Exception handling
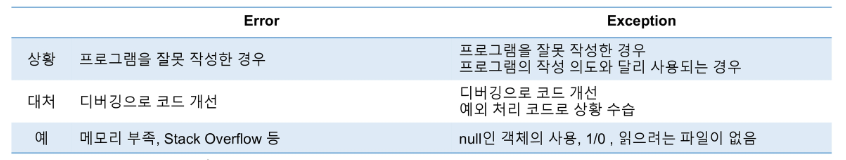
에러와 예외
- 어떤 원인에 의해 오작동 하거나 비정상적으로 종료되는 경우
- 심각도에 따른 분류
- exception handling이란?
- 예외 발생 시 프로그램의 비 정상 종료를 막고 정상적인 실행 상태를 유지하는 것
- 에외의 감지 및 예외 발생 시 동작할 코드 작성 필요
- 예외 발생 시 프로그램의 비 정상 종료를 막고 정상적인 실행 상태를 유지하는 것
예외 클래스의 계층
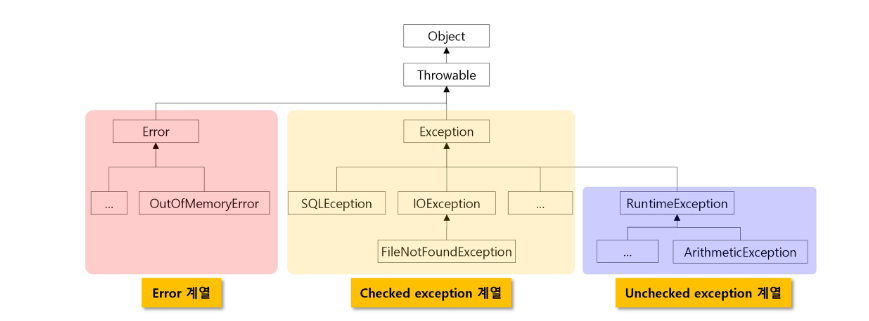
checked Exception- 예외에 대한 대처 코드가 없으면 컴파일이 진행되지 않음
unchecked exception- 예외에 대한 대처 코드가 없더라도 컴파일은 진행됨
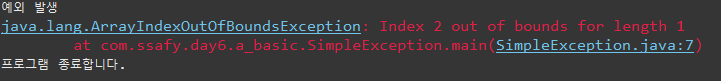
예외의 발생
public class SimpleException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = { 10 };
System.out.println(intArray[2]);
System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
}
}
런타임 오류 발생 : 컴파일은 됨 (unchecked Exception)
try ~ catch 구문
다음과 같이 수정 가능하다.
public class SimpleException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = { 10 };
try {
System.out.println(intArray[2]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("예외 발생");
e.print
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
}
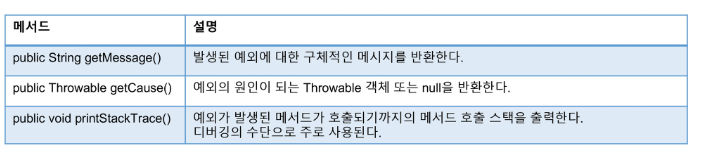
}Excapeion 객체의 정보 활용
- Throwable의 주요 메서드
public class SimpleException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = { 10 };
try {
System.out.println(intArray[2]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.printf("예외 발생 %s", e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료합니다.");
}
}
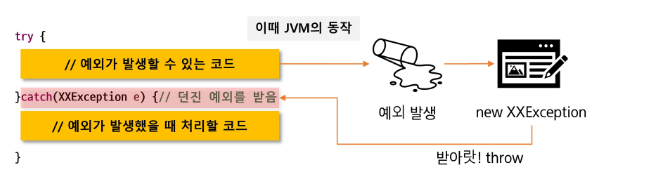
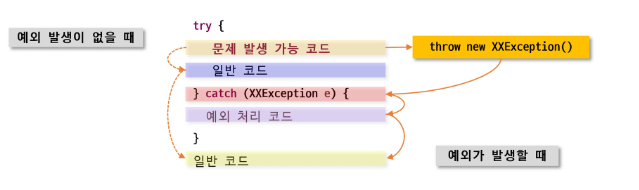
try-catch문에서의 흐름
- JVM이 해당 Exception 클래스의 객체 생성 후 던짐
- throw new XXException()
- 던져진 exception 을 처리할 수 있는 catch 블록에서 받은 후 처리
- 적당한 catch 블록을 만나지 못하면 예외처리는 실패
- 정상적으로 처리되면 try-catch 블록을 벗어나 다음 문장 진행
- try 블록에서 어떠한 예외도 발생하지 않은 경우
- catch 문을 거치지 않고 try-catch 블록의 다음 흐름 문장을 실행
public class ExceptionHandlingFlow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = new Random().nextInt(2);
try {
System.out.println("code 1, num: " + num);
int i = 1 / num;
System.out.println("code 2 - 예외 없음: " + i);
return;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("code 3 - exception handling 완료");
}
System.out.println("code 4");
}
}- num이 0일 때 출력되는 내용?
