UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
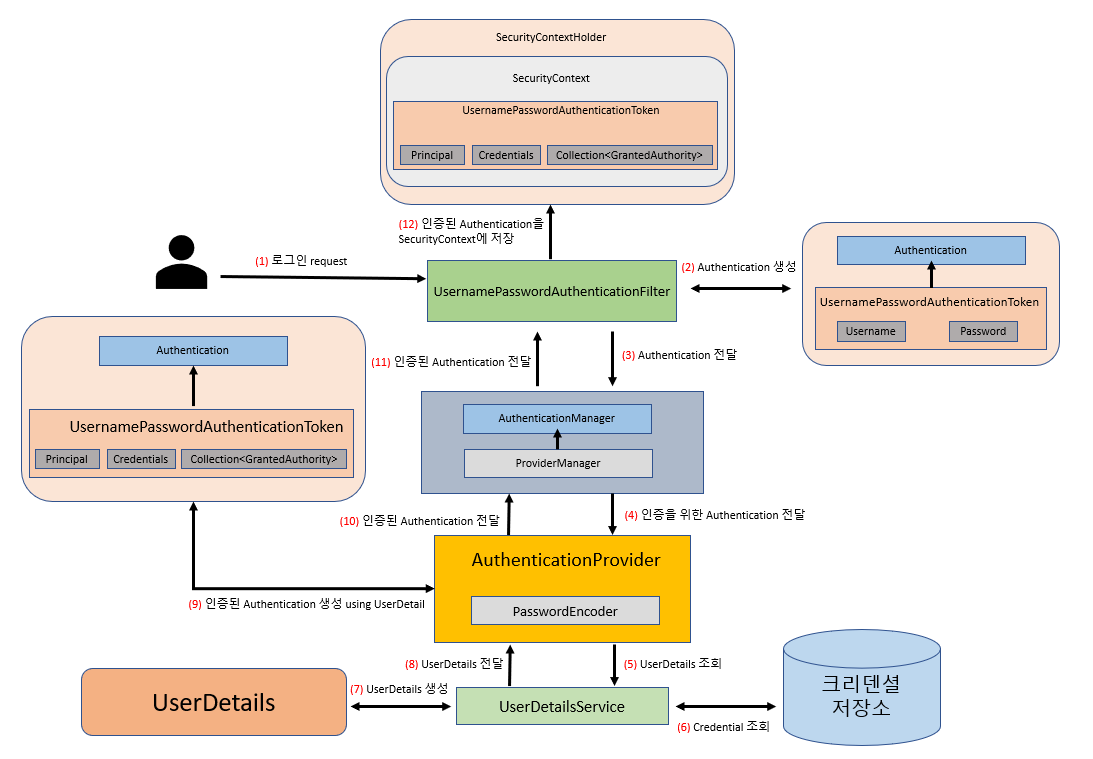
사용자의 로그인 request를 제일 먼저 만나는 컴포넌트는 바로 Spring Security Filter Chain의 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 이다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 는 일반적으로 로그인 폼에서 제출되는 Username과 Password를 통한 인증을 처리하는 Filter다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 는 클라이언트로부터 전달 받은 Username과 Password를 Spring Security가 인증 프로세스에서 이용할 수 있도록 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 생성한다.
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter { // (1)
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username"; // (2)
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password"; // (3)
private static final AntPathRequestMatcher DEFAULT_ANT_PATH_REQUEST_MATCHER = new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login","POST"); // (4)
...
...
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
super(DEFAULT_ANT_PATH_REQUEST_MATCHER, authenticationManager); // (5)
}
// (6)
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
// (6-1)
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
...
String password = obtainPassword(request);
...
// (6-2)
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username, password);
...
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); // (6-3)
}
...
...
}-
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter는 (1)과 같이AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter를 상속한다.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 클래스의 이름이 Filter로 끝나지만 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 클래스에는
doFilter()메서드가 존재하지 않다.상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스가
doFilter()메서드를 포함하고 있다.결과적으로 사용자의 로그인 request를 제일 먼저 전달 받는 클래스는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter의 상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스인 것이다.
