제목: Structural variation in the sequencing era (2020) : Review paper
링크: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41576-019-0180-9
0. Abstract
- Structural variation (SV)을 찾는 것은 genome interpretation에 굉장히 중요하지만, 현재 기술의 한계로 인해 어렵다.
- Ensemble algorithm과 새로 등장하는 시퀀싱 기술을 바탕으로 하는 detection method는 수천개의 SV를 발견하는데 도움을 줬으며, 질병과의 연관성을 밝히는데 많은 도움을 주고 있다.
- SV는 종류와 크기가 다양하고, 변이를 발굴하는 genomic platform 마다 detection 편향이 있기에, multiplatform discovery 방식으로 넓은 변이 스펙트럼을 잡아야 한다.
- 이 논문에서는 SV를 찾는 최신 방법들을 알아볼 것이다.
1. Introduction
- High-throughput sequencing (HTS) = NGS의 발전 덕분에 SNV, small indels(<50bp), 그리고 SV가 개개인마다 다르다는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
- SV 는 종류와 크기가 다양하고, 분류를 크게 하면 unbalanced SV (=CNV: deletions, duplications, insertions) 그리고 balanced된 (inversion, inter/intrachromosomal translocations)로 나누어진다.
- 이뿐만 아니라, mobile element insertion, multi-allelic CNVs, segmental duplication 그리고 complex rearrangements.
- SV detection을 위해 널리 쓰이고 있는 툴과 알고리즘은 주로 short read signature 를 이용해 reference genome와 비교를 함으로써 SV의 존재를 유추를 한다. Short-read 접근 방식은 SNV를 처리하는데 매우 효과적이지만, 한정된 sequence와 insert size의 단점을 가진 standard short-read HTS의 한계를 뛰어넘지는 못한다.
- SV는 SNV와 다르게 multiple short reads를 다루다 보니, computational inference가 요구 되고, SNV 발견하는 발전 속도에 많이 뒤쳐져 있는 상황이다.
- 이를 극복하기 위해, flow cell, advanced microfluidics, 그리고 protein pore를 이용한 새로운 시퀀싱 기술들이 많아졌고, 이로 인해 기존에는 잡지 못했던 SV들을 발견하기 시작했다.
- 이번 논문에서는 기존의 short-read approach의 한계를 극복할 수 있는 다양한 알고리즘과 신규 기술들을 소개할 것
1-Vocab. Introduction 용어
- Structural variations (SV) : Sequence variants >50 bp in size.
Complex rearrangements: 여러 종류의 SV들이 합쳐져 있는 복잡한 형태 - Read signatures: Specific marks that result from reads that map discordantly to the reference genome
- Short-read HTS: Standard sequencing where libraries are fragmented to ~600-800 bp in length.Two ends are sequenced ~100-250 bp with an unsequenced insert size of ~100-600 bp.
- Flow cell: Glass slides containing fluidic channels for sequencing reactions to occur.
- Microfluidics: Devices that precisely manipulate and control small amounts of fluids.
