유튜브에 React 까보기 시리즈 라는 영상으로 스터디를 진행하며 의미있는 강의는 자주 정리해 보려고 합니다.
강의를 찍으신 시점과 제가 학습하는 시점에 차이가 발생해 React 라이브러리의 코드가 다소 변화되었습니다. 이 글을 읽는 시점에도 코드가 다를 수 있음을 알려 드립니다.
어떻게 useState를 export 하는가
//react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
//159번줄
const {ReactCurrentDispatcher, ReactCurrentBatchConfig} = ReactSharedInternals;- 먼저 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current에 할당을 해야함
- 이 할당은
renderWithHooks함수에서 조건에 따라HooksDispatcherOnMount와HooksDispatcherOnUpdate이 결정된다.
//react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
//476번줄
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
...
if (__DEV__) {
if (current !== null && current.memoizedState !== null) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV;
} else if (hookTypesDev !== null) {
// This dispatcher handles an edge case where a component is updating,
// but no stateful hooks have been used.
// We want to match the production code behavior (which will use HooksDispatcherOnMount),
// but with the extra DEV validation to ensure hooks ordering hasn't changed.
// This dispatcher does that.
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnMountWithHookTypesInDEV;
} else {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnMountInDEV;
}
} else {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
}current === null || current.memoizedState === null이 된다면 Mount 해야하며, 아닐경우 Update 일경우로 생각- 강의랑 다름 강의에선 nextCurrentHook으로 나옴 → 결국 Mount 하냐 Update 하냐의 결정은 current가 Dom에 반영 여부로 확인
그럼 HooksDispatcherOnMount 안에 뭐가 있나?
- useState 가 안에 존재
//react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
//3470번줄
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
use,
useCallback: mountCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: mountEffect,
useImperativeHandle: mountImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: mountLayoutEffect,
useInsertionEffect: mountInsertionEffect,
useMemo: mountMemo,
useReducer: mountReducer,
useRef: mountRef,
useState: mountState,
useDebugValue: mountDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: mountDeferredValue,
useTransition: mountTransition,
useSyncExternalStore: mountSyncExternalStore,
useId: mountId,
};
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
use,
useCallback: updateCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: updateEffect,
useImperativeHandle: updateImperativeHandle,
useInsertionEffect: updateInsertionEffect,
useLayoutEffect: updateLayoutEffect,
useMemo: updateMemo,
useReducer: updateReducer,
useRef: updateRef,
useState: updateState,
useDebugValue: updateDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: updateDeferredValue,
useTransition: updateTransition,
useSyncExternalStore: updateSyncExternalStore,
useId: updateId,
};- Update 함수에는 updateState가 들어간다.
renderWithHooks
- renderWithHooks() → hook과 함께 render 즉, hook을 주입하는 역할을 한다
//react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
//476번줄
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber ... ): any {
renderLanes = nextRenderLanes;
**currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress; <- 이 코드가 핵심**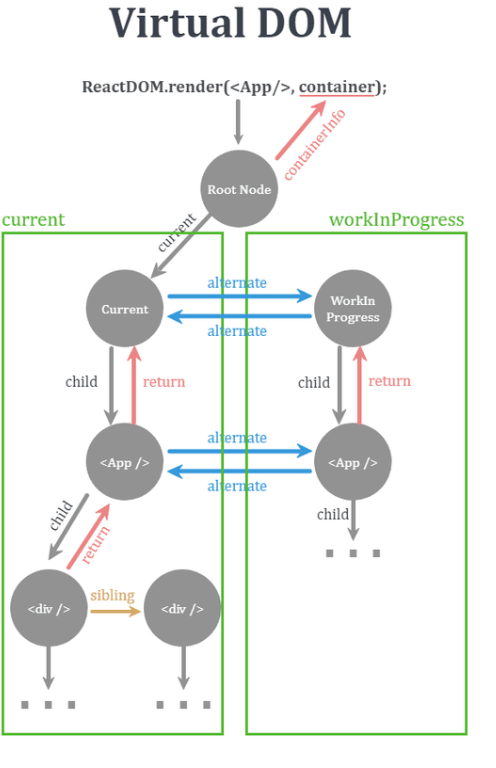
- 이 사진에서 WorkInProgress 작업물을 Current에 주입하는 역할
NextcurrentHook
- 강의의 코드와 다른점 존재. nextCurrentHook은 더이상 renderWithHooks에서 사용하지 않고
updateWorkInProgressHook함수에서 사용 - 이에 따라 돔에 반영되어있는지 아닌지 확인하는 조건은
=== null || current.memoizedState === null로 대체된다. - 이 memoizedState는 Hook이 들어있음을 추측
- renderWithHooks의 다른 역할은 컴포넌트를 호출한다.