code 1, 3, 4 - num이 1일 때 출력되는 내용?
code 1, 2, 4
다중 exception handling
-
try 블록에서 여러 종류의 예외가 발생할 경우
- 하나의 try 블록에 여러 개의 catch 블록 추가 가능
- 예외 종류별로 catch 블록 구성
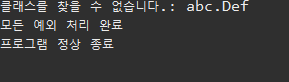
public class MultiExceptionHandling { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO: 다음에서 발생하는 예외를 처리해보자. try { Class.forName("abc.Def"); // ClassNotFoundException new FileInputStream("Hello.java"); // FileNotFoundException DriverManager.getConnection("Hello"); // SQLException } catch(ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.printf("클래스를 찾을 수 없습니다.: %s\n", e.getMessage()); }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.printf("파일을 찾을 수 없습니다.: %s\n", e.getMessage()); } catch(SQLException e) { System.out.printf("DB를 찾을 수 없습니다.: %s\n", e.getMessage()); } finally { System.out.println("모든 예외 처리 완료"); } // END System.out.println("프로그램 정상 종료"); } } - 하나의 try 블록에 여러 개의 catch 블록 추가 가능
-
다중 catch 문장 작성 순서 유의 사항
- JVM이 던진 예외는 catch문장을 찾을 떄는 다형성이 적용됨
- 상위 타입의 예외가 먼저 선언되는 경우 뒤에 등장하는 catch 블록은 동작할 기회가 없음
- Unreachable catch block for Exception
- 상속 관계가 없는 경우는 무관
- 상속 관계에서는 작은 범위에서 큰 범위 순으로 정의
다중 예외 처리를 이용한 Checked Exception 처리
-
발생하는 예외들을 하나로 처리
- 예외 상황 별 처리가 쉽지 않음
- 가급적 예외 상황 별로 처리하는 것을 권장
-
심각하지 않은 예외를 굳이 세분화 해서 처리하는 것도 낭비
-
I를 사용해 하나의 catch 구문에서 상속관계가 없는 여러 개의 exception 처리
public class MultiExceptionHandling {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO: 다음에서 발생하는 예외를 처리해보자.
try {
Class.forName("abc.Def"); // ClassNotFoundException
new FileInputStream("Hello.java"); // FileNotFoundException
DriverManager.getConnection("Hello"); // SQLException
} catch(ClassNotFoundException | FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.printf("자원을 찾을 수 없습니다.: %s\n", e.getMessage());
} catch(SQLException e) {
System.out.printf("DB를 찾을 수 없습니다.: %s\n", e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("모든 예외 처리 완료");
}
// END
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 종료");
}
}- 계층을 이루는 예외의 처리
public class HierachyException {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
String src = "./.project";
// TODO: 상속 관계를 고려하여 다음에서 예외를 처리해보자.
try {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(src);
int readData = -1;
while ((readData = input.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) readData);
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.printf("읽으려는 파일이 없습니다. : %s", e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.printf("파일 읽기에 실패해습니다. : %s", e.getMessage());
}
// END
System.out.println("파일 읽음 완료!");
}
}try ~ catch ~ finally 구문을 이용한 예외 처리
- finally는 예외 발생 여부와 상관 없이 언제나 실행
- 중간에 return을 만나는 경우도 finally 블록을 먼저 수행 후 리턴 실행
public class ExceptionHandlingFlow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = new Random().nextInt(2);
try {
System.out.println("code 1, num: " + num);
int i = 1 / num;
System.out.println("code 2 - 예외 없음: " + i);
return;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("code 3 - exception handling 완료");
} finally {
System.out.println("code 4 - 언제나 실행");
}
System.out.println("code 5");
}
}
- finally를 이용한 자원 정리
public class InstallApp {
void copy() {
System.out.println("파일 복사");
}
void install() throws Exception {
System.out.println("설치");
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new Exception();
}
}
void delete() {
System.out.println("파일 삭제");
}
}
public class InstallApp {
void copy() {
System.out.println("파일 복사");
}
void install() throws Exception {
System.out.println("설치");
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new Exception();
}
}
void delete() {
System.out.println("파일 삭제");
}
}를 다음과 같이 변경할 수 있다.
