1. 객체지향 프로그래밍
정의: 주체가 아닌 것, 주체가 활용하는 것 → 우리 주변에 있는 모든 것
→ 현실 세계를 반영하는 프로그래밍
객체지향 프로그래밍의 장점
-
신뢰성 높은 프로그래밍이 가능하다.
-
추가/수정/삭제가 용이하다
-
재사용성이 높다
-
클래스와 객체
-
현실의 객체가 갖는 속성과 기능은 추상화(abstraction)되어 클래스에 정의된다.
-
클래스는 구체화 되어 프로그램의 객체(instance,object)가 된다.
-
설계도는 하나의 Type이 되고 설계도를 통해 나온 제품을 객체라고 부르며 주체가 사용한다.
-
클래스: 객제를 정의해 놓은 것, 객체의 틀. 직접 사용x 객체를 만들기 위한 틀만 제공
-
객체: 클래스를 데이터 타입으로 메모리에 생성된 것
-
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
boolean isHungry;
void eat() {
System.out.println("냠냠");
isHungry = false;
}
void work() {
System.out.printf("%n");
System.out.println("열심히");
isHungry = true;
}
}public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "홍길동";
p.isHungry = true;
p.eat();
System.out.println(p.name+": "+p.isHungry+" "+p.age);
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.name = "장길산";
p2.work();
System.out.println(p2.name+": "+p2.isHungry+" "+p2.age);
}
}객체 생성과 메모리(JVM의 메모리 구조)
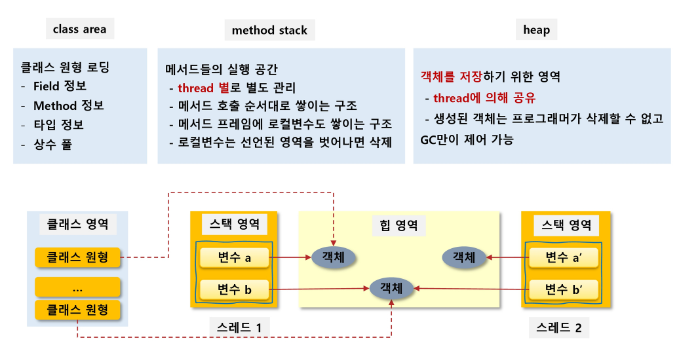
- class area는 클래스 틀이 올라가는 곳
- stack에는 메서드의 실행공간, 어떤 순서로 메서드를 실행? & 함수의 로컬 변수들이 쌓이는 공간 (thread별로 존재한다 )
- heap은 new를 통해 생성한 객체가 올라가는 곳이다 → 객체의 멤버변수는 heap에 올라간다 & 생성된 객체는 Garbage Collection으로만 제어 (thread들이 각자 공유한다)
- person1과 person2는 객체를 저장하고 있는 메모리 값, heap영역에 있는 멤버변수들은 primitive 값 → 그대로 값 대입, String과 같이 reference 타입일 땐 다시 한 번 참조
2. 변수
타입에 따른 분류 vs 선언 위치에 따른 분류
타입에 따른 분류 → Primitive Type vs Reference Type
선언 위치에 따른 분류 → 멤버변수 vs 지역변수
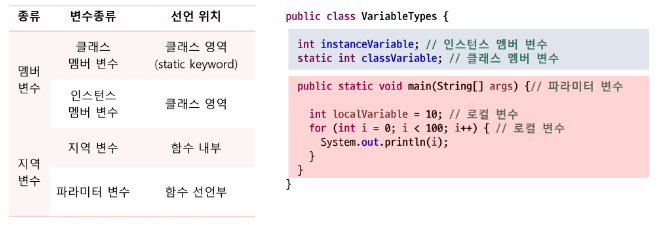
인스턴스 멤버 변수의 특징
- 선언 위치: 클래스 { } 영역에 선언
- 변수의 생성: 객체가 만들어질 때 객체 별로 생성됨
- 변수의 초기화: 타입 별로 default 초기화
- 변수에서의 접근: 객체 생성 후(메모리에 올린 후 ) 객체 이름으로 접근
→ 객체를 만들 때마다 객체 별로 생성 → 객체마다 고유한 상태유지
- 소멸 시점: GC에 의해 객체가 없어질 때, 프로그래머가 명시적으로 소멸 불가
클래스 멤버 변수의 특징
- 선언위치: 클래스 { }영역에 선언되며 static 키워드를 붙임
public class Person{
//모든 객체들에 대해서 같은 멤버변수 값을 가진다
static String scientificName = "Homo Sapiens";
String name;
}
System.out.println(Person.org);
-> 출력값: Homo Sapiens- 변수의 생성: 클래스 영역에 클래스 로딩시 메모리 등록 → 개별 객체의 생성과 무관 → 모든 객체가 공유하게 됨(공유 변수라고도 불림 )
- 변수의 초기화: 타입 별로 default 초기화
- 변수에서의 접근: 객체 생성과 무관하게 클래스 이름으로 접근
Person p = new Person();
p.scientificName = "객체를 통한 변경";
//static에 부합하는 내용은 아님
Person.scientificName = "클래스를 통한 변경";
//클래스를 통해 변경하는 것을 지향- if p2.scientificName = “변경” 해버리면 가능은 하지만 나머지 객체의 scientificName역시 모두 바뀌게 된다.
