🌞Spring
💻Spring 폴더 기본 세팅
-
C폴더 안에 spring 폴더를 만들고 Lec폴더를 만든다.
java tool에 있는 sts.zip을 복사한 후 압축 풀기
압축 풀 때 경고창이 뜨면 건너뛰기함

-
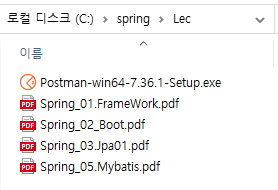
Lec 폴더안에 다음과 같은 파일을 복붙한다.
-
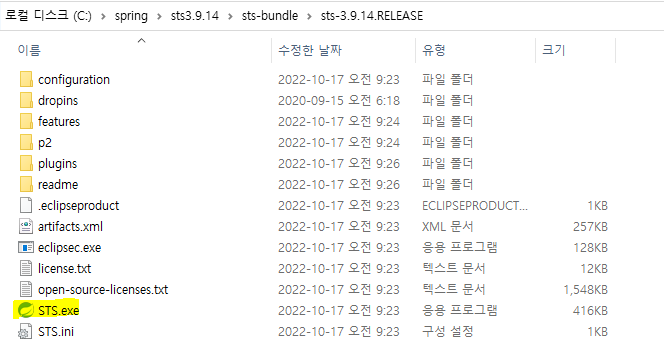
압축 푼 폴더 안에 sts 오른쪽 마우스-보내기-바탕화면에 바로가기 만든 후 이름을 STS로 변경
-
spring 폴더 안에 springSrc 폴더 생성
-
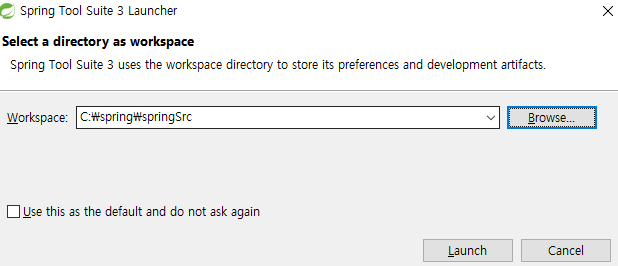
spring workspace 변경
-
서버를 탐캣을 맞추기 위해 기존 서버를 delete함
-
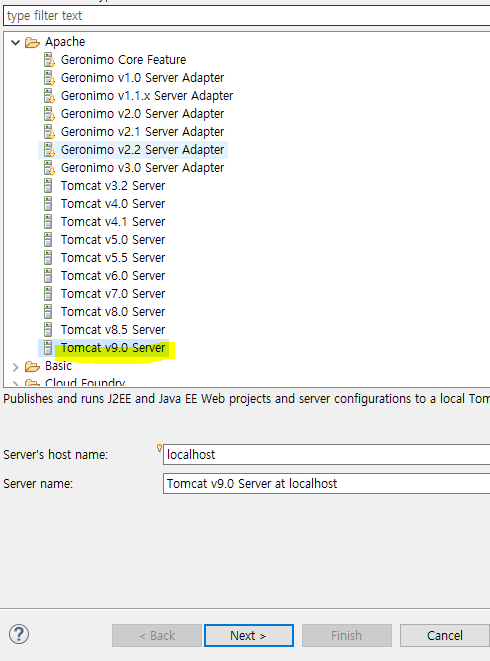
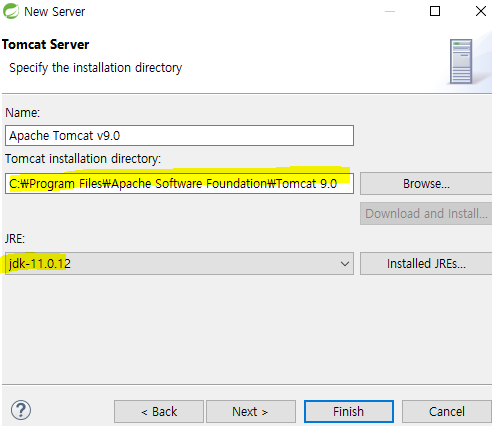
탐캣 서버 세팅
-
windows - web Browser - Chrome
-
windows - preference - workspace / web-css, html, jsp utf-8로 모두 변경+apply
💡 Spring 프레임워크
- 대표적 오픈소스기반의 어플리케이션 프레임 워크 - 스프링의 대표적인 프레임워크
- Spring MVC+ORM(DI 스프링의 기본)
💻IOC-DI 세팅
-
file - new - Maven project - 첫번째 체크박스 선택
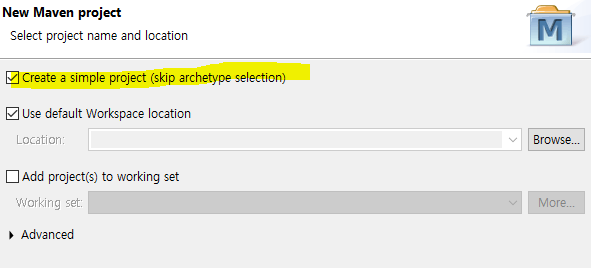
-
Maven project Setting
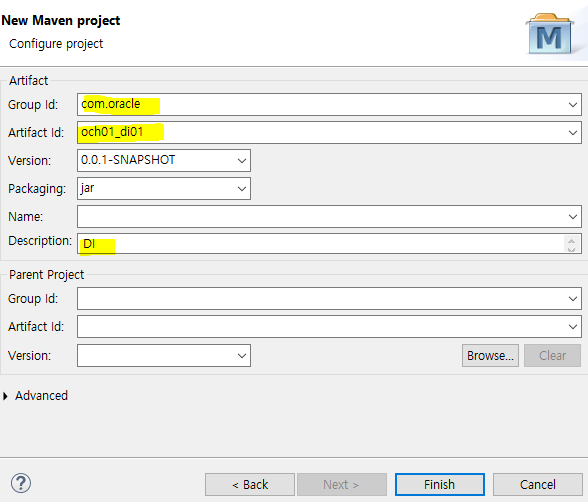
-
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>och01_di01</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<description>DI</description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- pom.xml에 dependencies을 적어주면 관련된 모듈이
Maven Dependecies와 연결되어 자동으로 다운로드 받아 들어감
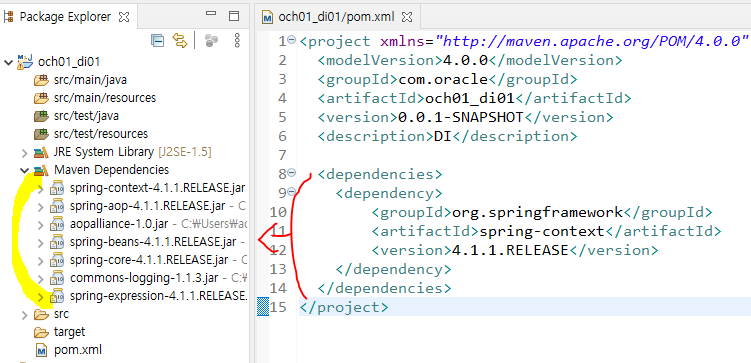
- java에 패키지 3개를 만듦(sam01, sam02, sam03)
🔻och01_di01
[sam01 - Message1]
- MessageBeanEn.java
package sam01;
public class MessageBeanEn {
void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+" Hello");
}
}- MessageBeanKo.java
package sam01;
public class MessageBeanKo {
void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+" 안녕");
}
}- Ex01.java(실행파일)
package sam01;
public class Ex01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MessageBeanEn mb = new MessageBeanEn();
MessageBeanKo mb = new MessageBeanKo();
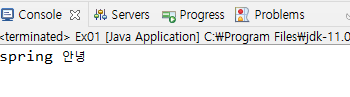
mb.sayHello("spring");
}
}
[sam02 - Message2/interface]
- MessageBean.java-interface
package sam02;
public interface MessageBean {
void sayHello(String name);
}- MessageBeanEn.java
package sam02;
public class MessageBeanEn implements MessageBean {
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+"! Hello");
}
}- MessageBeanKo.java
package sam02;
public class MessageBeanKo implements MessageBean {
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+"! 안녕하세요");
}
}- Ex02.java(실행파일)
package sam02;
public class Ex02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MessageBean mb = new MessageBeanKo();
MessageBean mb = new MessageBeanEn();
mb.sayHello("spring");
}
}[sam03 - Message3]
- MessageBean.java-interface
package sam03;
public interface MessageBean {
void sayHello();
}- MessageBeanImpl.java
package sam03;
public class MessageBeanImpl implements MessageBean {
private String name;
private String greet;
public MessageBeanImpl(String name, String greet) {
this.name = name;
this.greet = greet;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(name+"님!! "+greet);
}
}- Ex03.java(DI 호출 객체)
