1005 ACM Craft
문제
- 각 건물에는 소요되는 시간이 존재하고 건물 건설에는 규칙이있다. 이 때 특정 건물을 지으면 이긴다고 한다. 이기기 위해서 특정 건물을 짓기 위해 소요되는 최소 시간 구하기
입력
- 테스트 케이스의 개수 T와 건물의 개수 N, 각 건물을 짓기전 지어야 하는 건물 규칙의 개수 K가 주어진다.
- 그 다음줄에는 각 건물의 건설시간이 주어진다.
- 건물 규칙이 K개의 줄에 걸쳐 주어지고 마지막에 특정 건물의 번호가 주어진다.
출력
- 각테스트 케이스마다 특정 건물을 짓기 위해 필요한 최소한의 시간을 출력
처음에 문제를 풀 때 거리를 구하고 그래프를 탐색하며 가중치가 있기에 다익스트라로 최장 거리를 구하는 알고리즘을 짜봤다.
int sol(int n) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>>pq; // 최대힙
pq.push(make_pair(0, key));
while (!pq.empty()) {
int d = pq.top().first;
int p = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
for (auto i : links[p]) {
int dc = weight[i]+d;
int pc = i;
if (dist[i] < dc) {
dist[i] = dc;
pq.push(make_pair(dc, pc));
}
}
}
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
maxi = max(dist[i], maxi);
}
return maxi+weight[key];
}하지만 다익스트라는 최장거리를 구할 때는 O(ElogV)가 유지되지 않는다고 한다.

그래서 DFS를 이용해보기로 했다. 각 건물에 대하여 필요한 건물들이 트리 형태를 띄고 있으므로 각 가중치를 제일 첫건물부터 끌어올릴 필요가 있다 생각했기 때문이다.
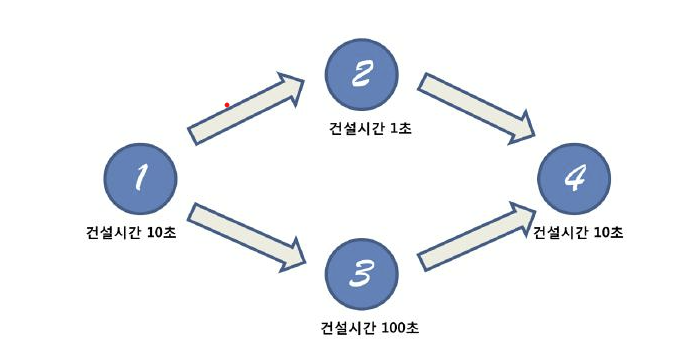
이 예제에서
- 4번 건물을 지어야 한다고 하면 4번과 연결돼 있는 2번과 3번을 탐색한다.
- 2번과 연결돼 있는 1번을 탐색한다.
- 1번은 연결돼 있는 것이 없으므로 가중치 +10을 반환
- 2번의 가중치는 11이 돼고 같은 과정을 거쳐 3은 110이 됀다.
- 2번과 3번의 가중치중 더 큰것은 3번이므로 결과적으로 4번의 총 가중치는 120이 되므로 120을 리턴해준다.
정답 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int>needs[1001];
int weight[1001];
bool visit[1001];
int key;
void set0() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {
needs[i].clear();
visit[i] = 0;
}
}
void input(int m) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
needs[b].push_back(a);
}
cin >> key;
}
void sol(int i) {
int maxi = 0;
for (auto p : needs[i]) {
if (!visit[p]) {
sol(p);
visit[p] = 1;
}
maxi = max(weight[p], maxi);
}
weight[i] += maxi;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int p = 0; p < t; p++) {
set0();
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> weight[i];
input(m);
sol(key);
cout << weight[key] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}