- 소멸 시점: 프로그램 종료 시
지역 변수 & 파라미터 변수
- 선언 위치: 클래스 영역의 { } 이외의 모든 중괄호 안에서 선언되는 변수들
- 메서드, 생성자, 초기화 블록
void call(String to){ //파라미터 변수
String beep = "띠"; //로컬 변수
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ //로컬변수
System.out.println(beep);
}
}- 변수의 생성: 선언된 라인이 실행될 때 → 생성 메모리 영역: thread 별로 생성된 stack 영역
- 변수의 초기화: 사용하기 전 명시적 초기화 필요
- 변수에서의 접근: 외부에서는 접근이 불가하므로 소속 불필요 → 내부에서는 이름에 바로 접근
- 소멸시점 → 선언된 영역인 { }를 벗어날 때
3. 메서드
메서드란?
→ 현실의 객체가 하는 동작을 프로그래밍으로 어떤 작업을 수행하는 명령문의 집합
→ 반복적으로 사용되는 코드의 중복 방지
→ 코드 양을 줄일 수 있고 유지 보수가 용이하다.
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
boolean isHungry;
static String org = "SSAFY";
//사람 정보에 대한 메서드
void printInfo() {
System.out.println(this.name+": "+this.isHungry+" "+this.age);
}
}public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Person.org);
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "홍길동";
p.isHungry = true;
p.eat();
//System.out.println(p.name+": "+p.isHungry+" "+p.age);
p.printInfo();
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.name = "장길산";
p2.work();
//System.out.println(p2.name+": "+p2.isHungry+" "+p2.age);
p2.printInfo();
}
}- variable arguments
- 메서드 선언 시 몇 개의 인자가 들어올 지 예상할 수 없을 경우(또는 가변적) → 배열 타입을 선언할 수 있으나, 메서드 호출 전 배열을 생성, 초기화 해야 하는 번거로움이 있다 → …을 이용해 파라미터를 선언하면 호출 시 넘겨준 값의 개수에 따라 자동으로 배열 생성 및 초기화
- 메서드 선언 시 몇 개의 인자가 들어올 지 예상할 수 없을 경우(또는 가변적) → 배열 타입을 선언할 수 있으나, 메서드 호출 전 배열을 생성, 초기화 해야 하는 번거로움이 있다 → …을 이용해 파라미터를 선언하면 호출 시 넘겨준 값의 개수에 따라 자동으로 배열 생성 및 초기화
public static void main(String[] args){
VariableTest vt = new VariableTest();
vt.variableArgs(1,2,3);
vt.variableArgs(1,2,3,4);
vt.variableArgs(1,2);
}
public void variableArgs(int... params){
int sum = 0;
for(int i: params){
sum += i;
}
}메서드 호출 → 메서드를 호출할 때는 메서드의 선언부에 맞춰 호출해야 함
- 메서드 이름: 반드시 동일
- 파라미터: 선언된 파라미터의 개수는 반드시 동일, 타입은 promotion 적용 가능
메서드 접근 → 멤버 변수와 마찬가지로 static 또는 non static 상태를 구분해서 호출
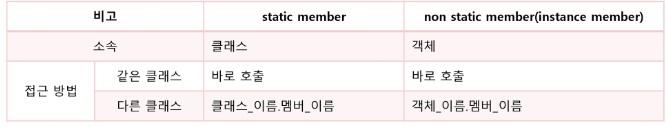
가장 중요한 것은 호출하려는 멤버가 메모리에 있는가? 를 생각해야한다.
