그래프의 표현
1.그래프의 정의/표현
그래프의 개념과 정의
열결되어 있는 원소 사이의 다:다 관계를 표현하는 자료구조이다.
연결할 객체를 나타내는 정점(Vertex)와 객체를 연결하는 간선(Edge)의 집합으로 구성된다.
그래프 G=(V,E)로 나타낸다.
그래프의 종류
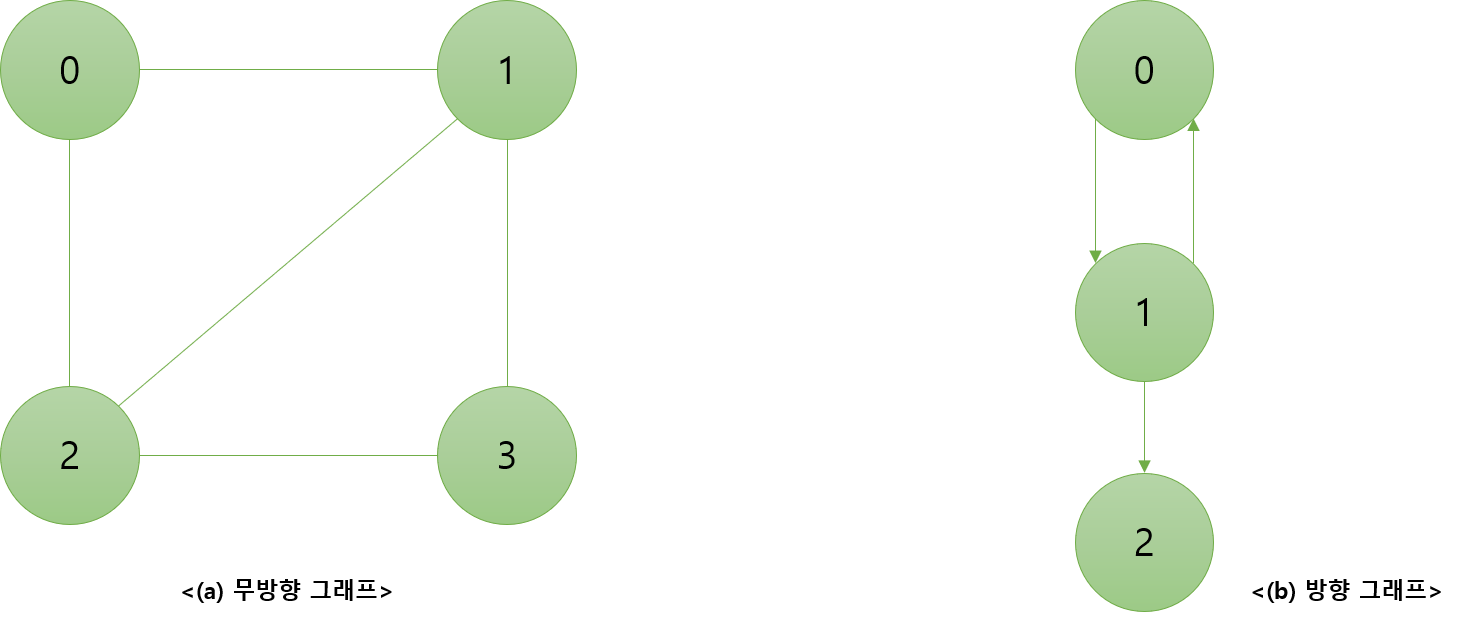
1. 무방향 그래프 : 두 정점을 연결하는 간선에 방향이 없는 그래프
2. 방향 그래프 : 간선에 방향이 있는 그래프로 다이 그래프(Digraph)라고도 한다.
