⚡ Context API
📌 Context API란?
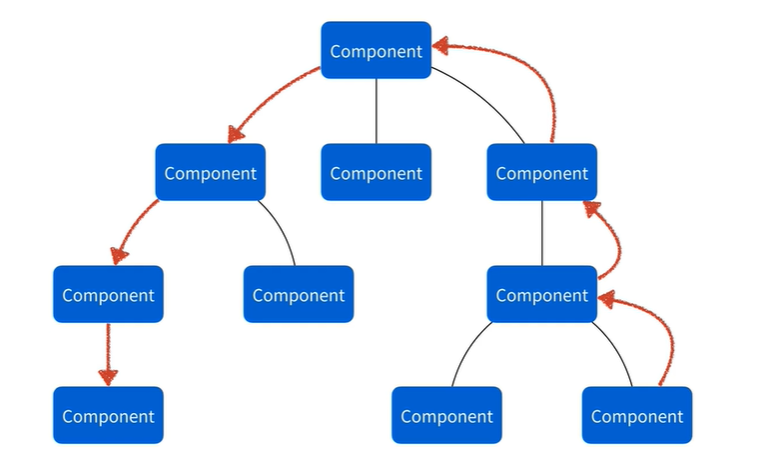
🔷 Prop Drilling 문제를 해결하는 방법 중 하나
💡 Prop Drilling
컴포넌트는 트리 구조로 이루어져있다.
그래서 트리 레벨이 깊어졌을 때 다른 컴포넌트로 prop을 넘기려면 목적지까지 계속해서 다른 컴포넌트를 통해 prop을 넘겨야하는데 이를 Prop Drilling이라고 한다.
이 Prop Drilling 문제를 해결하는 방법 중 하나가 Context API이다.
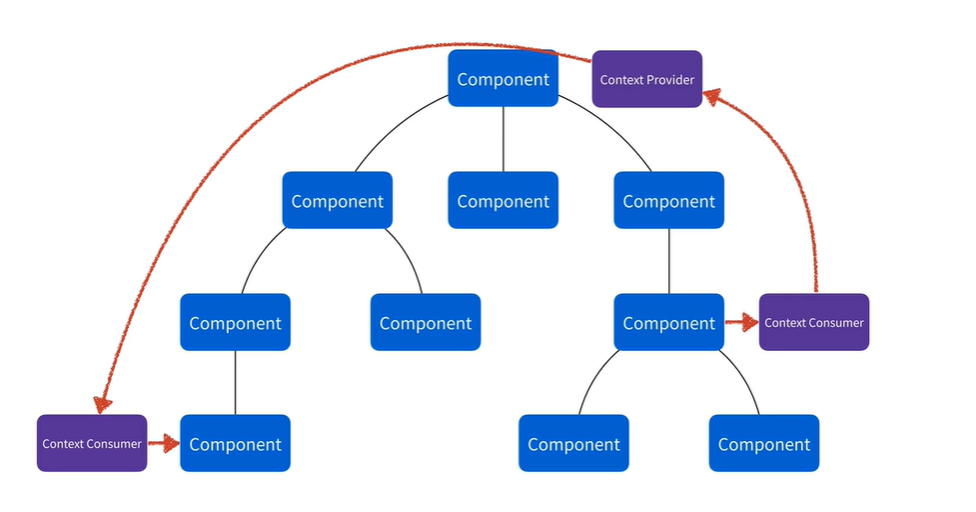
🔷 Context Provider: 데이터를 제공하고 관리한다.
🔷 Context Consumer: 데이터를 수령하여 처리한다.
- Provider가 정보를 넘겨받고 업데이트되면 반응형에 의해 Consumer가 다시 연산하기 시작한다.
- 이 두 가지를 이용하면 멀리 떨어져있는 컴포넌트에게도 쉽게 prop을 넘길 수 있다.
- 단, 남발하면 성능 저하의 우려가 있다. (Provider가 변화하면 Consumer와 관련된 컴포넌트들이 전부 다시 렌더링하기 때문이다.)
