터페이스인Developer를 생성 Developer객체를 사용하여person이라는 객체를 구현Developer인터페이스는Person인터페이스를 상속하고 있으므로,Person내부의 프로퍼티를 그대로 받아올 수 있다.
+ 여러가지 인터페이스를 상속받아 하나의 객체 생성 가능
interface FoodStuff {
name: string;
}
interface FoodAmount {
amount: number;
}
interface FoodFreshness extends FoodStuff, FoodAmount {
isFreshed: boolean;
}
const food = {} as FoodFreshness;
food.name = "egg";
food.amount = 2;
food.isFreshed = true;