package sam03;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Ex03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 기존 방식
MessageBean cmb = new MessageBeanImpl("허유나", "전통적 안녕");
cmb.sayHello();
// DI 호출 객체
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean03.xml");
MessageBean mb = (MessageBean) ac.getBean("mb3");
mb.sayHello();
}
}- bean03.xml
의존성을 외부에서 주입하는 방식 DI(dependency Injection)(src/main/resources) -> spring bean configuration file - 파일명 - bean checkbox<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="mb3" class="sam03.MessageBeanImpl">
<constructor-arg><value>홍성대</value></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="DI 메리 크리스마스"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>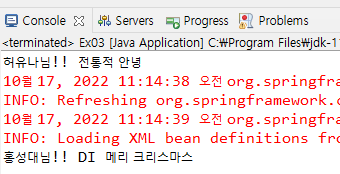
[sam05 - Message5]
- MessageBean.java-interface
package sam05;
public interface MessageBean {
void sayHello();
}- MessageBeanImpl.java(Getter/Setter)
package sam05;
public class MessageBeanImpl implements MessageBean {
private String name;
private String greet;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGreet() {
return greet;
}
public void setGreet(String greet) {
this.greet = greet;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(name+"님 "+greet+" !!");
}
}- Ex05.java(DI 호출 객체)
package sam05;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Ex05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageBeanImpl mb5 = new MessageBeanImpl();
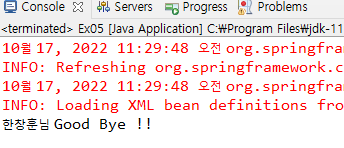
mb5.setGreet("Good Bye");
mb5.setName("한창훈");
mb5.sayHello();
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean05.xml");
MessageBean mb = (MessageBean) ac.getBean("mb5");
mb.sayHello();
}
}- bean05.xml
setter - properties 생성자 - constructor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="mb5" class="sam05.MessageBeanImpl">
<property name="name"><value>한창훈</value></property>
<property name="greet" value="Good Bye"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
[sam06 - vehicle/생성자와 setter 같이 세팅]
- vehicle.java-interface
package sam06;
public interface vehicle {
void ride();
}- VehicleImpl.java
name은 생성자로 가져오고 나머지는 setter만 가져온다
package sam06;
public class VehicleImpl implements vehicle {
private String name;
private String rider;
private int speed;
public VehicleImpl(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setRider(String rider) {
this.rider = rider;
}
public void setSpeed(int speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
public void ride() {
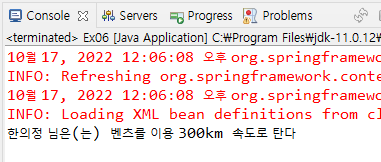
System.out.println(name+" 님은(는) "+rider+"를 이용 "+speed+"km 속도로 탄다");
}
}- Ex06.java(DI 호출 객체)
package sam06;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Ex06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean06.xml");
vehicle vh = (vehicle) ac.getBean("vh6");
vh.ride();
}
}- bean06.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="vh6" class="sam06.VehicleImpl">