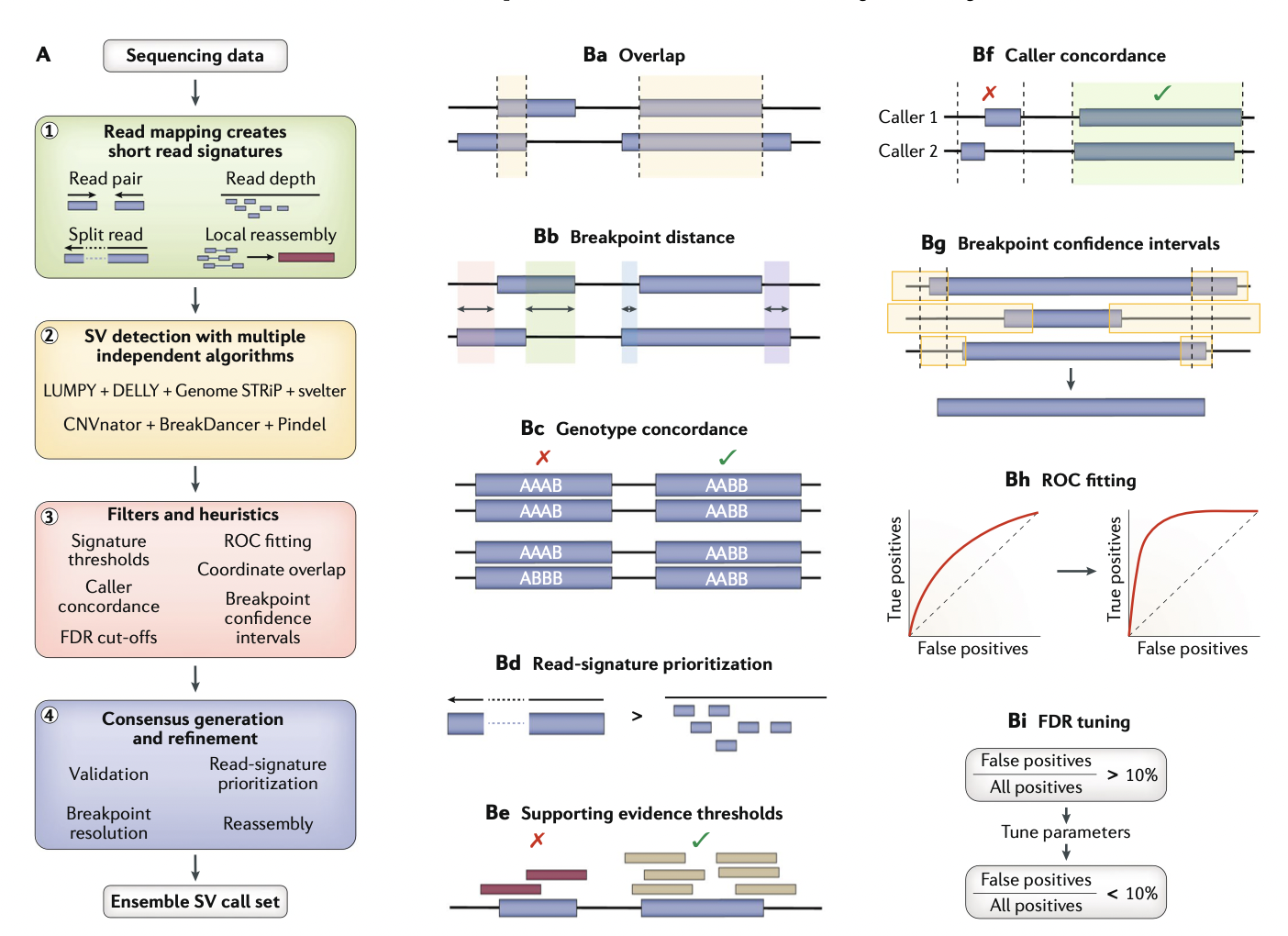
2. Ensemble Algorithms
- 시퀀싱 기반 SV detection은 sample read와 reference genome과의 맵핑 차이로 생기는 signature 정보를 사용한다.
- 4개의 주요 방식: read-pair, read-depth, split-read, de novo assembly
- 초기의 SV caller들은 (BreakDancer, CNVnator, etc.) 위의 4가지 방식 중 하나만 사용을 해서 만들었었다. 그후로, Hybrid-signature algorithm들은 위의 4가지 방식들 중 여러개를 조합해서 sensitivity를 늘릴 수 있었다 (DELLY, LUMPY, Manta)
- 그럼에도 불구하고, 아직도 모든 범위의 SV를 잡을 수 있는 ‘하나'의 caller는 없다.