- 그리고 Consumer가 있으면 반드시 Provider도 존재해야 하기 때문에 독립성의 문제 역시 제기된다.
💡 컴포넌트를 한 번 감싼 컴포넌트를 만드는 형태로 해결할 수 있다.
📌 To Do App에 적용하기
🔷 To do 컴포넌트에서 이벤트가 발생하여 데이터가 조작될 때 전체적으로 데이터를 관리하기 위해서 다른 컴포넌트에 prop을 계속 넘겨주거나 이벤트를 던져야하는데 이를 편하게 하기 위해 Context API를 사용한다.
🔷 요구사항
- 원하는 Todo를 타이핑하고 추가 버튼을 누르면 Todo가 리스트에 추가된다.
- 로컬 스토리지가 연결되어 새로고침을 하거나 창을 닫아도 데이터가 삭제되지 않는다.
- 토글 버튼을 누르면 취소선이 생기며 오늘 끝낸 일을 나타낼 수 있다.
- 삭제 버튼을 통해 Todo를 삭제할 수 있다.
💻 Header.js
import styled from "@emotion/styled";
const Header = styled.h1`
text-align: center;
`
export default Header;💻 NewTaskForm.js
import styled from "@emotion/styled";
import { useState } from "react";
import { useTasks } from "../contexts/TaskProvider";
const Form = styled.form`
width: 400px;
`
const Input = styled.input`
width: 332px;
height: 32px;
padding: 4px 6px;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 2px solid black;
box-sizing: border-box;
`
const SubmitButton = styled.button`
width: 60px;
height: 32px;
padding: 4px 6px;
margin-left: 8px;
color: white;
border-radius: 8px;
border: none;
background-color: black;
box-sizing: border-box;
cursor: pointer;
`
const NewTaskForm = (props) => {
const [task, setTask] = useState('');
const { addTask } = useTasks();
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
addTask(task);
setTask("");
}
return (
<Form {...props} onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<Input type="text" value={task} onChange={(e) => setTask(e.target.value)} required />
<SubmitButton>추가</SubmitButton>
</Form>
)
}
export default NewTaskForm;💻 Task.js
import styled from "@emotion/styled";
import { useTasks } from "../contexts/TaskProvider";
import Toggle from "./Toggle";
const ListItem = styled.li`
display: flex;
width: 400px;
height: 40px;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 8px;
border-radius: 16px;
background-color: white;
box-shadow: 0 0 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
list-style: none;
box-sizing: border-box;
`;
const Content = styled.span`
flex: 1;
margin-left: 8px;
font-size: 14px;