if : 메모리에 있으면 호출가능
else: 메모리에 없으면 호출 불가(먼저 메모리에 로딩 후 사용해야 함 )
static memeber는 언제나 메모리에 있어서 클래스 로딩 시 자동 등록
but instance memeber는 객체 생성 전에는 메모리에 없다
→ 객체 생성 시 모든 일반 멤버들은 메모리에 생성
→ 객체, 즉 레퍼런스를 통해서 접근
메서드 호출 스택
기본형 변수와 참조형 변수
- 메서드 호출 시 파라미터로 입력된 값을 복사해서 전달
- Java는 call by value
public class CallByTest{
int memberVar = 10;
static void change1(int var){
var += 10;
System.out.printf("change1: %d%n",var);
}
static void change2(CallByTest cbtl){
cbtl.memeberVar += 100;
System.out.printf("change2: %d%n",var);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
CallByTest cbt = new CallByTest();
cbt.memberVar = 5;
System.out.printf("change1 호출 전 memeberVar : %d%n",cbt.memberVar); //5
change1(cbt.memberVar); //얘는 값으로 전달 리턴되는 값이 없음 (지역변수)
System.out.printf("change1 호출 후 memeberVar : %d%n",cbt.memberVar); //5
change2(cbt); //얘는 객체의 주소 값을 메서드로 넣기 -> callByRefer
System.out.printf("change2 호출 후 memeberVar : %d%n",cbt.memberVar); //105
}
}4. 생성자(constructor)
- 객체가 만들어지면서 자동호출하는 함수이며, 객체의 초기작업을 할 경우에 이용 된다.
Emp ob = new Emp();
ob.setName("kim");
//객체 생성과 동시에 생성자를 통해 초기화
Emp ob = new Emp("lee");
작성 규칙: 메서드와 비슷하나 리턴 타입이 없고 이름은 클래스 이름과 동일
① 반드시 클래스 명과 동일해야 한다.
② 결과형(리턴값)이 없다.
③ 객체가 생성될때 자동 호출되며, 사용자가 임의로 호출할 수 없다
④ 멤버필드의 값을 초기화 한다
⑤ 생략하면 컴파일시 자동으로 default생성자를 만든다
⑥ 여러개의 생성자를 만들수 있다(생성자 overloading)
⑦ 생성자내부에서 첫번째라인에 this(매개변수)를 사용하여 다른 생성자를 호출할수 있다.
단, 1번만 호출이 가능하다
- 생성자의 종류 1: 기본 생성자(default constructor)
- 기본 생성자의 형태는 파라미터가 없고 구현부가 비어있는 형태
- 생성자 코드가 없으면 컴파일러가 기본 생성자 제공
public class DefaultPerson{
String name;
int age;
boolean isHungry;
//public DefaultPerson() {} --생략된 기본 생성자
public static void main(String[] args){
DefaultPerson person = new DefaultPerson();
person.name = "홍길동"
person.age = 10;
person. isHungry = false;
}
}- 생성자의 종류 2: 파라미터가 있는 생성자
- 생성자의 목적이 일반 멤버 변수의 초기화 → 생성자 호출 시 값을 넘겨줘서 초기화
- 주의! 파라미터가 있는 생성자를 만들면 기본 생성자는 추가되지 않는다.
public class ParameterPerson{
String name;
int age;
boolean isHungry;
ParameterPerson(String n, int a, boolean i){
name = n;
age = a;
isHungry = i;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ParameterPerson person = new ParameterPerson("홍길동",10,true);
ParameterPerson person2 = new ParameterPerson(); //오류
}
}this의 용법
1) this.