한 가지의 방법은, 동일한 시퀀스에 대해서 여러개의 알고리즘을 사용한 후, 결과를 통합해서 unified call set을 만드는 것. 이런 방법을 ensemble algorithm 이라고 이번 논문에서 지칭한다. - 여러개의 알고리즘을 합치고 나서, 중복으로 call 된 SV에 대해서는 필터를 거칠 필요가 있는데, 이 필터할 요소들은 breakpoint confidence overlap, breakpoint distances, false-discovery rate (FDR) cut-off thresholds, read-signature prioritization (split reads > read pair > read depth), caller concordance, signature thresholds와 같은 것을 포함한다.
- 그리고 coordinate overlap 이라는 요소도 있다. 이 수치를 조절하면서 sensitivity/FDR를 조절한다.
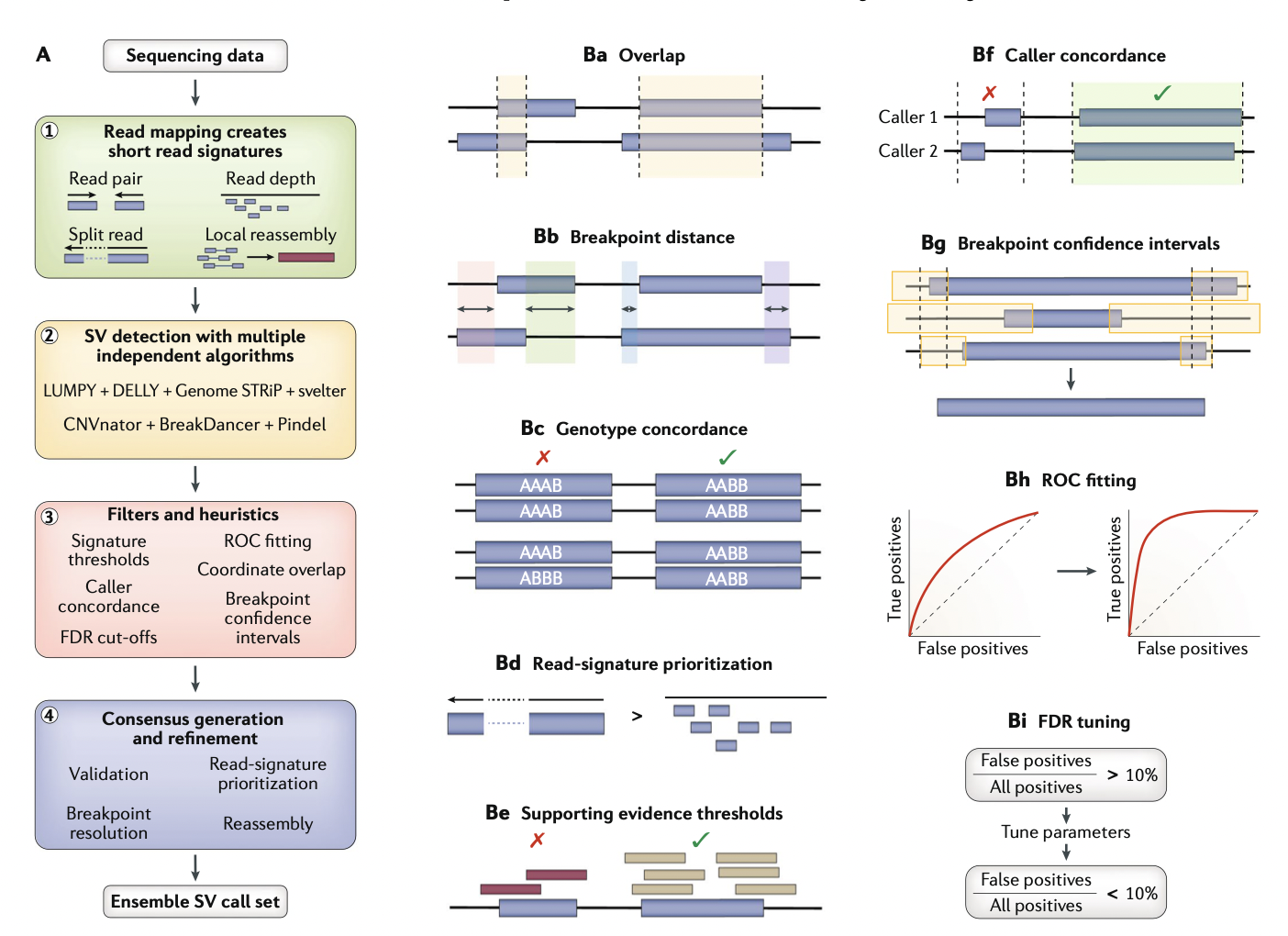
- 이런 ensemble algorithm을 표준화 하기 위한 stand-alone tool들이 여러개 있다
- 예시로:
- SpeedSeq는 LUMPY + CNVnator로 SR, PR, RD로 뭉쳐서 SVTyper로 validation해줌
- HugeSeq, iSVP, Parliament2, SVMerge는 intersect by coordinate overlap으로 call이 여러개의 caller로 나왔는지 요구한다.
