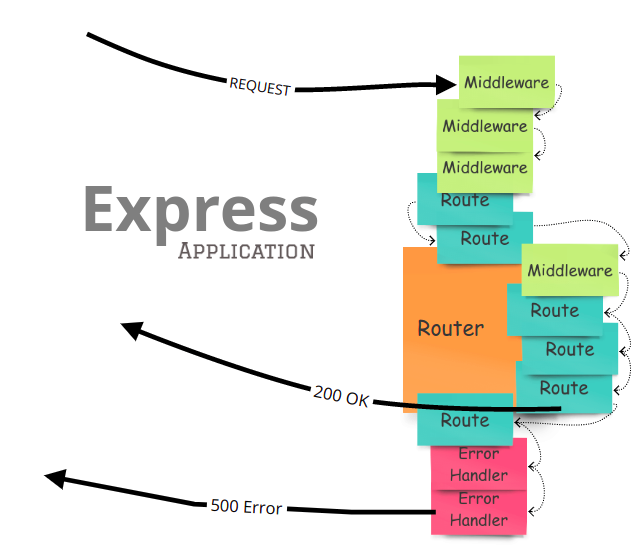
라우팅
라우팅은 해당 uri 의 클라이언트 요청에 알맞은 응답을 묶어주는 작업을 말한다.
그동안 nodejs 에서는 routing 시 pathname 설정, content-type 지정, end 설정 등을 반복해야했다면 express 에서는 app.method(path, handler) 로 라우팅 작업을 단순화 시켰다.
// node.js ... /////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
// pathname 작업
if (pathname === '/') {
// content-type 설정
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-type': 'text/html' });
res.end('<h1>hello-world<h1>');
}
server.listen(8000, '127.0.0.1', () => {
console.log('Listening to requests on port 8000');
});
// express.js ... /////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
const express = require('express')
const app = express() // = require('http').createServer()
app.get('/', function(req, res) {
res.send('<h1>hello-world<h1>')
})
// content-type, charset, res.status 등을 일일이 작업할 필요가 없다.
app.listen(8000, '127.0.0.1', () => {
console.log('Listening to requests on port 8000');
});
middleware
express 의 모든 method 호출은 비동기 형태로 움직인다. 서버 운영에는 함수 호출 순서가 큰 영향을 차지하는데 middleware 는 제 3의 인자인 next() 를 통해 더욱 쉽게 만들 수 있다.
const express = require("express");
const app = express(); // = require('http').createServer()
function a(req, res, next) {
console.log(1);
next();
}
function b(req, res, next) {
console.log(2);
next();
}
function c(req, res, next) {
console.log(3);
}
function d(req, res, next) {
console.log(4);
}
app.use("/", a, b, c, d);
// 호출 시에 console에 1,2,3,4가 호출되게 했다.
// c의 경우 next를 사용하지 않았기에 3 까지만 호출이 된다.
app.listen(8000, "127.0.0.1", () => {
console.log("Listening to requests on port 8000");
});middleware 의 가장 큰 장점은 오류의 확인 및 해결이 매우 빨라진다는 것이다. 각 호출 함수에 대해 error-handling 이 명확하게 되어있다면 해당 path 값 안의 어떤 함수에서 문제가 발생했는지 금방 찾을 수 있다.
또한 사용자의 인증 정보나 서드파티 미들웨어 라이브러리를 통해 client 요청을 통한 payload 나 cors 정보 역시 쉽게 찾을 수 있다.
get, post, put, patch, delete
서버 영역에서 가장 자주 사용되는 http request method로 각각의 역할을 나누면 이렇게 표현할 수 있다.
- Creating= post
- Reading = get
- Updating = put, patch
- Deleting = delete
여기서 중요한 점은put 과 patch 의 차이점인데, patch 는 기존 데이터의 부분적 수정을 의마한다면, put은 기존의 데이터를 새로운 데이터로 완전히 덮어씀을 의미한다. 따라서 데이터 손상을 없애기 위해서는 상황에 따라 알맞은 method를 사용해야한다.
{nama: 'beberiche' , age: 30, job: 'developer', hobbies: ['driving', 'game'] }
// 만약 직업을 수정하게 된다면...
// put 설정 시
{job: 'teacher'}
// patch 설정 시
{nama: 'beberiche' , age: 30, job: 'teacher', hobbies: ['driving', 'game'] }