-
(2)와 (3)을 통해 클라이언트의 로그인 폼을 통해 전송되는 request parameter의 디폴트 name은
username과password라는 것을 알 수 있다. -
(4)의
AntPathRequestMatcher는 클라이언트의 URL에 매치되는 매처다.(4)를 통해 클라이언트의 URL이
"/login"이고, HTTP Method가POST일 경우 매치 될거라는 사실을 예측할 수 있다.(4)에서 생성되는 AntPathRequestMatcher의 객체(
DEFAULT_ANT_PATH_REQUEST_MATCHER)는 (5)에서 상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스에 전달되어 Filter가 구체적인 작업을 수행할지 특별한 작업 없이 다른 Filter를 호출할지 결정하는데 사용된다. -
(5)에서 AntPathRequestMatcher의 객체(
DEFAULT_ANT_PATH_REQUEST_MATCHER)와AuthenticationManager를 상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter에 전달한다. -
(6)의
attemptAuthentication()메서드는 클라이언트에서 전달한 username과 password 정보를 이용해 인증을 시도하는 메서드다.attemptAuthentication()메서드는 상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter의doFilter()메서드에서 호출되는데 Filter에서 어떤 처리를 하는 시작점은doFilter()이다.(6-1)에서 HTTP Method가 POST가 아니면 Exception을 throw한다는 사실을 알 수 있다.
(6-2)에서는 클라이언트에서 전달한 username과 password 정보를 이용해
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 생성한다.
여기서의 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken은 인증을 하기 위해 필요한 인증 토큰이지 인증에 성공한 인증 토큰과는 상관이 없다.
(6-3)에서 AuthenticationManager의 authenticate() 메서드를 호출해 인증 처리를 위임하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter가 상속하는 상위 클래스로써 Spring Security에서 제공하는 Filter 중 하나다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 는 HTTP 기반의 인증 요청을 처리하지만 실질적인 인증 시도는 하위 클래스에 맡기고, 인증에 성공하면 인증된 사용자의 정보를 SecurityContext에 저장하는 역할을 한다.
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean
implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
...
...
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
doFilter((HttpServletRequest) request, (HttpServletResponse) response, chain);
}
// (1)
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// (1-1)
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response); // (1-2)
if (authenticationResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
// Authentication success
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult); // (1-3)
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); // (1-4)
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);
}
}
// (2)
protected boolean requiresAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
if (this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher.matches(request)) {
return true;
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger
.trace(LogMessage.format("Did not match request to %s", this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher));
}
return false;
}
...
...
// (3)
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult));
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass()));
}
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
// (4)
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
this.logger.trace("Failed to process authentication request", failed);
this.logger.trace("Cleared SecurityContextHolder");
this.logger.trace("Handling authentication failure");
this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
this.failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
...
...
}-
(1)을 통해 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스가 Spring Security의 Filter임을 알 수 있다.
-
(1-1)에서는 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 클래스가 인증 처리를 해야되는지 아니면 다음 Filter를 호출할지 여부를 결정하고 있다.
(1-1)에서 호출하는 requiresAuthentication() 메서드는 (2)에서 확인할 수 있듯이 하위 클래스에서 전달받은 requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher 객체를 통해 들어오는 요청이 인증 처리를 해야 되는지 여부를 결정하고 있다.
위 코드의 (4)에서 설명한 AntPathRequestMatcher("/login","POST")의 파라미터인 URL과 HTTP Method가 매칭 조건이 된다는 것을 참고한다.
-
(1-2)에서는 하위 클래스에 인증을 시도해 줄 것을 요청하고 있다. 여기서의 하위 클래스는
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter가 된다. -
(1-3)에서는 인증에 성공하면 처리할 동작을 수행하기 위해
successfulAuthentication()메서드를 호출한다.successfulAuthentication()메서드는 (3)에서 확인할 수 있다시피 인증에 성공한 이후,SecurityContextHolder를 통해 사용자의 인증 정보를SecurityContext에 저장한 뒤, SecurityContext를 HttpSession에 저장한다. -
만약 인증에 실패한다면 (1-4)와 같이
unsuccessfulAuthentication()메서드를 호출해 인증 실패 시 처리할 동작을 수행한다.unsuccessfulAuthentication()메서드는 (4)에서 확인할 수 있다시피 SeucurityContext를 초기화 하고,AuthenticationFailureHandler를 호출한다.
-
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 은 Spring Security에서 Username/Password로 인증을 수행하기 위해 필요한 토큰이며, 또한 인증 성공 후 인증에 성공한 사용자의 인증 정보가 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken에 포함되어 Authentication 객체 형태로 SecurityContext에 저장된다.
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
...
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
...
...
// (1)
public static UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken unauthenticated(Object principal, Object credentials) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials);
}
// (2)
public static UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticated(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials, authorities);
}
...
...
}UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 은 두 개의 필드를 가지고 있는데 principal 은 Username 등의 신원을 의미하고, credentials 는 Password를 의미한다.