- MetaSV는 union만을 가져오고, caller overlap을 요구하지 않는다
- SVmerge와 MetaSV는 call을 local reassembly로 검증을 하고, MetaSV는 resolution이 더 높은 signature를 우선시한다.
- Parliament2 allows users to decide on a combination of six short-read algorithms before merging calls with SURVIVOR and genotyping with SVTyper.
- 이렇게 연구자들은 이제 Ensemble 알고리즘으로 단순한 overlap을 넘어 세밀하게 설정을 해 precision을 높이고자 한다 (이 중, 실제 truth set을 만들어서 이에 바탕으로 진행을 많이 함)
2-1. Population-scale SV detection
- Ensemble algorithm 방법으로 진행한 population study에서 SV chracterization이 활발하게 진행되었음
- 1000 Genomes Project (1KGP) 에서는 19개의 algorithm을 사용해, 총 51개의 SV hotspot을 찾아 내었고, phase 3에서는 총 2,504명의 샘플에 대한 분석을 완료해, 가장 comprehensive하고 diverse한 reference set을 생성한 것으로 알려져 있다. 그러나 coverage가 낮은 (~6-7x) 시퀀싱으로 진행을 해서, rare variants를 찾기에는 어려움이 있었다.
- 이를 시작으로, 이제 점점 더 큰 규모의 study들이 진행이 되면서 SV에 대한 데이터는 많이 축적되고 있다.
2-2. Limitations
- 워낙 다양한 algorithm을 쓰다보니, 프로젝트마다 사용한 coverage가 굉장히 들쑥날쑥 (3x ~ 90x)하기 때문에 ad hoc/heuristic 하게 필터링을 하면서 결과에 대한 sensitivity나 결과 자체에 영향을 많이 준다.
- 그리고 어떤 알고리즘을 쓰는지, test로 사용하는 benchmark call을 어떤걸 쓰는지, 필터는 어떻게 하는지에 따라 성능이 천지차이다.
- 앞서 말한 Stand-alone ensemble 툴들은 simple overlap 만들 고려하기 때문에 굉장히 immature하고, 이 중에서도 벤치마킹할 수 있는 데이터셋이 없어 통합하기가 쉽지 않다.
- 이래서, ensemble algorithm 영역에서도 다 통용될 수 있는 벤치마크 데이터와 방법론이 생기는 것이 매우 중요할 것
2-Vocab. Ensemble algorithms 용어
- SV caller: algorithm designed to detect SV. Each putative SV detected by a caller is an individual ‘call’
- Ensemble algorithm: A detection method that combines the resulting call sets from multiple independent algorithms
- Coordinate overlap: Number of base pairs that are identical between two different variant calls
3. Emerging genomic technologies
- Short read의 한계를 넘기 위해 새로운 기술들이 많이 등장함.