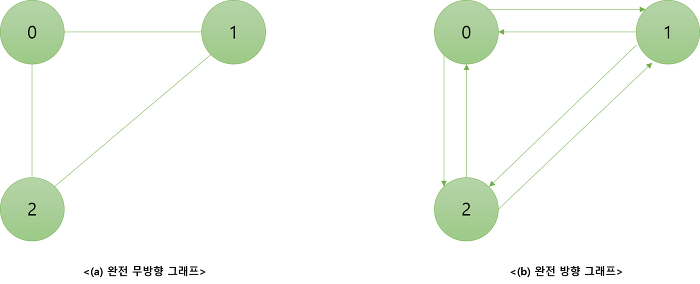
3. 완전 그래프 : 각 정점에서 다른 모든 정점을 연결하여 최대로 많은 간선 수를 가진 그래프
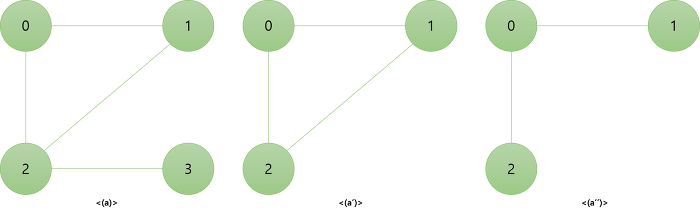
4. 부분 그래프 : 원래 그래프에서 정점이나 간선을 일부만 제외하여 만든 그래프
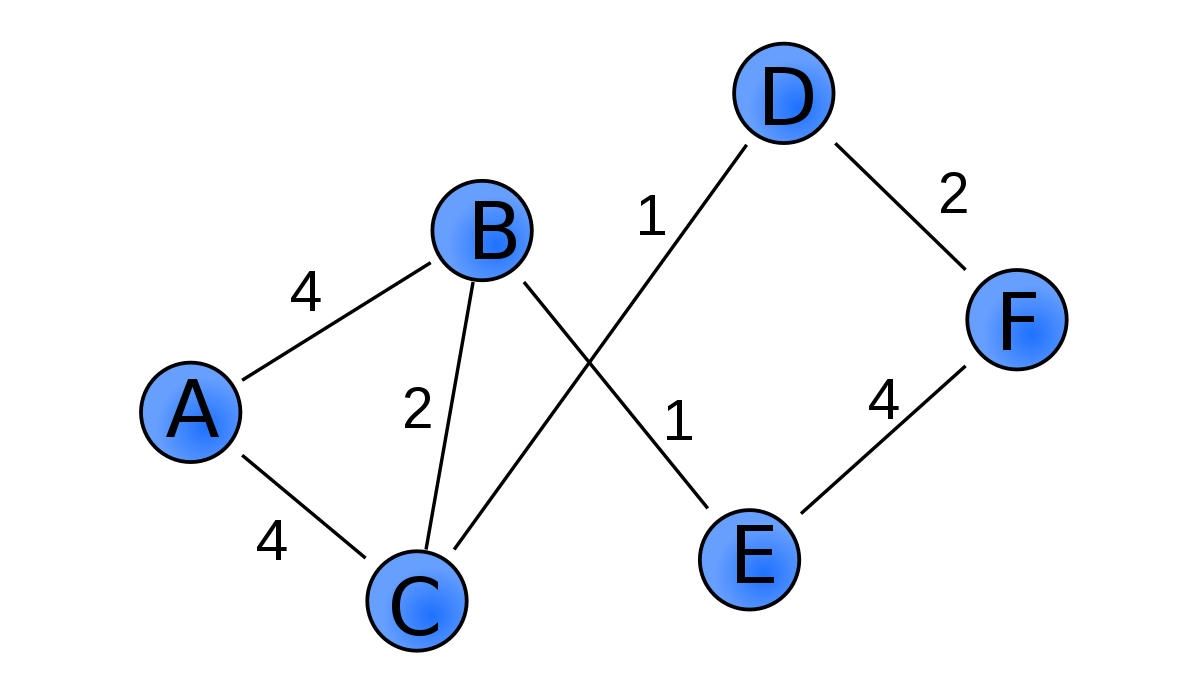
5. 가중 그래프 : 정점을 연결하는 간선에 가중치를 할당한 그래프
2. 그래프의 구현
- 인접행렬
2차원 배열을 사용
O(V^2) 만큼의 공간 필요함 - 인접 리스트
arraylist 사용
O(E)만큼의 공간 필요함
<가중치가 없는 그래프 구현>
인접행렬과 인접리스트를 사용한
package codeup100;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static Scanner scan =new Scanner(System.in);
//n : 정점의 개수, m: 간선의 갯수
static int n,m;
static int[][] arr;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> arrlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("정점의 수, 간선의 갯수를 입력");
n=scan.nextInt();
m=scan.nextInt();
array(n,m);
arraylist(n,m);
}
static void array(int n, int m) {
arr=new int[n+1][n+1];
System.out.print("간선 입력(배열)");
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
int a=scan.nextInt();
int b=scan.nextInt();
arr[a][b]=1;
arr[b][a]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<n+1;j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void arraylist(int n, int m) {
arrlist=new ArrayList<>();
System.out.print("간선 입력(리스트)");
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++) {
arrlist.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
int a=scan.nextInt();
int b=scan.nextInt();
arrlist.get(a).add(b);
arrlist.get(b).add(a);
}
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++) {
System.out.println(arrlist.get(i));
}
}
}
<가중치가 있는 그래프 구현>
인접리스트를 이용한
package codeup100;
import java.util.*;
class Edge<W, V> {
private W weight;
private V v;
public void setEdge(W weight, V v) {
this.weight = weight;
this.v = v;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = 4; // 노드의 갯수
int m = 5; // 간선의 갯수
ArrayList<Edge<Integer, Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new Edge<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { // 간선의 갯수만큼 반복