<constructor-arg value="한의정"></constructor-arg>
<property name="rider" value="벤츠"></property>
<property name="speed"><value>300</value></property>
</bean>
</beans>
[sam07 - Message5]
- MessageBean.java-interface
package sam07;
public interface MessageBean {
void sayHello();
}- MessageBeanImpl.java
package sam07;
public class MessageBeanImpl implements MessageBean {
private String name;
private String greet;
private Outputter outputter;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setGreet(String greet) {
this.greet = greet;
}
public void setOutputter(Outputter outputter) {
this.outputter = outputter;
}
public void sayHello() {
String msg = name+"님!! "+greet;
System.out.println(msg);
if(outputter!=null) outputter.output(msg);
}
}- Outputter.java-interface
package sam07;
public interface Outputter {
void output(String msg);
}- FileOutputter.java(순서가 가장 마지막으로 감)
package sam07;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutputter implements Outputter {
private String fileName;
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
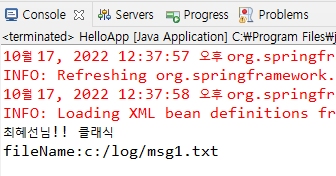
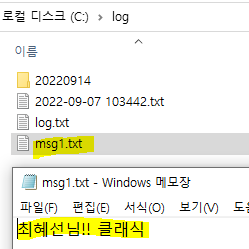
// 최혜선님!! 클래식
public void output(String msg) {
try {
System.out.println("fileName:"+fileName);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File(fileName));
fw.write(msg);
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- HelloApp.java(main)
package sam07;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/sam07/bean07.xml");
MessageBean mb = (MessageBean) ac.getBean("mb7");
mb.sayHello();
}
}
- bean07.xml(sam07 패키지 안에 넣음)
DI 방식으로 넘어갈 때 객체는 주소값을 넘어가야하기 때문에 reference방식으로 선언해줌 참조로 넣었기 때문에 helloApp에 없어도 xml 파일에 outputter이 알아서 호출됨 첫번째 bean의 outputter를 쓰기 위해서 다른 bean에 있는 property name도 outputter로 맞춰줌
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="outputter" class="sam07.FileOutputter">
<property name="fileName" value="c:/log/msg1.txt"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="mb7" class="sam07.MessageBeanImpl">
<property name="name" value="최혜선"></property>
<property name="greet"><value>클래식</value></property>
<property name="outputter"><ref bean="outputter"></ref></property>
</bean>
</beans>
💡 IOC / DI
IOC(Inversion of Control)
역순으로 객체를 생성
기존의 프로그래밍에서 객체의 생성, 제어, 소멸 등의 객체의 라이프 사이클을 개발자가 관리하던 것을 컨테이터에게 그 제어권을 위임하는 프로그래밍 기법
DI(Dependecy Injection)
의존성 검색, 저장소에 저장되어 있는 빈(Bean)에 접근하기 위하여 개발자들이 컨테이너에서 제공하는 API를 이용하여 사용하고자 하는 빈(Bean)을 Lookup하는 것
부품을 조립해준다.
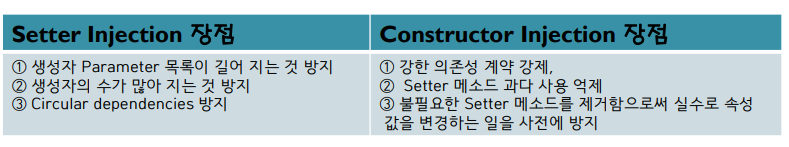
- Setter Inject과 Constructor Injection의 장점
🔻och03_di03
[DI01 - Calculator]
- Calculator.java
package DI01;
public class Calculator {
public void addition(int f, int s) {
System.out.println("addition()");
int result = f + s;
System.out.println(f + "+" + s + "=" +result);
}
public void subtraction(int f, int s) {
System.out.println("subtraction()");
int result = f - s;