3-1. Connected-molecule strategies:
- Long-insert short-read libraries와 비슷하다. Sequence coverage와 high physical coverage에 대한 trade-off를 조절하며 크고 작은 변이들을 추출한다.
Linked reads
- Pooled-clone sequencing과 Illumina의 synthetic long reads와 같이, short-read sequences들로 long-range information을 유추하는 방식이다.
- 현재는 10x Genomics Linked-Reads (LR) 플랫폼이 가장 많이 쓰이는 synthetic long-read platform이다.
- Short-read sequencing을 진행하기 전에, short-read fragment 앞에 partition/barcode를 넣어서, 바코드 정보를 토대로 long-range information을 쌓을 수 있는 방식 (10x Genomics 설명 링크: 링크)
- 같은 가격으로 physical coverage를 높일 수 있다보니 SV를 발견하는데 도움이 되고, haplotype phasing에도 도움이 많이 된다.
- Detection methods (Long Ranger, GROC-SVs) 즉, SV를 탐지하는 방법들은 read cloud를 주로 사용하는데, 이 read cloud는 short read의 cluster라고 생각하면 된다. Read cloud는 두 가지를 고려한다: density of overlapping barcodes (바코드가 확 많아지거나, 확 줄으면 breakpoint를 유추할 수 있기 때문), 그리고 distant genomic loci that share more barcode overlap.
- 장점: 바코딩으로 인해 큰 SV에 대해서도 visual interpretation이 효과적.
- Single-molecule approach와 비교했을 때 비슷한 양의 deletion 검출, 하지만 insertion에 대해서는 결과에 대한 차이가 있음. 여기에 대한 이유는: linked reads는 coverage drawback이 있기 때문이다. Read cloud에 있는 그 어느 molecule도 DNA fragment의 complete coverage가 없기 때문에 read pair 간의 gap이 많아서 repetitive region이나 insertion에서 mapping 성능이 매우 떨어질 것이다.
Strand-seq
- Strand-seq independently sequences template DNA strands by incorporating bromodeoxyuridine into the non-template strand during replication.
- As libraries only contain independent parental strands, Strand-seq is especially suited for haplotype phasing. The inherent directionality enables highly efficient detection of inversions.
- 완벽히 이해한건 모르겠지만, BRdU가 parent strand에 붙게 되면서 다른 strand는 directionality가 보장되는 형태로 만들어진다. 이게 SV detection에서는 inversion을 효과적으로 잡을 수 있게 되고, 다른 SV 종류는 read depth로 탐지가 가능해진다.
- 단점으로는 enzymatic clean-up step이 많아서, 결과적으로 sequence coverage를 굉장히 낮추기 때문에 작은 SV를 찾기 힘들다..
Hi-C
- Hi-C는 crosslinked chromatin을 시퀀싱함으로서 3D 공간에서 proximity를 볼 수 있는 방법이다.
- Hi-C read pair는 megabase 단위로도 설정이 가능하기 때문에 large SV 포착 가능
- 하지만 linear genome 상에서 몇 kb가 떨어져 있어서 resolution 자체에 한계가 있다 + coverage도 낮음
- Interactions between proximal loci are shown in the diagonal, diagonal에서 떨어져 있으면 long-range interactions.