- 참조 변수로써 객체 자신을 가리킴
→ 참조 변수를 통해 객체의 멤버에 접근했던 것처럼 this를 이용해 자신의 멤버에 접근 가능
- 용도
→ 로컬 변수와 멤버 변수의 이름이 동일할 경우 멤버 변수임을 명시적으로 나타냄
→ 명시적으로 멤버임을 나타낼 경우 사용
public class DefaultPerson{
String name = "아무개";
int age = 0;
boolean isHungry = true;
//public DefaultPerson() {} --생략된 기본 생성자
Person(String name, int age, boolean isHungry){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.isHungry = isHungry;
}
void walk(){
this.isHungry = true;
System.out.println("뚜벅 뚜벅");
}
}- this는 객체에 대한 참조 → 따라서 static 영역에서 this 사용불가
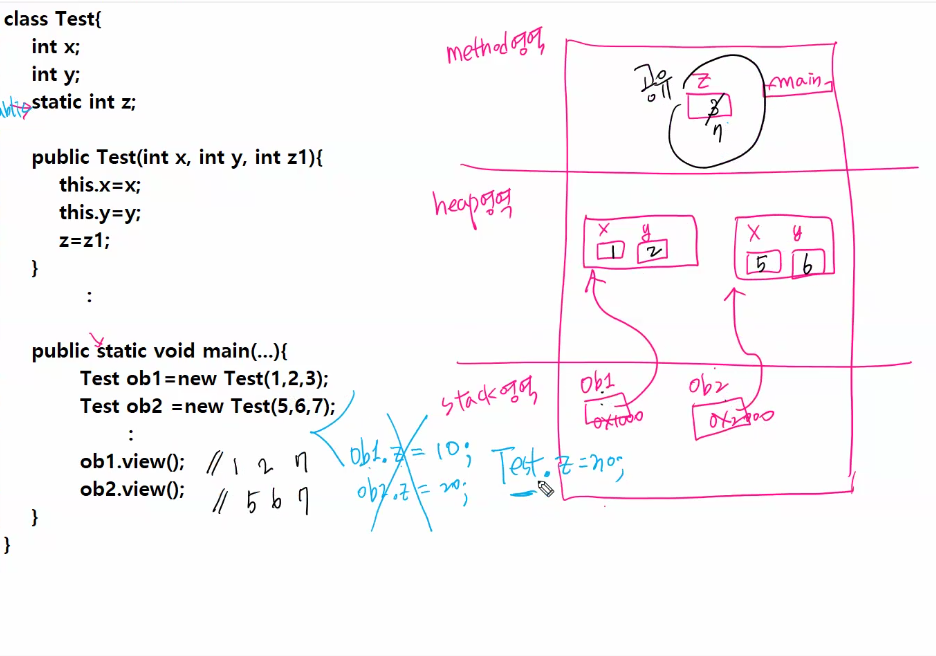
class Test{
int a;
int b;
static int c;
//static은 main실행하기 전에 한 번만 올려준다 static 변수는
//미리 메모리 영역에 올라감
static {
System.out.println("static 의 초기화 영역");
}
public Test(int a, int b, int c) {
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
Test.c = c;
System.out.println("객체의 초기화 영역");
}
public void view() {
System.out.println(a+" "+b+" "+c);
}
}
public class StaticEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test ob1=new Test(1,2,3);
Test ob2=new Test(5,6,7);
//ob1.c = 100; //권장하지 않는다
Test.c = 100;
ob1.view();
ob2.view();
}
}
출력값
static 의 초기화 영역
객체의 초기화 영역
객체의 초기화 영역
1 2 100
5 6 1002) this( )
- 반드시 첫 줄에서만 호출이 가능하다는 것이 포인트
- 생성자 호출 순서 예제
public class ConstructorEx2 {
public ConstructorEx2() {
this("ABC",100);
System.out.println("Default Constructor");
}
public ConstructorEx2(String str, int n) {
System.out.println(str+ " "+n+" constructor");
}
public ConstructorEx2(String str) {
this(); //default 생성자 호출
System.out.println(str+" constructor");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ConstructorEx2("ABC");
}
}
/*
ABC 100 constructor
default constructor
ABC constructor
*/5. 메서드 오버로딩
: 하나의 클래스에서 같은 이름의 메서드가 여러 번 구현된경우
사용하는 이유 ⇒ 메서드 이름을 절약하기 위해서 사용
ex) public void size(int a), public void size(int a, int b), public void size(double a, int b)
다 다른 함수 오버로딩 if 없었으면 함수 이름을 다 다르게 해야 오류가 안 난다.
(1) 메서드의 이름이 같아야 한다
(2) 매개변수의 갯수 또는 타입이 달라야 한다
(3) 매개변수는 같고 리턴타입이 다른경우는 오버로딩이 성립되지 않는다
(리턴타입은 오버로딩을 구현하는데 아무런 영향을 주지 못한다)
ex) void show(int a,int b){ }와 오버로딩인 메서드는?
①int show(int a,int b){ }
②void show(double a,double b){ }
③void show(int a){ }
④int show(char a){ }
** 객체지향 프로그래밍 코딩 Tip ** - 멤버변수는 웬만하면 private으로
- 멤버변수를 수정할 일이 있다면 set, get 메서드를 통해서 수정
- static변수를 변환할 경우 모든 객체의 변수가 바뀐다는 거 생각
- static 변수를 변경할 때도 static + 메서드를 통해서 변경