public class InstallAppTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InstallApp app = new InstallApp();
try {
app.copy();
//app.delete();
} catch(Exception e) {
//app.delete();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
app.delete();
}
}
}-
주요 목적 : try 블록에서 사용한 리소스 반납

-
생성한 시스템 자원을 반납하지않으면 장래 resource leak 발생 가능 -> close처리
public void useStream() {
FileInputStream fileInput = null;
try {
fileInput = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
fileInput.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileInput != null) {
try {
fileInput.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}- 지저분할 수 밖에 없는 finally 블록
- close 메서드 자체가 IOException 유발 가능
- FileInputStream 생성자에서 IOException 발생 시 fileInput은 null인 상황
try- with-resources
- JDK 1.7 이상에서 리소스의 자동 close 처리
- try 선언문에 선언된 객체들에 대해 자동 close 호출 (finally 역할)
- 단 해당 객체들이 AutoCloseable interface를 구현할 것
- 각종 I/O stream, socket, connection ...
- 해당 객체는 try 블록에서 다시 할당될 수 없음
- 단 해당 객체들이 AutoCloseable interface를 구현할 것
public void useStreamNewStye() {
// TODO: useStream을 try~with~resource 문장으로 변경하세요.
try(FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");){
input.read();
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// END
}throws 키워드를 통한 처리 위임
- method에서 처리해야 할 하나 이상의 예외를 호출한 곳으로 전달(처리 위임)
- 예외가 없어지는 것이 아니라 단순히 전달됨
- 예외를 전달받은 메서드는 다시 예외 처리의 책임 발생
- 처리하려는 예외의 조상 타입으로 throws 처리 가능
checked exception과 throws
public class ThrowsTest {
// TODO: 1. methodCall2()에서 uncheckedExceptionMethod()를 호출할 때 발생하는 예외를
// throws로 처리하세요.
// TODO: 2. methodCall2()에서 checkedExceptionMethod()를 호출할 때 발생하는 예외를
// throws로 처리하세요.
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
methodCall1();
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("done");
}
private static void methodCall1()throws ClassNotFoundException {
methodCall2();
}
private static void methodCall2()throws ClassNotFoundException {
uncheckedExceptionMethod();
checkedExceptionMethod();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private static void checkedExceptionMethod() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("Hello");
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private static void uncheckedExceptionMethod() {
int i = 1 / 0;
}
}- checked exception은 반드시 try ~ catch 또는 throws 필요
- 필요한 곳에서 try ~ catch 처리
로그 분석과 예외의 추적
- Throwable의 printStackTrace는 메서드 호출 스택 정보 조회 가능
- 최초 호출 메서드에서부터 예외 발생 메서드 까지의 스택 정보 출력
- 꼭 확인해야할 정보
- 어떤 예외인가? - 예외의 정보
- 예외 객체의 메세지는 무엇인가 ? - 예외 원인
- 어디서 발생했는가? - 디버깅 출발점
- 직접 작성한 코드를 디버깅 대상으로 삼을 것
- 참조하는 라이브러리(java.xx등)는 과감히 건너뛰기
throws의 목적과 API 활용
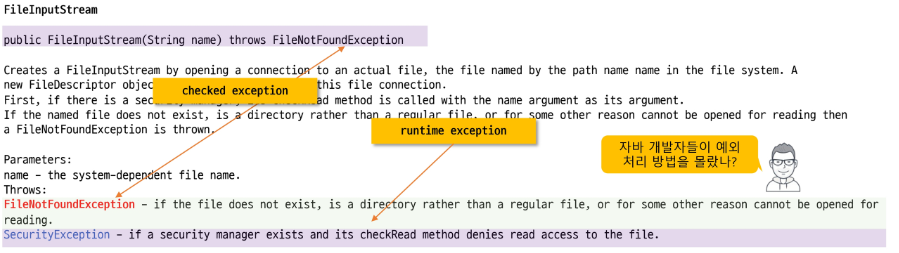
- API가 제동하는 메서드들은 사전에 예외가 발생할 수 있음을 선언부에 명시하고 프로그래머가 그 예외에 대처 하도록 강요

메서드 재정의와 throws
-
메서드 재정의 시 조상 클래스 메서드가 던지는 예외보다 부모예외를 던질 수 없다.