- 3D 구조로 SV를 탐지하고 설명하는 것은 아직 많은 연구가 필요하기 때문에, Hi-C의 결과를 reliable하게 사용하려면 아직 멀었다
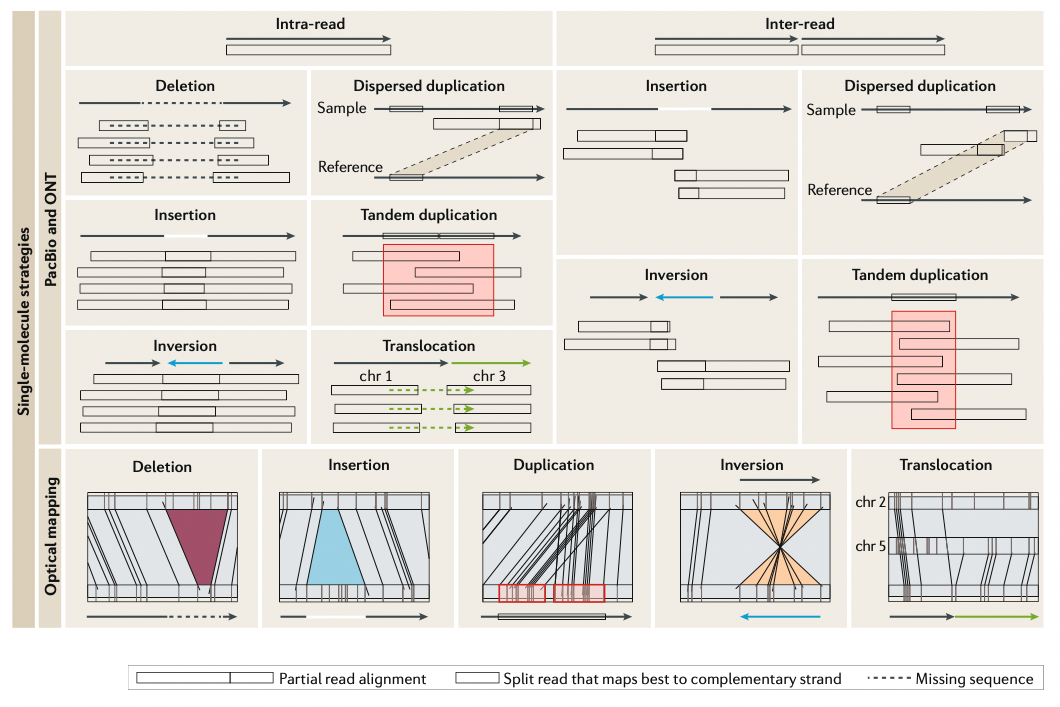
3-2. Single-molecule strategies
Single-molecule real-time sequencing (SMRT)
- PacBio’s SMRT sequencing leverages a stationary polymerase attached to the bottom of a nano-sized well and passages single DNA strands through the enzyme to produce long reads that significantly improve unambiguous mappability across the genome.
- SMRT 데이터로 SV를 찾기 위한 알고리즘들은 intra-read와 inter-read signature를 사용한다.
- Intra-read signature는 SV를 직접적으로 찾을 수 있다 (missing sequence = deletion, soft-clip = insertion).
- Inter-read는 여러개의 read를 사용하며, orientation, location, size의 불일치를 토대로 SV를 찾는다
- Signature를 포착한 후에, caller들은 비슷한 signature들끼리 뭉쳐서 SV를 찾는다. (Caller 예시: CORGi, PBHoney, pbsv, Sniffles, SMRT-SV, SVIM 등등)
- 아직까지는 비싼 가격, input으로 요구하는 많은 양의 DNA 때문에 short-read study보다는 적은 수의 genome에서 실행이 됐었다.
- 비록 base-calling error rate가 short-read 방법보다는 높지만, 이는 coverage를 높이거나, circular consensus sequencing을 사용하면 나아짐. SMRT coverage를 높이면 더 정확해지지만, enzyme degradation으로 인해 read length가 줄어든다 - 그래서 그 trade-off threshold를 잘 정해야함.
- (...더 많은 내용) 정리 하자면, long-read technology는 예전에 찾지 못했던 SV들을 대량으로 검출하고 있음
Nanopore sequencing
- Nanopore sequencing 기반 SV 탐지 알고리즘은 아직 시작된지 별로 안 됐지만, ONT (Oxford Nanopore Technology) Sequencing을 통해 점점 접근성이 좋아지고 있다.