System.out.println(f + "-" + s + "=" +result);
}
public void multiplication(int f, int s) {
System.out.println("multiplication()");
int result = f * s;
System.out.println(f + "*" + s + "=" +result);
}
public void division(int f, int s) {
System.out.println("division()");
int result = f / s;
System.out.println(f + "/" + s + "=" +result);
}
}
- MyCalculator.java
package DI01;
public class MyCalculator {
Calculator calculator;
private int firstNum;
private int secondNum;
public MyCalculator() {
}
public void add() {
calculator.addition(firstNum, secondNum);
}
public void sub() {
calculator.subtraction(firstNum, secondNum);
}
public void mul() {
calculator.multiplication(firstNum, secondNum);
}
public void div() {
calculator.division(firstNum, secondNum);
}
public void setCalculator(Calculator calculator) {
this.calculator = calculator;
}
public void setFirstNum(int firstNum) {
this.firstNum = firstNum;
}
public void setSecondNum(int secondNum) {
this.secondNum = secondNum;
}
}- MainClass01.java
porm.xml에 관련 모듈 다운로드 클라스 명이 지정되어 casting을 쓰지 않는다
package DI01;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainClass01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String configLocation = "classpath:applicationCTX01.xml";
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(configLocation);
MyCalculator myCalculator = ctx.getBean("myCalculator", MyCalculator.class);
myCalculator.add();
myCalculator.sub();
myCalculator.mul();
myCalculator.div();
// 기존 방식
System.out.println("===========myCalculator03============");
MyCalculator myCalculator03 = new MyCalculator();
// Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
// myCalculator03.setCalculator(calculator);
myCalculator03.setCalculator(new Calculator());
myCalculator03.setFirstNum(20);
myCalculator03.setSecondNum(2);
myCalculator03.add();
myCalculator03.sub();
myCalculator03.mul();
myCalculator03.div();
}
}- applicationCTX01.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="calculator" class="DI01.Calculator"></bean>
<bean id="myCalculator" class="DI01.MyCalculator">
<property name="calculator"><ref bean="calculator"></ref></property>
<property name="firstNum" value="20"></property>
<property name="secondNum" value="2"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
[DI02 - BMICalculator]
- BMICalculator.java
package DI02;
public class BMICalculator {
private double lowWeight;
private double normal;
private double overWeight; // 과제충
private double obesity; // 비만
public void bmicalculation(double weight, double height) {
double h = height * 0.01;
double result = weight / (h*h);
System.out.println("BMI 지수 : "+(int)result);
if(result > obesity) {
System.out.println("비만 .");
} else if(result > overWeight) {
System.out.println("과체중 .");
} else if(result > normal) {
System.out.println("정상 .");
} else {
System.out.println("저체중 .");
}
}
public void setLowWeight(double lowWeight) {