(1)의 unauthenticated() 메서드는 인증에 필요한 용도의 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 객체를 생성하고, (2)의 authenticated() 메서드는 인증에 성공한 이후 SecurityContext에 저장될 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 객체를 생성한다.
Authentication
Authentication 은 Spring Security에서의 인증 자체를 표현하는 인터페이스다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken은 AbstractAuthenticationToken 추상 클래스를 상속하는 확장 클래스이자 Authentication 인터페이스의 메서드 일부를 구현하는 구현 클래스이기도 하다.
애플리케이션의 코드 상에서 인증을 위해 생성되는 인증 토큰 또는 인증 성공 후 생성되는 토큰은 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken과 같은 하위 클래스의 형태로 생성되지만 생성된 토큰을 리턴 받거나 SecurityContext에 저장될 경우에 Authentication 형태로 리턴 받거나 저장된다.
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}-
Principal
-
Principal은 사용자를 식별하는 고유 정보다.일반적으로 Username/Password 기반 인증에서
Username이 Principal이 되며, 다른 인증 방식에서는UserDetails가 Principal이 된다.
-
-
Credentials
- 사용자 인증에 필요한 Password를 의미하며 인증이 이루어지고 난 직후,
ProviderManager가 해당 Credentials를 삭제한다.
- 사용자 인증에 필요한 Password를 의미하며 인증이 이루어지고 난 직후,
-
Authorities
AuthenticationProvider에 의해 부여된 사용자의 접근 권한 목록이다.
일반적으로GrantedAuthority인터페이스의 구현 클래스는SimpleGrantedAuthority이다.
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager 는 인증 처리를 총괄하는 매니저 역할을 하는 인터페이스다.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}AuthenticationManager에는 authenticate()메서드 하나만 정의되어 있다.
인증을 위한 Filter는 AuthenticationManager를 통해 느슨한 결합을 유지하고 있으며, 인증을 위한 실질적인 관리는 AuthenticationManager를 구현하는 구현 클래스를 통해 이루어진다.
ProviderManager
Spring Security에서 AuthenticationManager 인터페이스의 구현 클래스라고 하면 일반적으로 ProviderManager 를 가리킨다.
AuthenticationProvider를 관리하고, AuthenticationProvider에게 인증 처리를 위임하는 역할을 한다.
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean {
...
...
// (1)
public ProviderManager(List<AuthenticationProvider> providers, AuthenticationManager parent) {
Assert.notNull(providers, "providers list cannot be null");
this.providers = providers;
this.parent = parent;
checkState();
}
...
...
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
// (2)
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication); // (3)
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
...
...
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials(); // (4)
}
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
...
...
}
...
...
}-
(1)에서 ProviderManager 클래스가 Bean으로 등록 시,
List<AuthenticationProvider>객체를 DI 받는다는 것을 알 수 있다. -
DI 받은 List를 이용해 (2)와 같이 for문으로 적절한 AuthenticationProvider를 찾는다.
-
적절한 AuthenticationProvider를 찾았다면 (3)과 같이 해당 AuthenticationProvider에게 인증 처리를 위임한다.
-
인증이 정상적으로 처리되었다면 (4)와 같이 인증에 사용된 Credentials를 제거한다.
AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider 는 AuthenticationManager로부터 인증 처리를 위임 받아 실질적인 인증 수행을 담당하는 컴포넌트다.
Username/Password 기반의 인증 처리는 DaoAuthenticationProvider 가 담당하고 있으며, DaoAuthenticationProvider 는 UserDetailsService로부터 전달 받은 UserDetails를 이용해 인증을 처리한다.
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider { // (1)
...
...
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
...
...
// (2)
@Override
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username); // (2-1)
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
// (3)
@Override
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) { // (3-1)
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
...
...
}1)을 보면 DaoAuthenticationProvider 는 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 를 상속하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
AuthenticationProvider 인터페이스의 구현 클래스는 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 이고, DaoAuthenticationProvider는 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 를 상속한 확장 클래스다.
따라서 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 추상 클래스의 authenticate() 메서드에서부터 실질적인 인증 처리가 시작된다.
(2)의 retrieveUser() 메서드는 UserDetailsService로부터 UserDetails를 조회하는 역할을 한다. 조회된 UserDetails는 사용자를 인증하는데 사용될 뿐만 아니라 인증에 성공할 경우, 인증된 Authentication 객체를 생성하는데 사용된다.