// 572번
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// **업데이트 정보를 스케쥴러와 패키지에게 전달 했음?을 확인 -> Mount 일경우는 false**
if (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass) {
// Keep rendering until the component stabilizes (there are no more render
// phase updates).
children = renderWithHooksAgain(
workInProgress,
Component,
props,
secondArg,
);
}// 607번
function finishRenderingHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
): void {
// **이것을 왜?**
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
const didRenderTooFewHooks =
currentHook !== null && currentHook.next !== null;
renderLanes = NoLanes;
currentlyRenderingFiber = (null: any);
currentHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;이 코드가 의미하는 것은 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current를 재할당 하는 것이 아니라 위에서 컴포넌트를 호출한 뒤 더 이상 Hook을 요청해서는 안될때 Error를 알려주기 위함을 의미
//3432번줄
export const ContextOnlyDispatcher: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
use,
useCallback: throwInvalidHookError,
useContext: throwInvalidHookError,
useEffect: throwInvalidHookError,
useImperativeHandle: throwInvalidHookError,
useInsertionEffect: throwInvalidHookError,
useLayoutEffect: throwInvalidHookError,
useMemo: throwInvalidHookError,
useReducer: throwInvalidHookError,
useRef: throwInvalidHookError,
useState: throwInvalidHookError,
useDebugValue: throwInvalidHookError,
useDeferredValue: throwInvalidHookError,
useTransition: throwInvalidHookError,
useSyncExternalStore: throwInvalidHookError,
useId: throwInvalidHookError,
};
function throwInvalidHookError() {
throw new Error(
'Invalid hook call. Hooks can only be called inside of the body of a function component. This could happen for' +
' one of the following reasons:\n' +
'1. You might have mismatching versions of React and the renderer (such as React DOM)\n' +
'2. You might be breaking the Rules of Hooks\n' +
'3. You might have more than one copy of React in the same app\n' +
'See https://react.dev/link/invalid-hook-call for tips about how to debug and fix this problem.',
);
}- 이 코드를 보면 useState에 Error를 던지는 것을 할 수 있음
// 926번줄
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
- 이 코드는 memoizedState에 hook이 대입되는 것을 알 수 있음
- 이 코드는 Mount State 에서 불린다.
// 1750번
function mountStateImpl<S>(initialState: (() => S) | S): Hook {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
const initialStateInitializer = initialState;
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use]: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialState = initialStateInitializer();
if (shouldDoubleInvokeUserFnsInHooksDEV) {
setIsStrictModeForDevtools(true);
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use]: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialStateInitializer();
setIsStrictModeForDevtools(false);
}
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, BasicStateAction<S>> = {
pending: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
return hook;
}
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const hook = mountStateImpl(initialState);
const queue = hook.queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>> = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any);
queue.dispatch = dispatch;
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}- Reconciler는 Fiber에 Hook 정보를 담아주는 역할을 한다.
///607 번줄
function finishRenderingHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
): void {
if (__DEV__) {
workInProgress._debugHookTypes = hookTypesDev;
}
// We can assume the previous dispatcher is always this one, since we set it
// at the beginning of the render phase and there's no re-entrance.
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
// This check uses currentHook so that it works the same in DEV and prod bundles.
// hookTypesDev could catch more cases (e.g. context) but only in DEV bundles.
const didRenderTooFewHooks =
currentHook !== null && currentHook.next !== null;
renderLanes = NoLanes;
currentlyRenderingFiber = (null: any);
currentHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;- 이곳에서 null로 초기화를 하는 이유는 이 Hook들은 전역으로 사용하고 있기 때문에 다른 컴포넌트들도 사용될 수 있어 초기화를 진행
