연습문제 #1
- 입력한 숫자의 소수를 구하여라
inputNum = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력: '))
listA = []
listB = []
for number in range(2, inputNum+1):
flag = True
for n in range(2, number): #1과 자기자신을 제외해야함
if number % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag:
listB.append(number)
print('소수 : {}'.format(listB))
#출력값
1보다 큰 정수 입력: 50
소수 : [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47]연습문제 #2
- 1부터 100사이에 난수 10개를 생성한 후 짝수와 홀수를 구분해서 리스트에 저장하고 각각의 개수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
import random
randomNum = random.sample(range(1,101),10)
evenList = []
oddList = []
for number in randomNum:
if number % 2 == 0:
evenList.append(number)
else:
oddList.append(number)
print('짝수 :{}, {}개'.format(evenList, len(evenList)))
print('홀수 :{}, {}개'.format(oddList, len(oddList)))
#출력값
짝수 :[16, 86, 70, 4, 34, 8], 6개
홀수 :[59, 27, 99, 77], 4개연습문제 #3
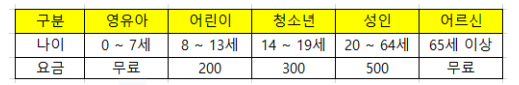
- 1일 총 공원 입장객이 100명이라고 할때, 1일 전체 입장 요금을 구하는 프로그램을 만들어보자. 입장 고객의 나이는 난수를 이용한다.
import random
visitors = []
for n in range(100):
visitors.append(random.randint(1,100))
print(visitors)
group1,group2,group3,group4,group5 = 0,0,0,0,0
for age in visitors:
if age > 0 and age < 7:
group1 +=1
elif age >= 8 and age <= 13:
group2 +=1
elif age >= 14 and age <= 19:
group3 += 1
elif age >= 20 and age <= 64:
group4 += 1
elif age >= 65:
group5 += 1
group1Price = group1 * 0
group2Price = group2 * 200
group3Price = group3 * 300
group4Price = group4 * 500
group5Price = group5 * 0
sum = group1Price+group2Price+group3Price+group4Price+group5Price
print('-'*30)
print('영유아\t:{}명 \t :{}원'.format(group1, group1Price))
print('어린이\t:{}명 \t :{}원'.format(group2, format(group2Price,',')))
print('청소년\t:{}명 \t :{}원'.format(group3, format(group4Price,',')))
print('성인 \t:{}명\t :{}원'.format(group4, format(group4Price,',')))
print('어르신\t:{}명\t :{}원'.format(group5, group5Price))
print('-'*30)
print('1일 요금 총 합계: {}원'.format(format(sum,',')))
print('-'*30)
#실행결과
------------------------------
영유아 :6명 :0원
어린이 :4명 :800원
청소년 :5명 :21,500원
성인 :43명 :21,500원
어르신 :40명 :0원
------------------------------
1일 요금 총 합계: 23,800원
------------------------------group += 1은 각 나이 그룹에 방문자가 들어올 때마다 해당 그룹에 속하는 변수를 1씩 증가시키는 역할
연습문제 #4
- 다음 리스트에서 중복아이템(숫자)를 제거하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
list = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,1,3,5,7,9,10]
idx = 0
while True:
if idx >= len(list):
break
if list.count(list[idx]) >= 2:
list.remove(list[idx])
continue
idx += 1
print(list)
#실행결과
[2, 4, 6, 8, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10]하지만 set을 사용하여 중복된 값을 제거하는 코드를 만드는 것이 더 효율적이다.
first_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10]
# 중복된 값을 제거한 새로운 집합(set) 생성
unique_set = set(first_list)
# 다시 리스트로 변환
result_list = list(unique_set)
print(result_list)
#실행결과
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]연습문제 #5
- 아래 숫자 4개 중 2개를 뽑아 만들 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자(순열)
numbers = [4,6,7,9]
result = []
for num1 in numbers:
for num2 in numbers:
if num1 == num2:
continue
result.append([num1,num2])
print(result)
print('length of result:{}'.format(len(result)))
#실행결과
[[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 9], [6, 4], [6, 7], [6, 9], [7, 4], [7, 6], [7, 9], [9, 4], [9, 6], [9, 7]]
length of result:12continue를 사용하여 현재 반복을 건너뛰고 다음 반복으로 이동한다. 이렇게 함으로써 같은 숫자를 자기 자신과의 조합으로 추가하지 않는다.
