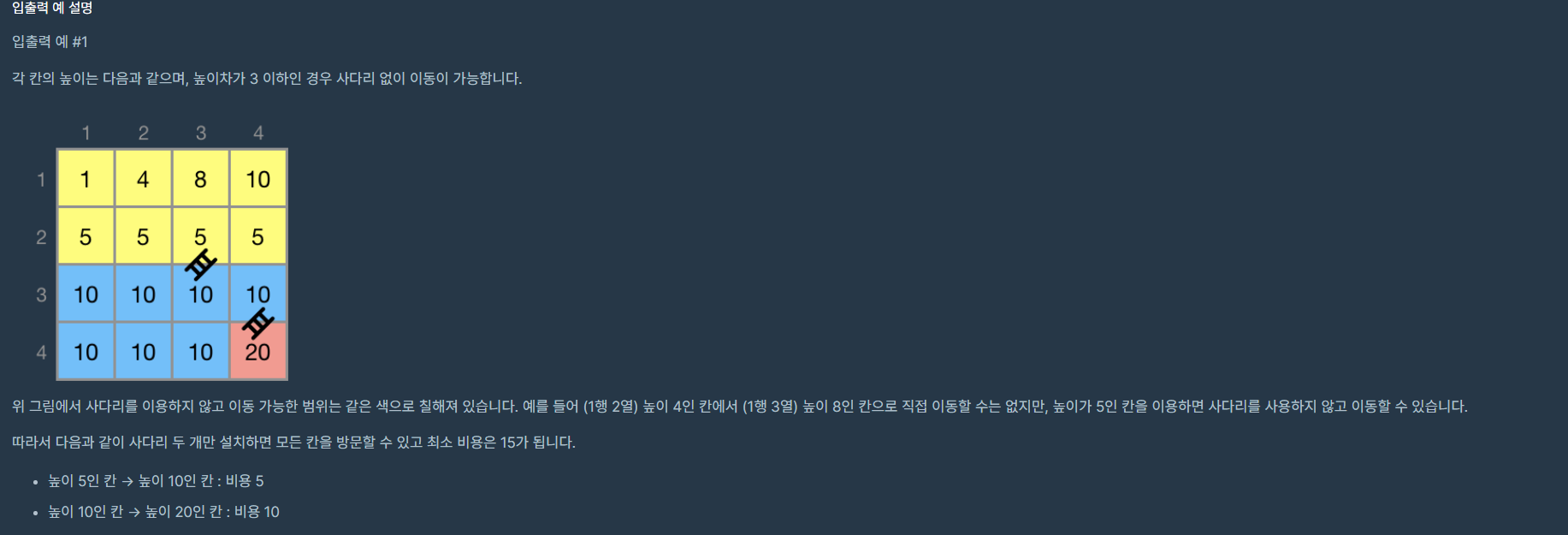
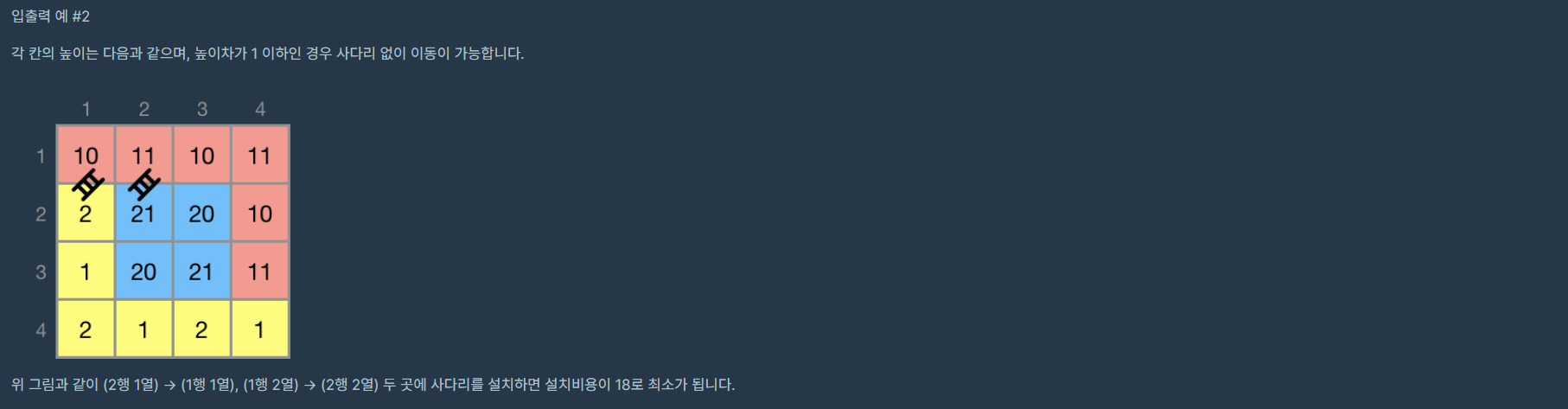
문제
풀이
BFS + 우선순위 큐로 해결했다.
-
(0,0) 에서 시작해 사다리 설치 없이 방문할 수 있는 모든 지역을 방문한다.
-
방문할 수 없는 지역은 필요한 비용과 함께 우선순위 큐에 넣어준다.
-
사다리 설치 없이 방문할 수 있는 지역을 모두 방문하고 나면 우선순위 큐에서 비용을 가장 적게 들여 방문할 수 있는 지역에 사다리를 설치한다.
-
이후 사다리를 설치한 지역에서 다시 bfs로 방문가능한 지역을 방문한다.
위 과정을 우선순위 큐가 빌 때까지 반복하면 된다.
코드
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct wallInfo {
int cost;
int x, y;
}wallInfo;
struct compare {
bool operator()(const wallInfo& m1, const wallInfo& m2) {
return m1.cost > m2.cost;
}
};
int dx[4]{ 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[4]{ 1,-1,0,0 };
void go(int x,int y, int height, bool vi[][301], vector<vector<int>> &land, priority_queue<wallInfo, vector<wallInfo>, compare> &pq) {
int n = land.size(), m = land[0].size();
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
vi[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x,y });
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowX = q.front().first;
int nowY = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextX = nowX + dx[i];
int nextY = nowY + dy[i];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= n || nextY < 0 || nextY >= m || vi[nextX][nextY]) continue;
int cost = abs(land[nowX][nowY] - land[nextX][nextY]);
if (cost > height) {
wallInfo tmp = { cost,nextX,nextY };
pq.push(tmp);
continue;
}
vi[nextX][nextY] = true;
q.push({ nextX,nextY });
}
}
}
int solution(vector<vector<int>> land, int height) {
int answer = 0;
priority_queue<wallInfo, vector<wallInfo>, compare> pq;
bool vi[301][301];
fill(&vi[0][0], &vi[300][301], false);
wallInfo tmp = { 0,0,0 };
pq.push(tmp);
while (!pq.empty()) {
int x = pq.top().x;
int y = pq.top().y;
int cost = pq.top().cost;
pq.pop();
if (vi[x][y]) continue;
answer += cost;
go(x, y, height, vi, land, pq);
}
return answer;
}
int main() {
cout<<solution({{10, 11, 10, 11}, {2, 21, 20, 10}, {1, 20, 21, 11}, {2, 1, 2, 1}}, 1);
}후기
다 풀고보니 다익스트라와 돌아가는 모양이 비슷하다.
우선순위 큐에 구조체를 기준으로 정렬하는 방법에 대해 복습했다.
https://unluckyjung.github.io/cpp/2020/06/27/Priority_Queue_Compare/