text-decoration: ${({complete}) => (complete ? 'line-through' : 'none')};
`
const RemoveButton = styled.button`
width: 60px;
height: 24px;
margin-left: 8px;
color: white;
border-radius: 8px;
border: none;
background-color: red;
cursor: pointer;
`
const Task = ({ id, content, complete, ...props }) => {
const { updateTask, removeTask } = useTasks();
return (
<ListItem {...props}>
<Toggle on={complete} onChange={(e) => updateTask(id, e.target.value)} />
<Content complete={complete}>{content}</Content>
<RemoveButton onClick={(e) => removeTask(id)} >삭제</RemoveButton>
</ListItem>
)
}
export default Task;💻 TaskList.js
import styled from "@emotion/styled"
import { useTasks } from "../contexts/TaskProvider";
import Task from "./Task"
const UnorderedList = styled.ul`
width: 400px;
margin: 16 0 0 0;
padding: 0;
& > li {
&:not(:first-child) {
margin-top: 8px;
}
}
`
const TaskList = (props) => {
const {tasks} = useTasks();
return (
<UnorderedList {...props}>
{
tasks.map(item => (
<Task
key={item.id}
id={item.id}
content={item.content}
complete={item.complete}
/>
))
}
</UnorderedList>
)
}
export default TaskList;💻 Toggle.js
import styled from "@emotion/styled";
import useToggle from "../hooks/useToggle";
const ToggleContainer = styled.label`
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
`
const ToggleSwitch = styled.div`
width: 64px;
height: 30px;
padding: 2px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #ccc;
box-sizing: border-box;
transition: background-color 0.2s ease-out;
&:after {
content: '';
position: relative;
left: 0;
display: block;
width: 26px;
height: 26px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: white;
transition: left 0.2s ease-out;
}
`
const ToggleInput = styled.input`
display: none;
&:checked + div {
background: lightgreen;
}
&:checked + div:after {
left: calc(100% - 26px);
}
`
const Toggle = ({on = false, onChange, ...props}) => {
const [checked, toggle] = useToggle(on);
const handleChange = (e) => {
toggle();
onChange && onChange(e);
}
return (
<ToggleContainer {...props}>