- 세가지 경우의 수도 마찬가지로 for문을 하나더 추가하기만 하면된다.
numbers = [4,6,7,9]
result = []
for num1 in numbers:
for num2 in numbers:
if num1 == num2: continue
for num3 in numbers:
if num1 == num3 or num2 == num3:
continue
result.append([num1,num2,num3])
print(result)
print('length of result:{}'.format(len(result)))
#실행결과
[[4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 9], [4, 7, 6], [4, 7, 9], [4, 9, 6], [4, 9, 7], [6, 4, 7], [6, 4, 9], [6, 7, 4], [6, 7, 9], [6, 9, 4], [6, 9, 7], [7, 4, 6], [7, 4, 9], [7, 6, 4], [7, 6, 9], [7, 9, 4], [7, 9, 6], [9, 4, 6], [9, 4, 7], [9, 6, 4], [9, 6, 7], [9, 7, 4], [9, 7, 6]]
length of result:24연습문제 #6
- 대학생 길동이의 1,2,3학년의 성적이 다음과 같다. 졸업할 때 4.0 이상의 학점을 받기 위해 길동이가 받아야하는 4학년 1,2학기의 최소 학점을 구해보자.
scores = ((3.7,4.2),(2.9,4.3),(4.1,4.2))
sumScore = 0
avg = sumScore / 6
for score1 in scores: #scores 튜플 안에 있는 각 학기(score1)를 가져온다.
for score2 in score1: #학기(score1) 안에 있는 성적(score2)을 가져온다.
sumScore += score2 #성적(score2)을 sumScore에 더한다. 이것은 성적의 총합을 계산하는 부분임
sumScore = round(sumScore,1)
print('3학년때까지의 성적 총합: {}'.format(sumScore))
print('3학년때까지의 평균 학점: {}'.format(avg))
totalTargetScore = round((4.0 * 8) - sumScore,1)
print('4학년때까지 학점 평균 4.0이 되기 위해 필요한 4학년 학점 총 합:{}'.format(totalTargetScore))
minScore4Grade = totalTargetScore / 2
print('4학년 학기 최소 학점:{}'.format(minScore4Grade))
scores = list(scores)
scores.append((minScore4Grade,minScore4Grade))
scores = tuple(scores)
print('학점 리스트:{}'.format(scores))
#출력값
3학년때까지의 성적 총합: 23.4
3학년때까지의 평균 학점: 3.9
4학년때까지 학점 평균 4.0이 되기 위해 필요한 4학년 학점 총 합:8.6
4학년 학기 최소 학점:4.3
학점 리스트:((3.7, 4.2), (2.9, 4.3), (4.1, 4.2), (4.3, 4.3))연습문제 #7
tuple1 = (1,3,2,6,12,5,7,8)
tuple2 = (0,5,2,9,8,6,17,3)
tuple1Hap = list(tuple1)
tuple2Gyo = list()
for n in tuple2:
if n not in tuple1:
tuple1Hap.append(n)
else:
tuple2Gyo.append(n)
tuple1 = tuple(sorted(tuple1Hap))
tuple2 = tuple(sorted(tuple2Gyo))
print('합집합: {}'.format(tuple1))
print('교집합: {}'.format(tuple2))
#실행결과
합집합: (0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 17)
교집합: (2, 3, 5, 6, 8)- tuple1Hap은 tuple1의 합집합을 구하기 위한 임시 리스트다. 처음에 tuple1을 리스트로 변환한 이유는 합집합을 넣는 리스트이기때문에 tuple2에서 겹치지 않는 요소들만 추가하기 위해서다.
- tuple2Gyo는 tuple1과 tuple2에서 겹치는 요소들만 넣기 위해서 빈 리스트를 만들었다.
