
📎 문제링크
1. 시간복잡도
2 ≤ N(정점) ≤ 300,000, 1 ≤ M(간선) ≤ 1,000,000 범위 이므로 BFS로 풀어도 시간복잡도는 충분하다.
그래도 알고리즘 분류가 다익스트라로 되어있으므로 이를 계산해보면,
사실 더 오래걸리는거 같지만 실제 제출결과는
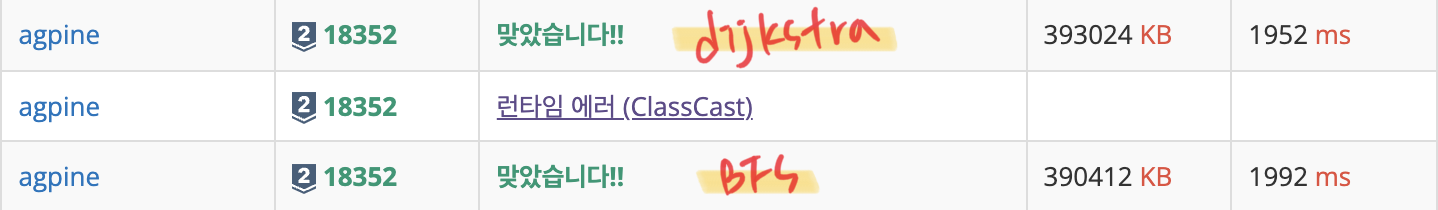
이상하다 🧐 근소한 차이지만, 다익스트라가 빠르다. 원인은 잘 모르겠다. (중간의 런타임 에러에 대한 내용은 2.1 우선순위큐에서 확인해보자.)
💡 BFS와 DFS의 시간복잡도는
인접행렬일때인접리스트일때 로 계산된다.
1.2 다익스트라 (dijkstra)
다익스트라는 양의 가중치가 있을때(음의 가중치가 있으면 사용 불가) 하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로의 최단거리를 구하는 알고리즘이다.
BFS + 가중치라고 생각하면 편할거 같다. 여기서 BFS와의 차이점인 가중치를 고려하기 위해 우선순위큐(PriorityQueue)를 사용한다.
사실 해당 문제에서 가중치는 모두 1로 동일하다. 그래서 BFS로도 문제가 풀리기는 하는거 같다.
2. 풀이
2.1 우선순위큐
다익스트라로 문제를 풀기위해 우선순위큐를 사용했다. 무지성으로 클래스타입만 변경한 결과 런타임 에러가 발생했다.
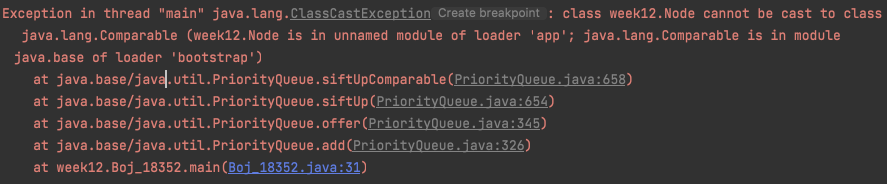
stack trace에서 볼수 있듯이 PriorityQueue 내부에서 객체를 add 할때, siftUpComparable 함수에서 Comparable 로 캐스팅이 안된다는 내용이다.
여기서 Comparable은 public int compareTo(T o); 하나의 추상메서드를 가지고 있는 인터페이스이다.
즉, PriorityQueue 에 들어가는 객체는 반드시 Comparable 인터페이스를 구현한 구현체여야 한다.
PriorityQueue.siftUpComparable
private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = es[parent];
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
es[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
es[k] = key;
}Comparable
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}3. 유사문제
4. 코드
package week12;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Boj_18352 {
static int N, M, K, X;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] line = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
N = line[0];
M = line[1];
K = line[2];
X = line[3];
Map<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> edge = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<Integer> l;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int[] e = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
l = edge.getOrDefault(e[0], new ArrayList<>());
l.add(e[1]);
edge.put(e[0], l);
}
ArrayList<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<>();
// dijkstra
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean[] visit = new boolean[N+1];
q.add(new Node(X, 0));
visit[X] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
if (cur.dis >= K) {
if (cur.dis == K) answer.add(cur.num);
continue;
}
for (int e : edge.getOrDefault(cur.num, new ArrayList<>())) {
if (!visit[e]) {
visit[e] = true;
q.add(new Node(e, cur.dis + 1));
}
}
}
// print
if (answer.size() == 0) System.out.println(-1);
else answer.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int num;
int dis;
public Node(int num, int dis) {
this.num = num;
this.dis = dis;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return dis - o.dis;
}
}