this.lowWeight = lowWeight;
}
public void setNormal(double normal) {
this.normal = normal;
}
public void setOverWeight(double overWeight) {
this.overWeight = overWeight;
}
public void setObesity(double obesity) {
this.obesity = obesity;
}
}- MyInfo.java
package DI02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyInfo {
private String name;
private double height;
private double weight;
private ArrayList<String> hobbys;
private BMICalculator bmiCalculator;
public void bmiCalculator() {
bmiCalculator.bmicalculation(weight, height);
}
public void getInfo() {
System.out.println("이름 : "+name);
System.out.println("키 : "+height);
System.out.println("몸무게 : "+weight);
System.out.println("취미 : "+hobbys);
bmiCalculator();
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public void setHobbys(ArrayList<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public void setBmiCalculator(BMICalculator bmiCalculator) {
this.bmiCalculator = bmiCalculator;
}
}- MainClass02.java
package DI02;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainClass02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String configLocation = "classpath:applicationCTX02.xml";
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(configLocation);
MyInfo myInfo = ctx.getBean("myInfo", MyInfo.class);
myInfo.getInfo();
ctx.close();
}
}- applicationCTX02.xml
// list를 넣을 때
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>바둑</value>
<value>낙시</value>
<value>대화</value>
</list><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="bmiCalculator" class="DI02.BMICalculator">
<property name="lowWeight" value="18.5"></property>
<property name="normal" value="23"></property>
<property name="overWeight" value="25"></property>
<property name="obesity" value="30"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myInfo" class="DI02.MyInfo">
<property name="name" value="김춘추"></property>
<property name="height" value="170"></property>
<property name="weight" value="72"></property>
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>말타기</value>
<value>활쏘기</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="bmiCalculator"><ref bean="bmiCalculator"></ref></property>
</bean>
</beans>
💡 POJO 기반
스프링은 다른 프레임워크들과 달리 이 관계를 구성할 때 별도의 API 등을 사용하지 않는 POJO(Plain Old Java Object)의 구성만으로 가능하도록 제작되어 있습니다.
[DI03 - Student]
- Student.java
package DI03;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String gradeNum;
private String classNum;
public Student(String name, int age, String gradeNum, String classNum) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gradeNum = gradeNum;
this.classNum = classNum;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGradeNum() {
return gradeNum;
}
public void setGradeNum(String gradeNum) {
this.gradeNum = gradeNum;
}
public String getClassNum() {
return classNum;
}
public void setClassNum(String classNum) {
this.classNum = classNum;
}
}