int n1 = input.nextInt(); // 노드 1
int n2 = input.nextInt(); // 노드 2
int weight = input.nextInt();
graph.get(n1).setEdge(n2, weight);
graph.get(n2).setEdge(n1, weight);
}
}
}3. BFS 와 DFS
-
BFS (넓이 우선 탐색)
Queue를 이용해서 구현 -
DFS (깊이 우선 탐색)
STACK이나 재귀를 이용해서 구현
package codeup100;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static Scanner scan =new Scanner(System.in);
public static StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
public static StringBuilder sb2=new StringBuilder();
static int n,m,v;
static int[][] arr;
static Queue<Integer> q;
static Stack<Integer> stack;
static int[] visited;
static int[] visited2;
static String command;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("노드, 간선 ,시작노드 입력");
n=scan.nextInt();
m=scan.nextInt();
v=scan.nextInt();
arr=new int[n+1][n+1];
visited=new int[n+1];
visited2=new int[n+1];
System.out.println("간선 입력");
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
int a=scan.nextInt();
int b=scan.nextInt();
arr[a][b]=1;
arr[b][a]=1;
}
DFS(v);
System.out.println("DFS");
System.out.println(sb);
BFS(v);
System.out.println("BFS");
System.out.println(sb2);
}
public static void DFS(int v) {
stack =new Stack<>();
stack.push(v);
while(!stack.empty()) {
int curr=stack.pop(); //노드를 pop
if(visited[curr]==1)continue; //방문한 노드이면 skip
//그렇지 않으면
visited[curr]=1;
sb.append(curr+" ");
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++) {
if(visited[i]==0&&arr[curr][i]==1) {//방문하지 않은 노드이고 간선이 존재하는 경우
stack.push(i);
}
}
}
}
public static void BFS(int v) {
q=new LinkedList<>();
visited2[v]=1;
q.offer(v);
while(q.isEmpty()==false) {
int curr=q.poll();
sb2.append(curr+" "); //실제 방문
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++) {
if(visited2[i]==0&&arr[curr][i]==1) {//방문하지 않은 노드이고 간선이 존재하는 경우
visited2[i]=1;
q.offer(i);
}
}
}
}
}
bfs와 dfs visited 체크하는 위치 주의