연습문제 #8
- 과목 점수를 입력하여 튜플에 저장하고 과목별 학점을 출력해보자
korScore = int(input('국어 점수 입력:'))
engScore = int(input('영어 점수 입력:'))
matScore = int(input('수학 점수 입력:'))
sciScore = int(input('과학 점수 입력:'))
scores = (
{'kor':korScore},
{'eng':engScore},
{'mat':matScore},
{'sci':sciScore}
)
for score in scores:
for key in score.keys():
if score[key] >= 90:
score[key] = 'A'
elif score[key] >= 80:
score[key] = 'B'
elif score[key] >= 70:
score[key] = 'C'
else:
score[key] = 'D'
print(scores)
#실행결과
국어 점수 입력:50
영어 점수 입력:70
수학 점수 입력:80
과학 점수 입력:90
({'kor': 'D'}, {'eng': 'C'}, {'mat': 'B'}, {'sci': 'A'})연습문제 #9
fruits = ({'수박': 8}, {'포도': 13}, {'참외': 12}, {'사과': 17}, {'자두': 19}, {'자몽': 15})
fruits = list(fruits)
cIdx = 0; nIdx = 1
eIdx = len(fruits) - 1
flag = True
while flag:
curDic = fruits[cIdx]
nextDic = fruits[nIdx]
curDicCnt = list(curDic.values())[0]
nextDicCnt = list(nextDic.values())[0]
if nextDicCnt < curDicCnt: #>로 바꾸면 내림차순
fruits.insert(cIdx, fruits.pop(nIdx))
nIdx = cIdx + 1
continue
nIdx += 1
if nIdx > eIdx:
cIdx += 1
nIdx = cIdx + 1
if cIdx == 5:
flag = False
print(tuple(fruits))
key 함수를 이용하면 더 쉽게 풀기 가능
연습문제 #10
- 학급별 학생 수를 나타낸 튜플을 이용해서, 요구 사항에 맞는 데이터를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
studentCnt = ({'cls01':18},
{'cls01':21},
{'cls01':20},
{'cls01':19},
{'cls01':22},
{'cls01':20},
{'cls01':23},
{'cls01':17})
# 학급별 학생 수를 저장하기 위한 딕셔너리 초기화
class_students = {}
# 전체 학생 수 계산
total_students = 0
for data in studentCnt:
for cls, cnt in data.items():
# 학급별 학생 수 누적
if cls in class_students:
class_students[cls] += cnt
else:
class_students[cls] = cnt
# 전체 학생 수 누적
total_students += cnt
# 평균 학생 수 계산
average_students = total_students / len(class_students)
# 학생 수가 가장 적은 학급 찾기
min_class = min(class_students, key=class_students.get)
min_students = class_students[min_class]
# 학생 수가 가장 많은 학급 찾기
max_class = max(class_students, key=class_students.get)
max_students = class_students[max_class]
# 학급별 학생 편차 계산
deviations = {}
for cls, cnt in class_students.items():
deviation = cnt - average_students
deviations[cls] = deviation
print("전체 학생 수:", total_students)
print("평균 학생 수:", average_students)
print("학생 수가 가장 적은 학급:", min_class, "({}명)".format(min_students))
print("학생 수가 가장 많은 학급:", max_class, "({}명)".format(max_students))
print("학급별 학생 편차:", deviations)key=class_students.get는 파이썬의 min 또는 max 함수와 함께 사용되는 기능이다. 이렇게 사용하면 최솟값 또는 최댓값을 기준으로 정렬할 때 어떤 값을 기준으로 정렬할지를 지정할 수 있다.
연습문제 #11
- 삼각형부터 십각형까지의 내각의 합과 내각을 딕셔너리에 저장하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
(n각형의 내각의 합 : 180 × (n-2))
dic = {}
for n in range(3, 11):
hap = 180 * (n - 2)
ang = int(hap/n)
dic[n] = [hap, ang]
print(dic)
#출력값
{3: [180, 60], 4: [360, 90], 5: [540, 108], 6: [720, 120], 7: [900, 128], 8: [1080, 135], 9: [1260, 140], 10: [1440, 144]}연습문제 #12
- 다음 문장에서 비속어를 찾고 비속어를 표준어로 변경하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
‘강도는 서로 쪼개다, 짭새를 보고 빠르게 따돌리며 먹튀했다.'
words = {'꺼지다':'가다',
'쩔다': '엄청나다',
'짭새': '경찰관',
'꼽사리': '중간에 낀 사람',
'먹튀': '먹고 도망',
'지린다': '겁을 먹다',
'쪼개다': '웃다',
'뒷담 까다': '험담하다'}
txt = '강도는 서로 쪼개다, 짭새를 보고 빠르게 따돌리며 먹튀했다.'
keys = list(words.keys())
for key in keys:
if key in txt:
print('key: {}'.format(key))
print('words: [{}]'.format(key, words[key]))
txt = txt.replace(key, words[key])
print(txt)
#출력값
key: 짭새
words: [짭새]
key: 먹튀
words: [먹튀]
key: 쪼개다
words: [쪼개다]
강도는 서로 웃다, 경찰관를 보고 빠르게 따돌리며 먹고 도망했다.
연습문제 #13
- 딕셔너리를 이용해서 5명의 회원을 가입 받고 전체 회원 정보를 출력하고 특정 회원 계정을 삭제하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
members = {}
n = 1
while n < 6:
mail = input('메일 입력: ')
pw = input('비번 입력: ')
if mail in members:
print('이미 사용 중인 메일 계정입니다. ')
continue
else:
members[mail] = pw
n += 1
for key in members.keys():
print(f'{key} : {members[key]}')
while True:
delMail = input('삭제할 계정(메일) 입력: ')
if delMail in members:
delPw = input('비번 입력: ')
if members[delMail] == delPw:
del members[delMail]
print(f'{delMail} 게정 삭제 완료!!')
break
else:
print('비번 확인 요망!!')
else:
print('계정 확인 요망!!')
for key in members.keys():
print(f'{key} : {members[key]}')