- 부모가 치지 않은 사고를 자식이 칠 수 없다.
class Parent{ void methodA() throws IOException{} void methodB() throws ClassNotFoundException{} } public clas OverridingTest extends Parent{ @Override void methodA() throws FileNotFoundException{ } @Override void methodB() throws Exception{ //더 넓은 Exception을 처리하려고 하므로 오류 } }
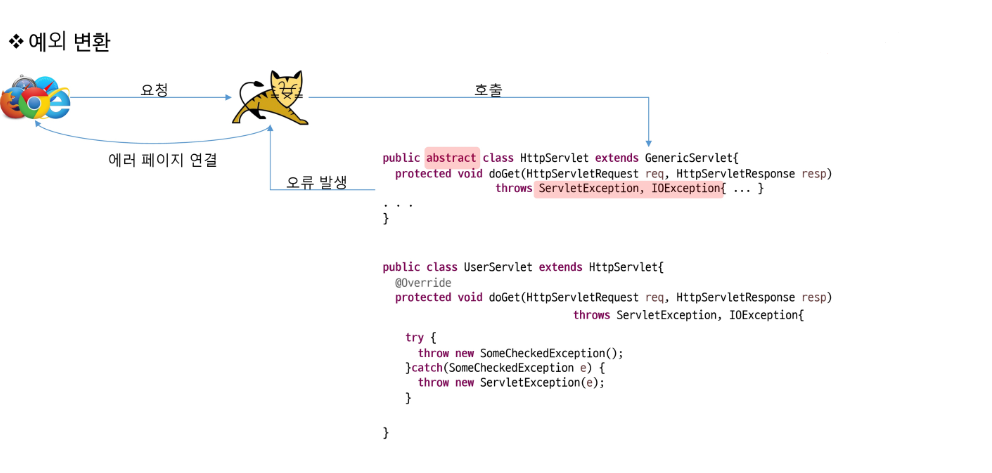
예외 변환
-
하위 계층에서 발생한 예외는 상위계층에 맞는 예외로 바꿔서 던져야 한다.
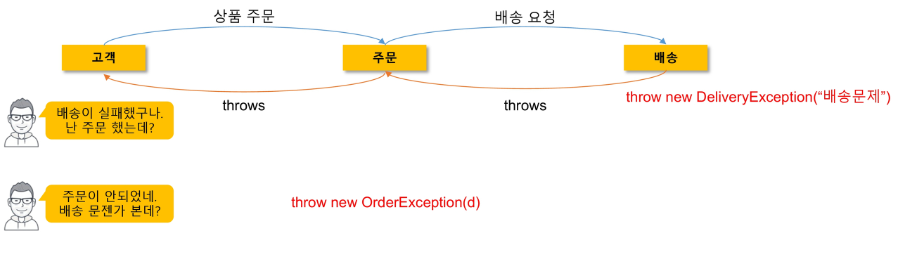
-
Exception Chaining
- 하위 계층에서 발생한 예외 정보가 상위 계층의 디버깅하는데 유용할 경우 사용
- 하위 계층의 예외를 원인으로 상위 계층에서 예외를 발생
- 하위 계층에서 발생한 예외 정보가 상위 계층의 디버깅하는데 유용할 경우 사용
public class ExceptionChaining {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OnlineShop shop = new OnlineShop();
// TODO: 03. shop을 통해 주문해보자.
shop.order();
// END
System.out.println("상품 주문 사용 완료!");
}
}
class OnlineShop {
public void order() {
// TODO: 02. 주문 처리 과정에서 발생하는 예외를 처리하고 IllegalStateException을 발생시켜보자.
try {
packaging();
delivery();
System.out.println("상품이 정상적으로 배송 되었습니다.");
} catch(RuntimeException e) {
new IllegalStateException(e); //chaining
}
// END
}
private void packaging() {
System.out.println("상품을 포장합니다.");
}
private void delivery() {
deliveryToWareHouse();
deliveryToCustomer();
}
private void deliveryToWareHouse() {
System.out.println("물류 창고로 배송합니다.");
}
private void deliveryToCustomer() {
System.out.println("고객에게 배송합니다.");
// TODO: 01. 임의로 RuntimeException 계열의 예외를 발생시켜 보자.
throw new RuntimeException("도로가 결빙입니다.");
// END
}
}