CORS
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any origins (domain, scheme, or port) other than its own from which a browser should permit loading resources. CORS also relies on a mechanism by which browsers make a "preflight" request to the server hosting the cross-origin resource, in order to check that the server will permit the actual request. In that preflight, the browser sends headers that indicate the HTTP method and headers that will be used in the actual request.
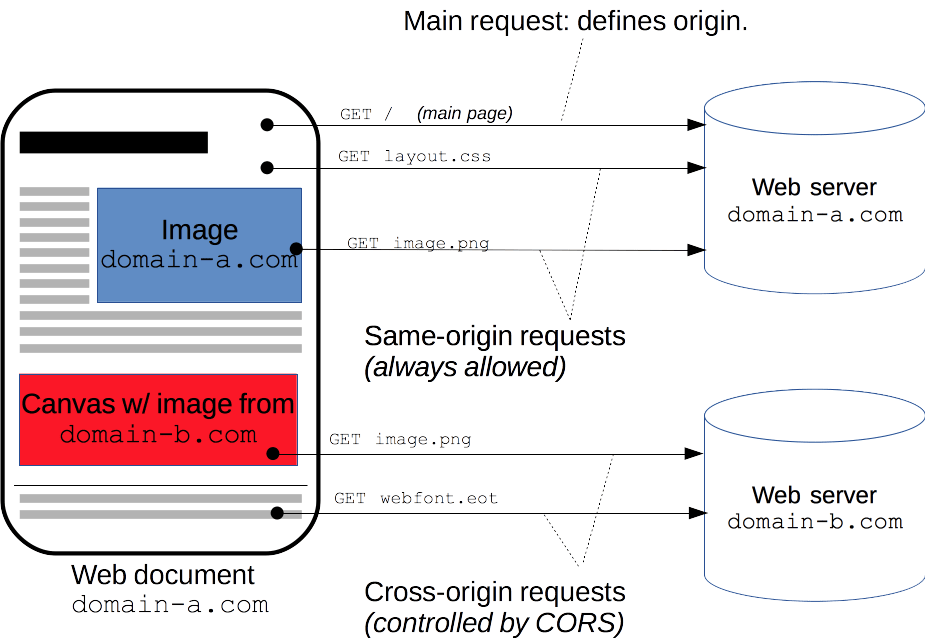
The Cross-Origin Resource Sharing standard works by adding new HTTP headers that let servers describe which origins are permitted to read that information from a web browser. Additionally, for HTTP request methods that can cause side-effects on server data (in particular, HTTP methods other than GET, or POST with certain MIME types), the specification mandates that browsers "preflight" the request, soliciting supported methods from the server with the HTTP OPTIONS request method, and then, upon "approval" from the server, sending the actual request. Servers can also inform clients whether "credentials" (such as Cookies and HTTP Authentication) should be sent with requests.
CORS failures result in errors but for security reasons, specifics about the error are not available to JavaScript. All the code knows is that an error occurred. The only way to determine what specifically went wrong is to look at the browser's console for details.
source : MDN