<ToggleInput type="checkbox" onChange={handleChange} checked={checked} />
<ToggleSwitch />
</ToggleContainer>
)
}
export default Toggle;💻 useToggle.js (Hook)
import { useCallback, useState } from "react";
const useToggle = (initialState) => {
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
const toggle = useCallback(() => setState((state) => !state), []);
return [state, toggle];
}
export default useToggle;💻 useLocalStorage.js (Hook)
import { useState } from "react"
const useLocalStorage = (key, initialValue) => {
const [storedValue, setStoredValue] = useState(() => {
try {
const item = localStorage.getItem(key);
return item ? JSON.parse(item) : initialValue
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
return initialValue;
}
})
const setValue = (value) => {
try {
setStoredValue(value);
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(value));
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
return [storedValue, setValue]
}
export default useLocalStorage;💻 🌟 TaskProvider.js (context)
import { createContext, useContext } from "react"
import { v4 } from "uuid";
import useLocalStorage from "../hooks/useLocalStorage";
const TaskContext = createContext();
export const useTasks = () => useContext(TaskContext);
const TaskProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [tasks, setTasks] = useLocalStorage('tasks', []);
const addTask = (content) => {
setTasks([
...tasks,
{
id: v4(),
content,
complete: false
}
])
}
const updateTask = (id, status) => {
setTasks(tasks.map(item => item.id === id ? {...item, complete: status} : item))
}
const removeTask = (id) => {
setTasks(tasks.filter(item => item.id !== id))
}
return (
<TaskContext.Provider value={{ tasks, addTask, updateTask, removeTask }}>
{children}
</TaskContext.Provider>
)
}
export default TaskProvider;💡 uuid
겹치지 않는 id를 생성해주는 라이브러리
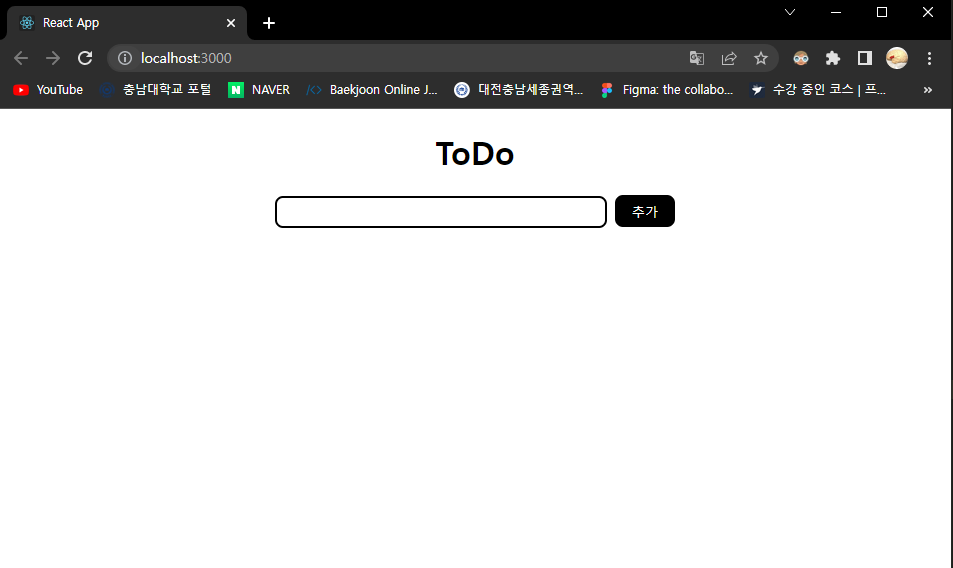
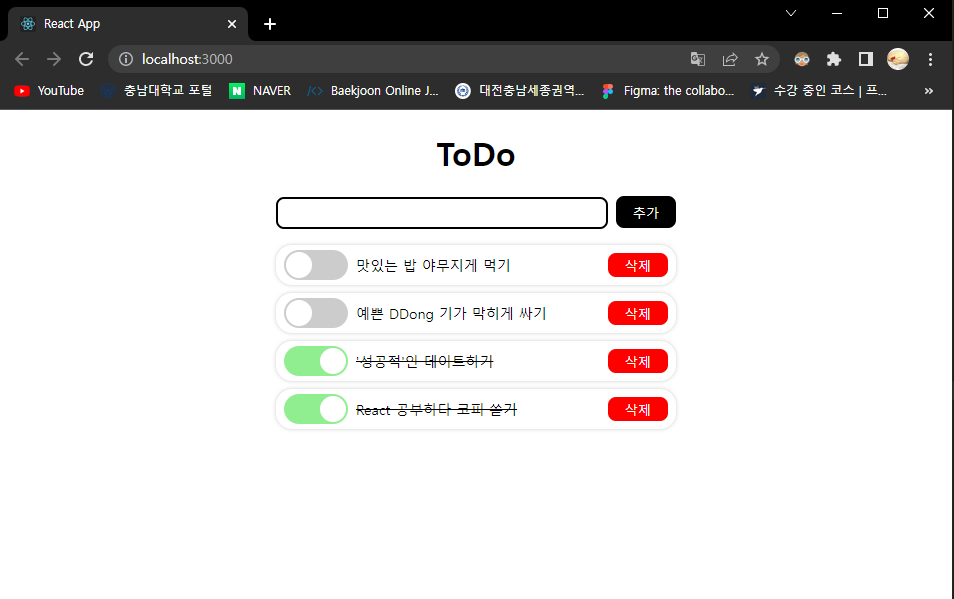
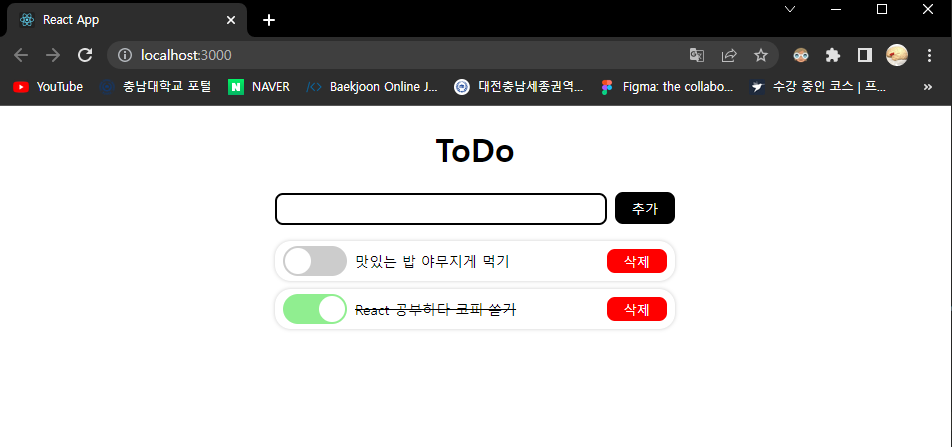
🖨 출력 화면
- 시작 화면
- To do 추가 및 끝난 일정 표시
- To do 삭제
오늘은 Context API에 대해 공부하고 실습해보았다.
해당 구조에 대해서는 조금 더 감을 익혀야할 것 같다.