(2-1)의 this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username); 에서 UserDetails를 조회하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
(3)의 additionalAuthenticationChecks() 메서드에서 PasswordEncoder를 이용해 사용자의 패스워드를 검증하고 있습니다.
(3-1)에서 클라이언트로부터 전달 받은 패스워드와 데이터베이스에서 조회한 패스워드가 일치하는지 검증하고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 메서드가 호출되는 순서
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider의 authenticated() 메서드 호출DaoAuthenticationProvider의 retrieveUser() 메서드 호출DaoAuthenticationProvider의 additionalAuthenticationChecks() 메서드 호출DaoAuthenticationProvider의 createSuccessAuthentication() 메서드 호출AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider의 createSuccessAuthentication() 메서드 호출- 인증된 Authentication을
ProviderManager에게 리턴
UserDetails
UserDetails 는 데이터베이스 등의 저장소에 저장된 사용자의 Username과 사용자의 자격을 증명해주는 크리덴셜(Credential)인 Password 그리고 사용자의 권한 정보를 포함하는 컴포넌트이며, AuthenticationProvider 는 UserDetails 를 이용해 자격 증명을 수행한다.
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); // (1) 권한 정보
String getPassword(); // (2) 패스워드
String getUsername(); // (3) Username
boolean isAccountNonExpired(); // (4) 사용자 계정의 만료 여부
boolean isAccountNonLocked(); // (5) 사용자 계정의 Lock 여부
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired(); // (6) Credentials(Password)의 만료 여부
boolean isEnabled(); // (7) 사용자의 활성화 여부
}UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService 는 UserDetails를 로드(load)하는 핵심 인터페이스이다.
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}UserDetailsService는 loadUserByUsername(String username) 메서드 하나만 정의하고 있으며, UserDetailsService 를 구현하는 클래스는 loadUserByUsername(String username) 을 통해 사용자의 정보를 로드한다.
사용자의 정보를 어디에서 로드하는지는 애플리케이션에서 사용자의 정보를 어디에서 관리하고 있는지에 따라서 달라진다.
즉, 사용자의 정보를 메모리에서 로드하든 데이터베이스에서 로드하든 Spring Security가 이해할 수 있는 UserDetails로 리턴해주기만 하면 된다.
SecurityContext와 SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContext 는 인증된 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 컴포넌트이고, SecurityContextHolder 는 SecurityContext를 관리하는 역할을 담당한다.
Spring Security 입장에서는 SecurityContextHolder에 의해 SecurityContext에 값이 채워져 있다면 인증된 사용자로 간주한다.
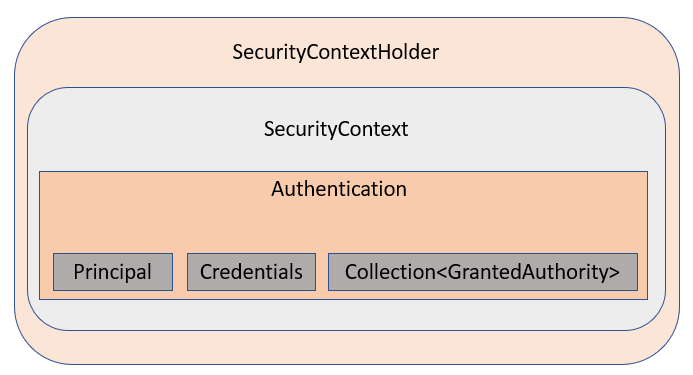
SecurityContextHolder가 SecurityContext를 포함하고 있는 것은 SecurityContextHolder 를 통해 인증된 Authentication을 SecurityContext에 설정할 수 있고 또한 SecurityContextHolder 를 통해 인증된 Authentication 객체에 접근할 수 있다는 것을 의미한다.
public class SecurityContextHolder {
...
...
private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy; // (1)
...
...
// (2)
public static SecurityContext getContext() {
return strategy.getContext();
}
...
...
// (3)
public static void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
strategy.setContext(context);
}
...
...
}-
(1)은 SecurityContextHolder에서 사용하는 전략을 의미하며, SecurityContextHolder 기본 전략은 ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy 이다.
이 전략은 현재 실행 스레드에 SecurityContext를 연결하기 위해 ThreadLocal을 사용하는 전략이다.
-
(2)의
getContext()메서드를 통해 현재 실행 스레드에서 SecurityContext를 얻을 수 있다. -
(3)의
setContext()메서드는 현재 실행 스레드에 SecurityContext를 연결한다.
setContext()는 대부분 인증된 Authentication을 포함한 SecurityContext를 현재 실행 스레드에 연결하는데 사용된다.