- Nanopore Sequencing은 single-stranded DNA가 protein pore를 통과하면서 고유의 base간의 전류 차이로 DNA sequence를 인식하는 방식이다.
- Nanopore Sequencing도 single-molecule sequencing을 기반으로 하기 때문에 signature는 PacBio 데이터와 굉장히 유사하다.
- 대표적인 caller로는 NanoSV, Picky, Sniffle, SVIM. 하지만 뒤의 3개는 PacBio 데이터에서도 calling이 가능하다.
- PacBio와 비교했을 때 Nanopore에서만 발견되는 small deletion이 굉장히 많다. 하지만 이 small deletion들은 repeat region과 base-calling error에서 일어나는 것을 보아 small SV를 탐지하는데 굉장히 취약하다.
- ONT는 improved read length, lower adaption cost, higher throughput의 장점이 있지만, 위에서 말한대로 error rate가 너무 높아 specificity가 낮은 (특히 small SV에서) 약점이 있다.
Optical mapping
- Sequencing 기반 기술의 대안으로, Optical mapping은 single DNA strand에 nicking endonuclease를 마킹을 하면서 genome map이라는 physical map을 생성한다. 그리고 그 찍힌 map을 관찰하며 SV를 탐지한다
- Restriction enzyme site에 의존도가 있어서, sequence 자체를 만들지 못하고, 고로 base-pair resolution이 없는 대신 breakpoint estimation만 가능하다.
- 그래서 대부분 optical mapping은 큰 SV를 genome map으로 찾고, 작은 SV들은 short-read sequencing을 이용
- 에러가 굉장히 많고 해상도도 좋지는 않지만, amplification-free하고 HTS보다 훨씬 싸다 (60x coverage)에서도, 그래서 대규모 코호트 스터디에서는 경제적인 선택이 된다.
3-3. Multiplatform discovery
- 그 어느 기술도 깊고 넓은 종류의 SV를 잡을 수 없기에, 여러 플랫폼을 합쳐서 사용하는 방법도 등장을 한다.
- Short reads는 base-calling accuracy 가 좋기 때문에 long read들의 error를 잡는 역할을 하고 (“polishing”이라고 한다), 그리고 좀 더 최신 기술들은 좀 더 규모가 크고 복잡한 구조들은 잡는데 사용.
- 여기에 대한 실용적인 예로: Short-read sequencing으로 coverage를 높게 잡고 (>30x) + single-molecule sequencing으로는 coverage를 낮게 잡아서 (~10x), 경제적이면서 sensitivity를 높이는 선택을 할 수 있다.
- 그래서 각자 요구에 맞게 구성을 하면 된다.
- Genome assembly도 여러 개의 플랫폼을 합쳐서 사용하기도 함 (hybrid assembly)
- 여러 기술을 통합하는 Ensemble algorithm 방식이랑 똑같다.
3-Vocab. Emerging genomic technologies 용어
- Connected-molecule strategies: Genomic methods that connect shorter reads of a DNA molecule together
- Sequence coverage: The avg. number of times a given locus is covered by a sequence read
- Physical coverage: The avg. number of times a given locus is covered by the cumulative length of the reads, including unsequenced inserts.
- Base-calling error: Errors in determining the respective nucleotide from raw signals during sequencing
- Circular consensus sequencing : SMRT sequencing method that improves accuracy through multiples passes of template molecule
- Hybrid Assembly : Genome assembly that leverages sequencing data from multiple platforms to reconstruct the original sequence
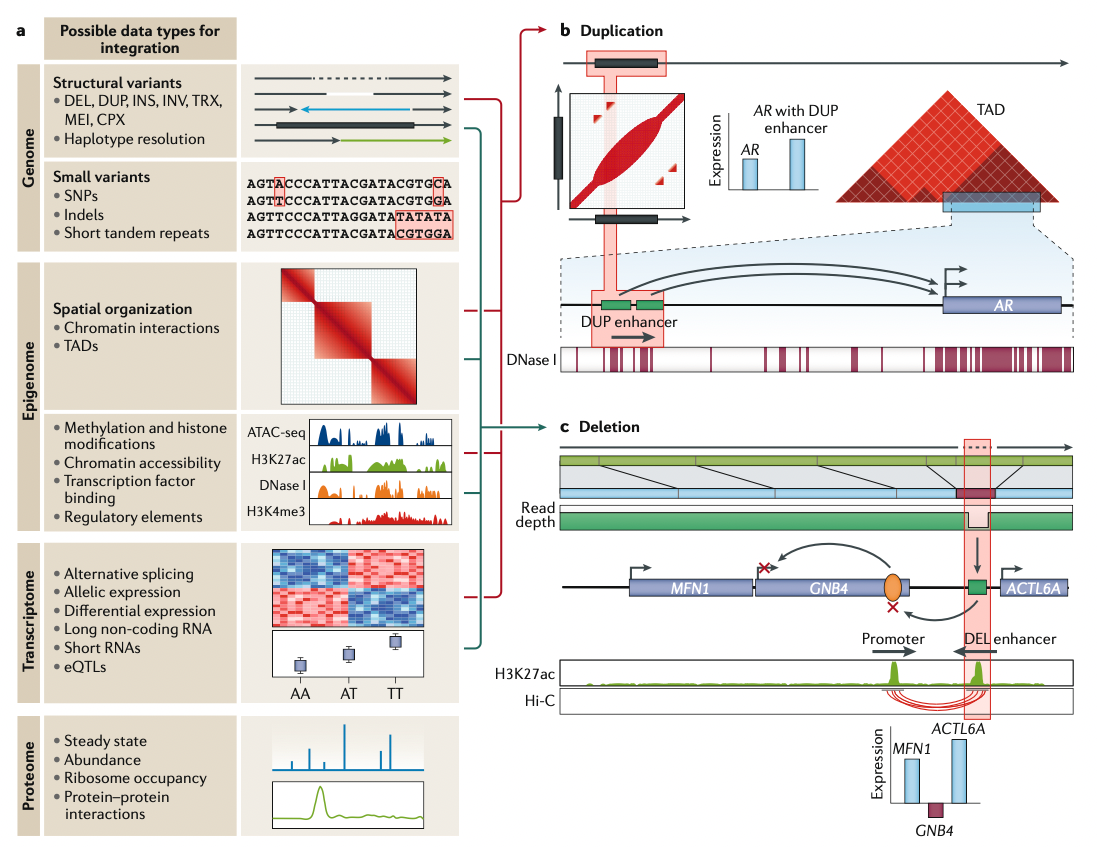
4. Integrating SVs with biological information
- 기술적인 발전에도 불구하고 아직은 이 변이들의 functional consequence가 어떻게 되는지에 대한 해석이 불가능하다
- 이제는 gene expression, epigenetics, 3D genome structure와 같은 정보로 변이 해석 시도가 시작되고 있음
- -최근 연구들에 의하면 SV의 gene expression 영향이 SNV/indel에 비해 53배까지 컸다는 것도 밝혔고 SV의 functionally 큰 영향을 보여준다.
- 좀 더 holistically하게 이해를 하려면 여러 biological context에서의 데이터를 응용하면 functional effect 해석이 가능해진다
5. Conclusions
- 기술의 발전과 방법론의 발전으로 인해 SV에 대한 지식도 넓어졌다.
- 이제는 Human genome에 약 >20,000개의 SV가 있는 것으로 추정이 되고 (대부분이 short read로는 포착할 수 없었던 영역이라 더 의미가 있다)
- Detection 자체도 매우 중요하지만, 이 SV들이 어떤 영향을 (functional effect) 줄지에 대한 방법도 매우 중요하다. 그렇기 때문에 이 interpretation에 대한 발전도 동시에 이루어져야 한다.
